Which organelle is this?
The mitochondria
What is a hypertonic solution?
A solution with more solute
What type of transport requires ATP?
Active or Passive
Active transport requires ATP
What is the purpose of the cell membrane?
To let things in and out of the cell
Support
What kind of cells are these? 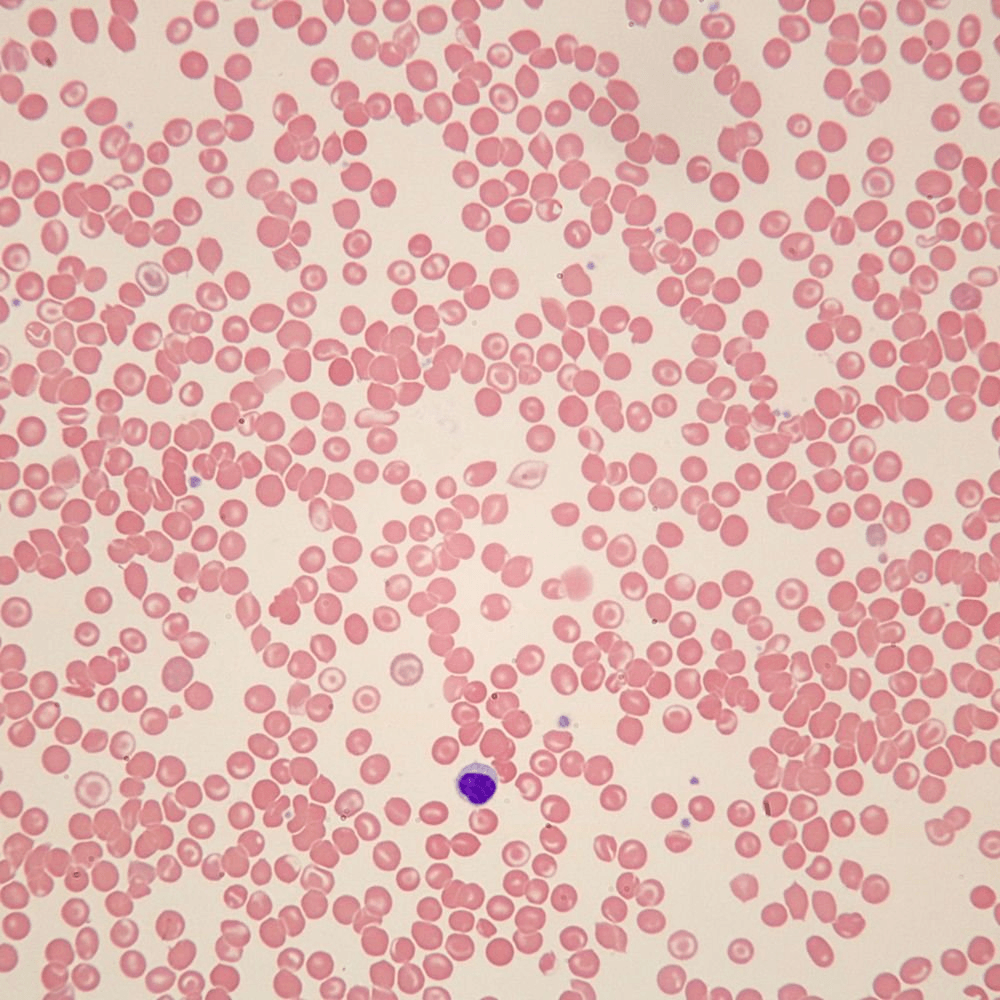
Red blood cells (with some white blood cells)
What do eukaryotic cells (plant and animal cells) have than prokaryotic ones don't?
Membrane bound organelles
A distinct nucleus
What is the relationship between the inside and the outside of the cells? 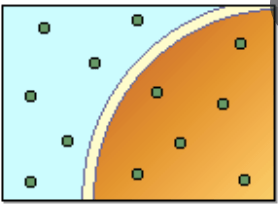
They are isotonic because the have the same amount of solute inside and out
What is endocytosis? What is exocytosis?
Endo (inside) when materials move into the cell
Exo (outside) when materials move out of the cell
What type of diffusion uses a protein to allow molecules to move across the cell membrane?
Facilitated diffusion! The protein facilitates molecule movement
What happens when a red blood cell is in a hypotonic solution?
It will lyse and die due to the amount of extracellular fluid flowing in to dilute its solutes :(
Name an organelle that is in a plant cell, but absent or not as prominent in an animal cell?
Vacuole (not as prominent)
Chloroplast
Cell Wall
Label the cells isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic.
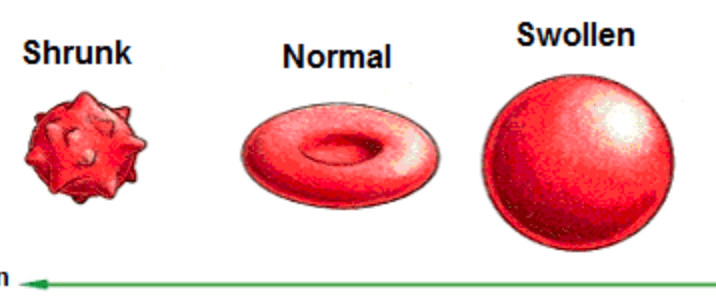
Hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic
What is the purpose of diffusion?
