T/F When applying color doppler, arterial blood always appears red.
False.
The Doppler effect explains that when there is relative motion between a sound’s source and an observer, there is a change in the perceived frequency of a sound wave.
Clinically, the transducer produces the sound waves as well as observes the returning echoes. Doppler shift occurs when movement of blood creates a change or shift in the frequency of the echoes.
If the source moves towards the transducer, the wavelength gets shorter in this direction and the frequency increases. This is a positive Doppler shift (red)
If the source moves away from the transducer, the wavelength gets longer and the frequency decreases. This is a negative Doppler shift (blue)
What is the proper ETT placement? How can you identify this on chest X-Ray?
The ETT should be placed 3-5 cm above the carina. The carina is normally at the level of the 6th posterior rib or T4-T5 interspace. The level of the medial ends of the clavicles is also consistent with proper positioning.
________ is a measure of pitch. It tells us how many cycles occur in a given period of time. It is measured in Hertz (cycles/second)
Frequency
High frequencies have shorter wavelengths and produce the best resolution at the expense of being unable to visualize deep structures.
Low frequencies have longer wavelengths and allow us to see deeper in the body while sacrificing image resolution
What pathology is this?
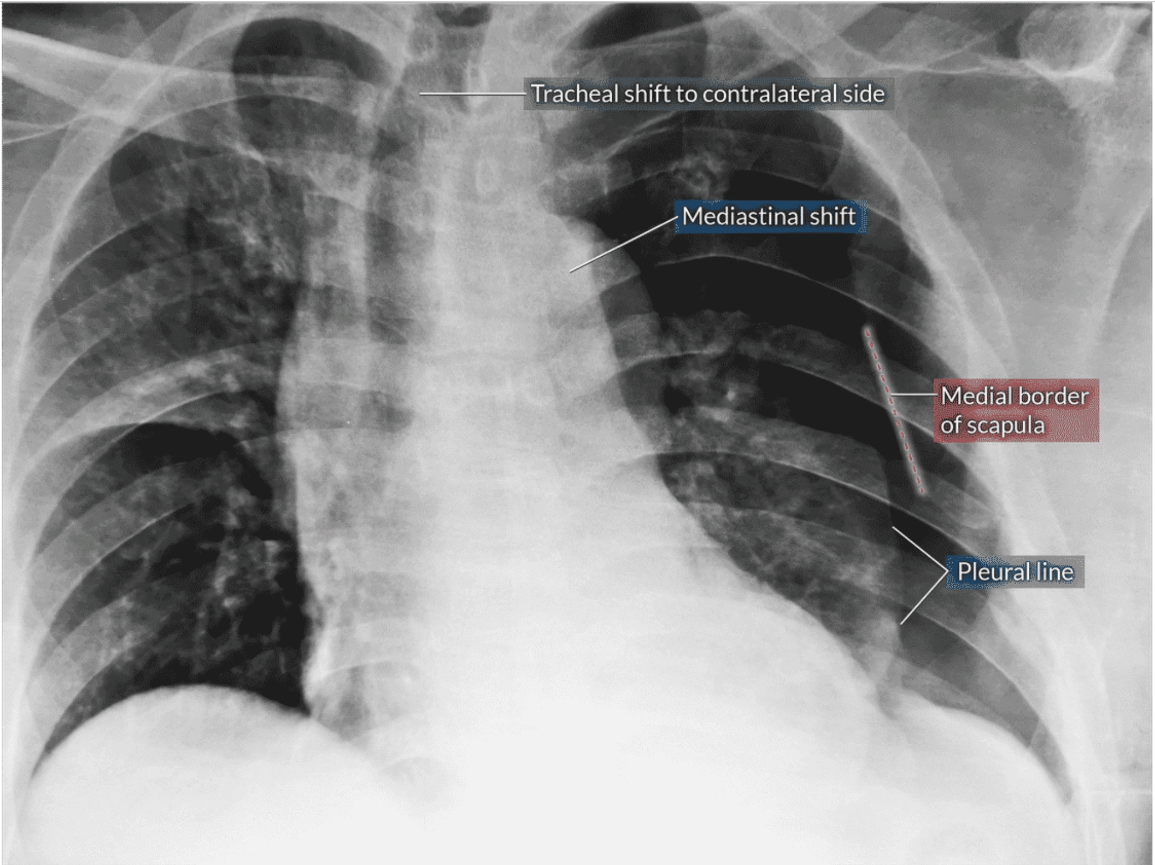
Tension pneumothorax presents with a depressed diaphragm, flattened cardiac border, and contralateral mediastinal shift
In what plane is this needling approach? Is it short or long axis?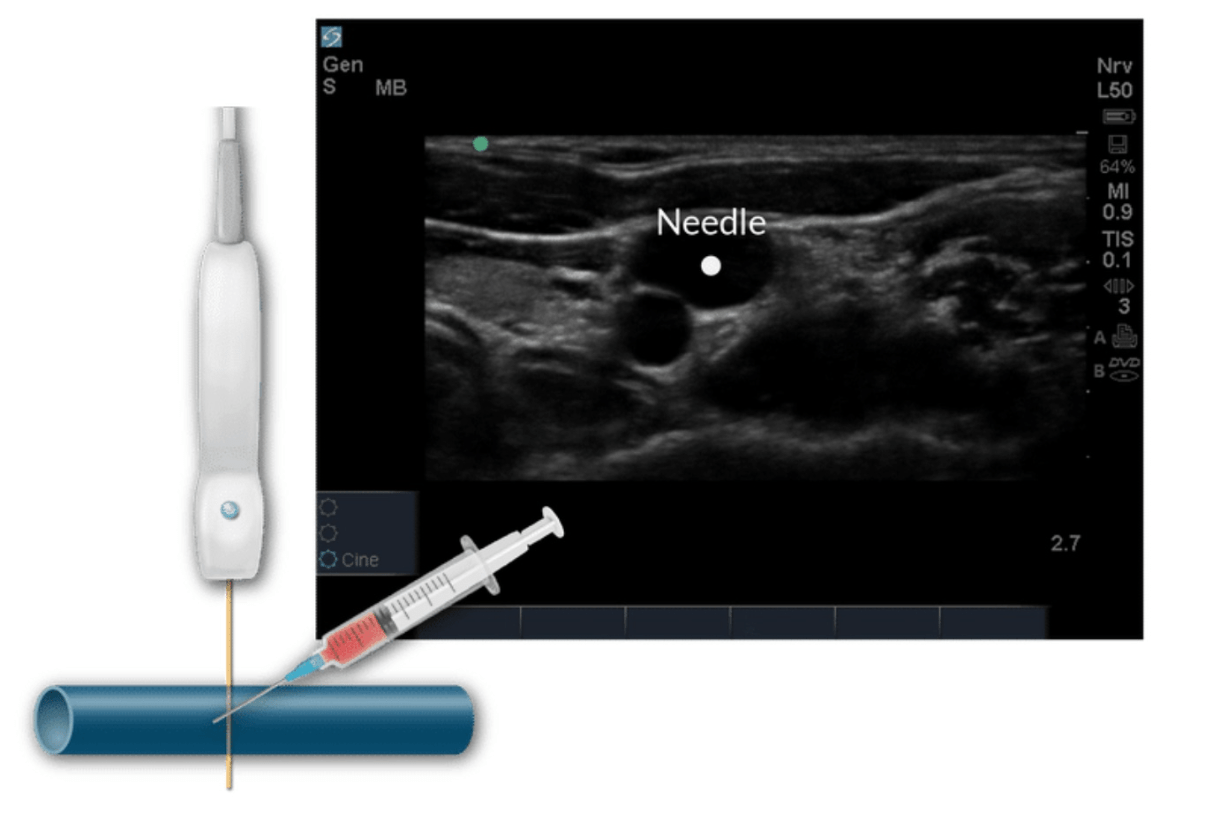
Out-of-plane
Short axis
How does ultrasound work?
An electric current is applied to the piezoelectric crystals inside the transducer, causing them to vibrate
The piezoelectric elements generate ultrasound waves that travel through the body
When an ultrasound wave encounters tissues of different acoustic impedance, the waves echo and return back to the transducer
The echoes hitting the piezoelectric elements in the transducer cause them to vibrate and the mechanical energy is transduced into electrical information
The electrical information enters an algorithm in the ultrasound system that plots corresponding dots or images on the screen
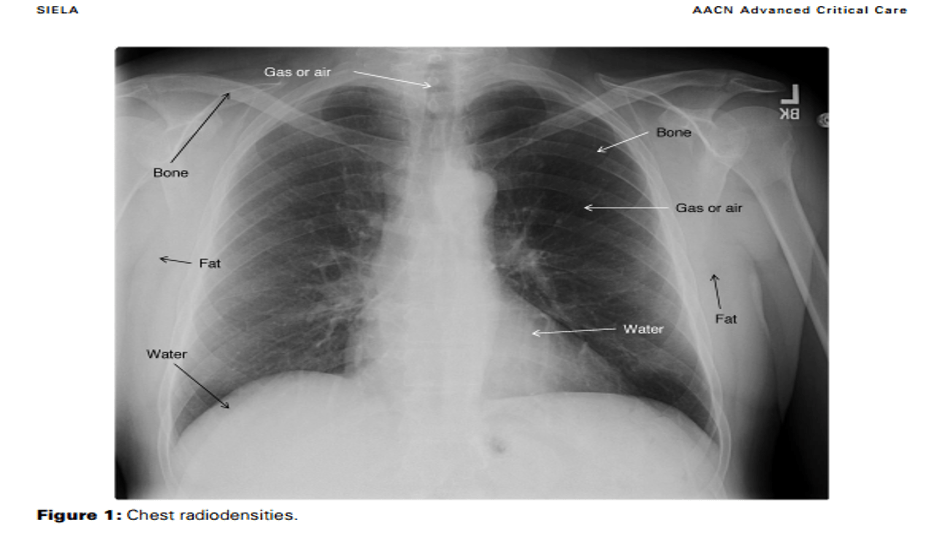
What might appear black or radiolucent on chest X-Ray?
Gas or air in the trachea, bronchi, or stomach appears black or radiolucent because it has low density
X-rays pass more easily though low density structures and less easily through high density structures.
Fat appears gray or less radiolucent than air
Water/soft tissue appears white with slight radiopacity (heart, muscle, and diaphragm)
Bone or metal appears white or radiopaque
_______ is the distance between two points on two adjacent cycles in a sound wave.
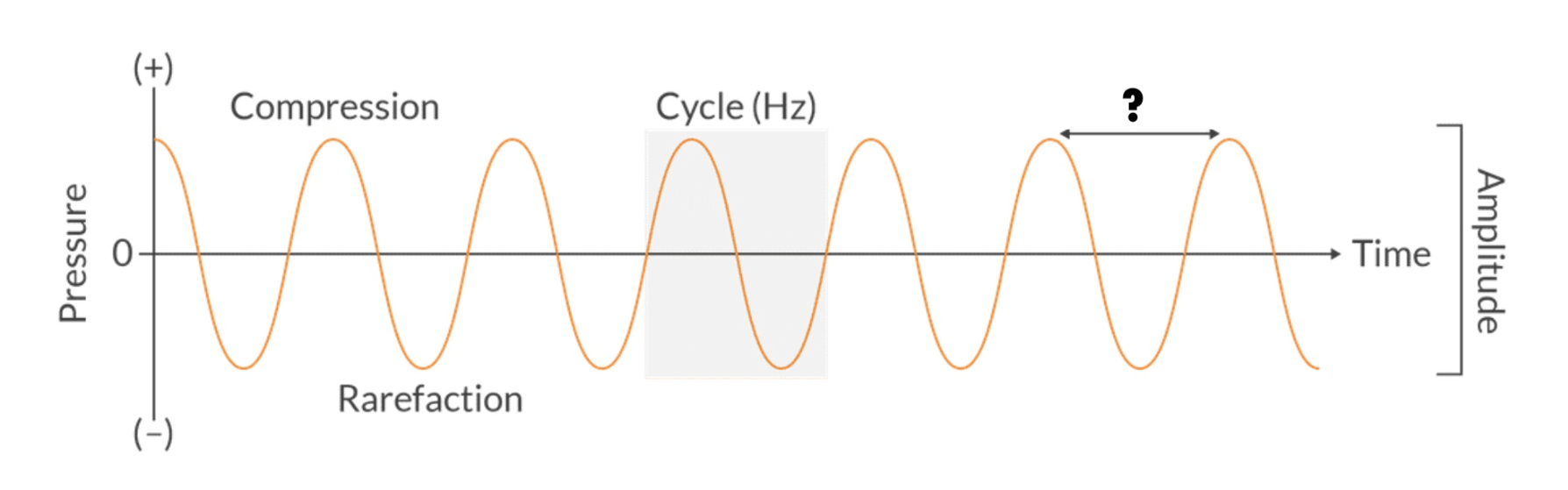
Wavelength
There are 3 main features on a sound wave: wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
Higher frequencies produce shorter wavelengths. And lower frequencies produce longer wavelengths.