To equalize the concentration inside and outside of the cell by moving solutes
Can charged molecules move through the cell membrane freely?
No!
What is the purpose of this type of cell? 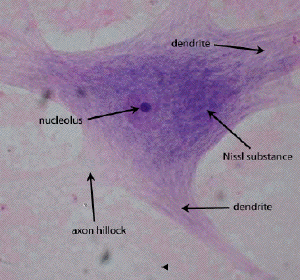
Nerve tissue - To send and receive messages throughout the body as electrical signals.
What organelle is responsible for packaging and sending proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to targeted destinations?
The Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Complex
In a 0% solution, is the potato core hypertonic, isotonic or hypotonic to the solution?
Hypertonic, 0% solution has no salt
How does osmosis work?
Fluid moves across membranes to equalize the concentration inside and outside of the cell
Which part of the phospholipid likes the water, the head or the tail?
The hydrophilic head of the phospholipid comes into contact with water
You had carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids for dinner. What organelle will be ready to break them down in digestion?
Lysosomes
What does the chloroplast store? What does the mitochondria release?
The mitochondria releases ATP
The chloroplast stores glucose
What is happening to the elodea cells in the 5% salt solution?
The environment is hypertonic so water is escaping the hypotonic elodea cells
What happens step by step in the endomembrane system?
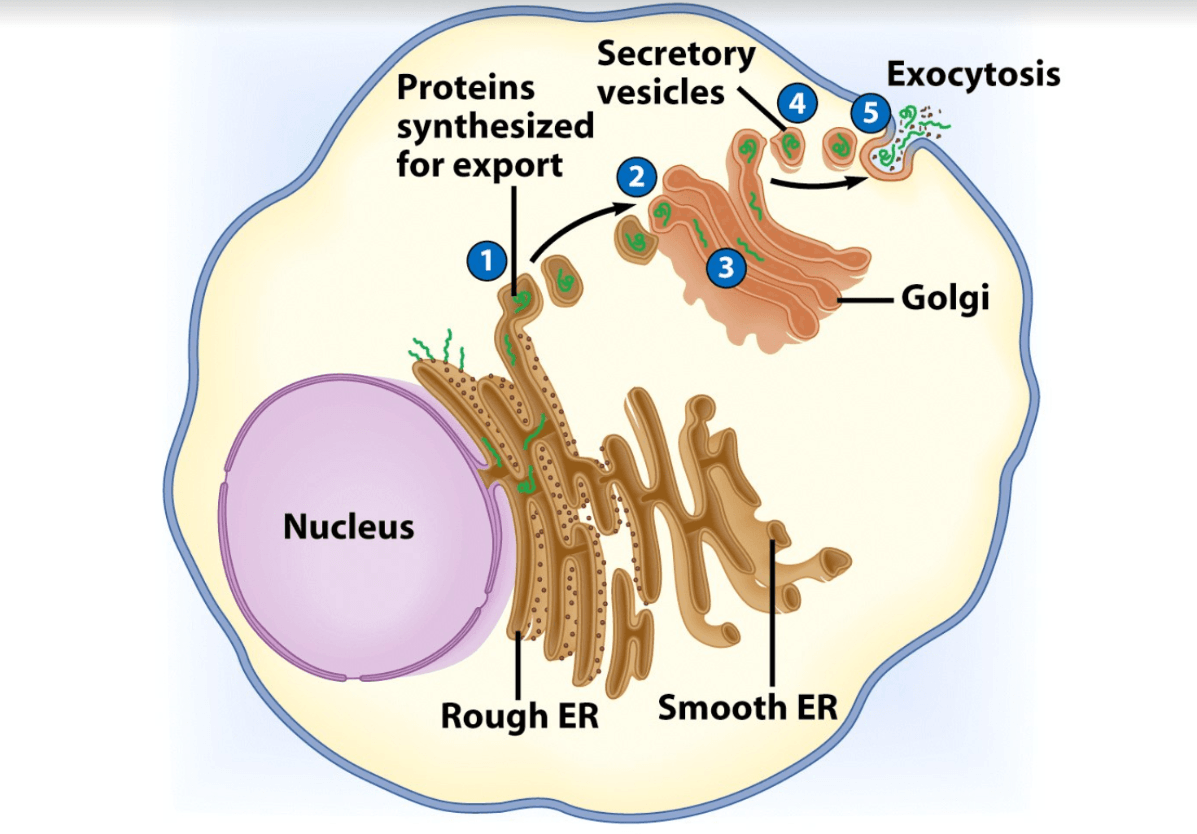
What are 2 of the materials found on the cell membrane?
Proteins, Carbohydrates, Cholesterol
Organize the following from largest scale to smallest scale: organ, tissue, cell, organ systems
organ systems < organ < tissue < cell