This patient is presenting with hyperinflation of the lung or thorax, widened intercostal spaces, and a flattened diaphragm. What disease process causes this?
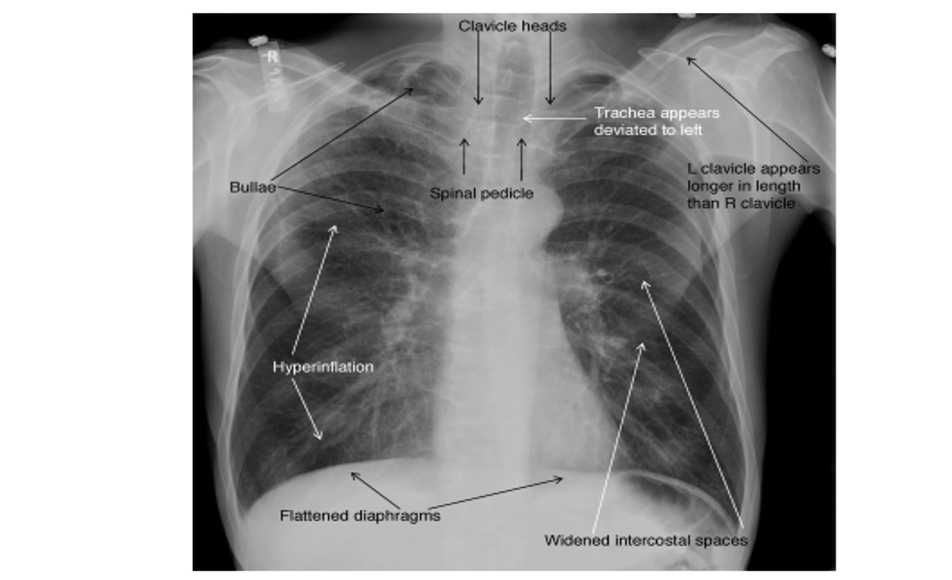
COPD
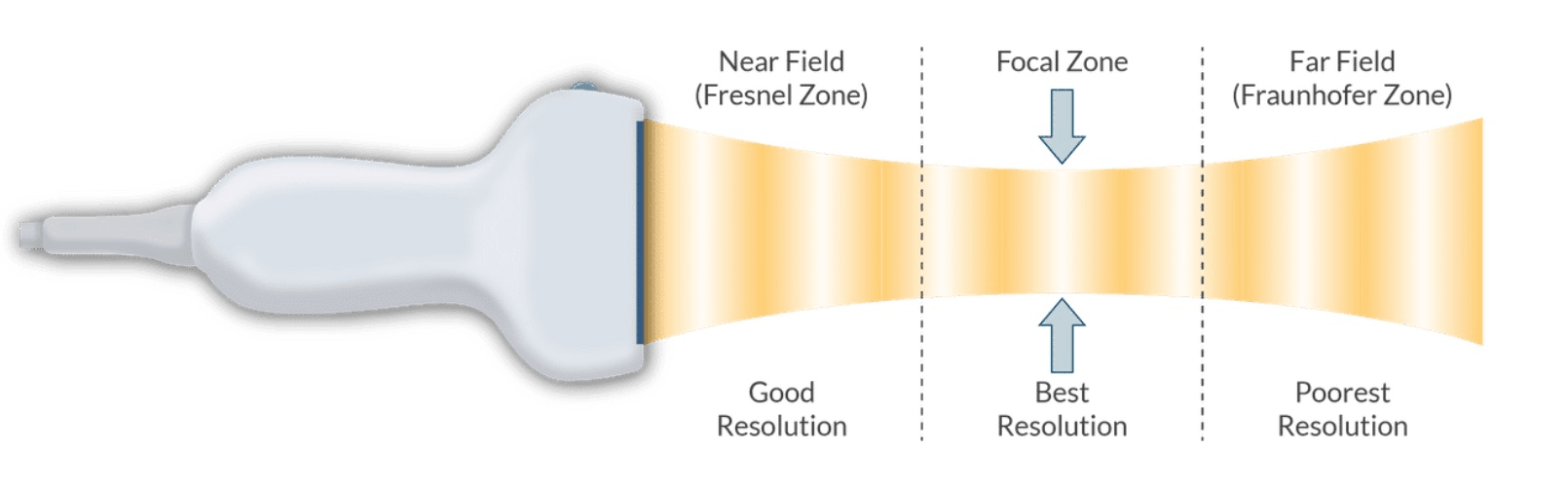
In what zone is image resolution the best on ultrasound?
Focal zone
What term describes structures that don't produce any echo and appear black on the ultrasound screen?
Ex: arteries, veins, cysts, ascites
Anechoic
Echogenicity is a tissue’s ability to transmit or reflect sound waves in the context of the surrounding tissues.
Hyperechoic structures produce strong, high amplitude echoes and appear bright or white (fascia, connective tissue).
Hypoechoic structures produce weak, low amplitude echoes and appear grey (muscle, fat).
Anechoic structures don’t produce any echo (blood vessels).
Where should the tip of a central venous catheter reside?
Distal 1/3rd of the SVC between the right atrium and the most proximal venous valves
When the tip is in the proximal 1/3rd of the SVC it is 16x more likely to thrombose. If it is too deep it can produce arrhythmias or cardiac perforation.
What transducer array configuration has a convex footprint that produces a fan-like image that’s somewhat narrow at the top and widens as the signal moves deeper into the body?
Hint:These transducers generally operate in the lower frequency range.
Curvilinear array transducer
Which abnormality presents with the deep sulcus sign on chest X-Ray?
Pneumothorax
The deep sulcus sign is an abnormal lucency over the ipsilateral costophrenic angle in a supine patient with pneumothorax.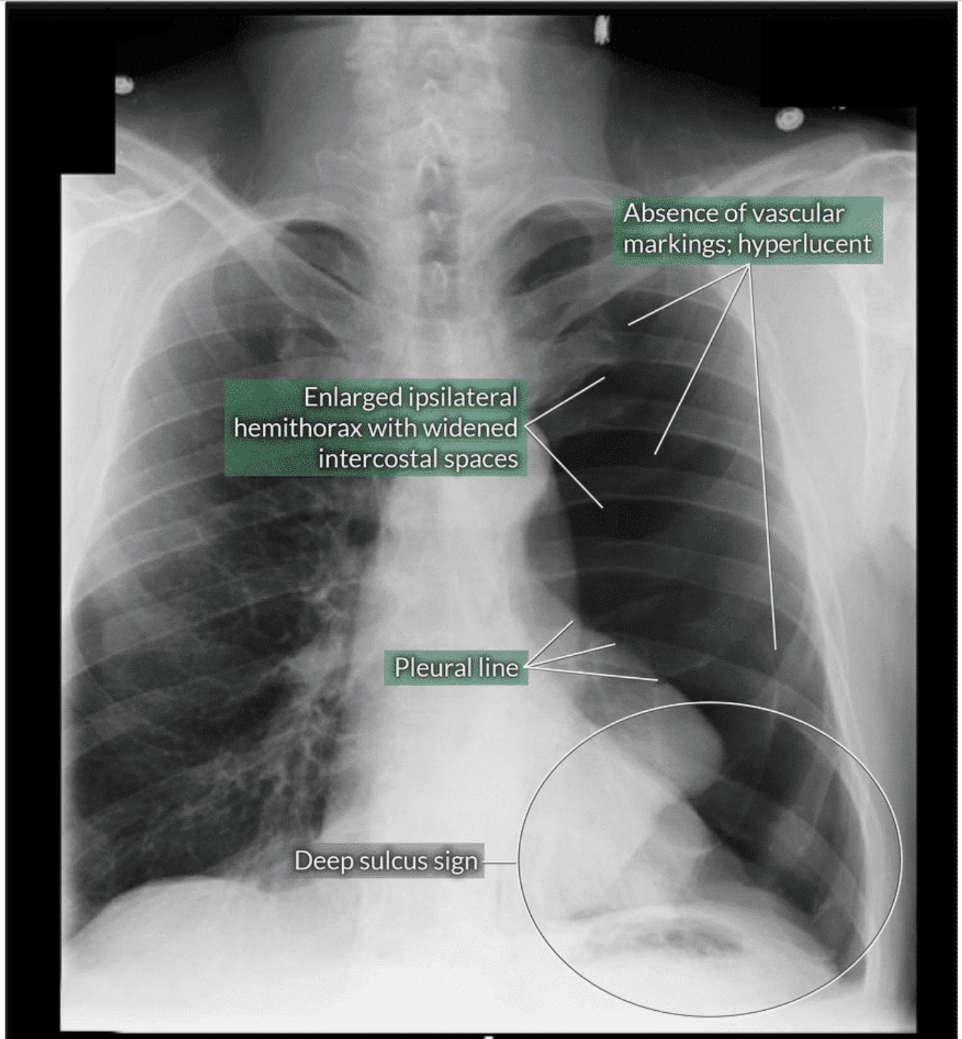
What phenomenon can make the needle appear to bend as it passes through adjacent tissues of different acoustic impedance on ultrasound?
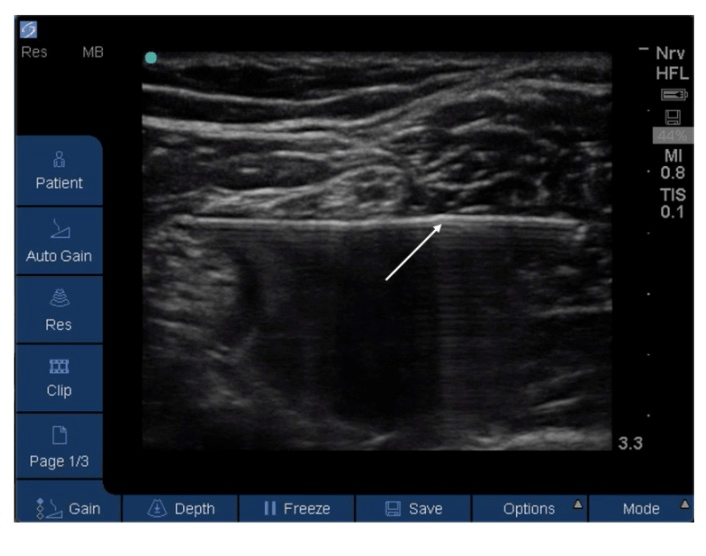
Bayoneting
This occurs because the ultrasound machine assumes that all sound waves travel through soft tissue at 1540 m/sec, however each tissue actually has a unique propagation velocity.
T/F Peripheral nerves closest to the brain and spinal cord tend to appear hyperechoic, but distal peripheral nerves are anechoic with a characteristic honeycomb appearance.
False.
Peripheral nerves near the neuraxis tend to be anechoic (black) and may sometimes be confused with vascular structures.
Distal peripheral nerves are hyperechoic (white) with a honeycomb appearance because they are typically surrounded by fat/connective tissue.
What is the normal cardiothoracic ratio on a chest X-Ray?
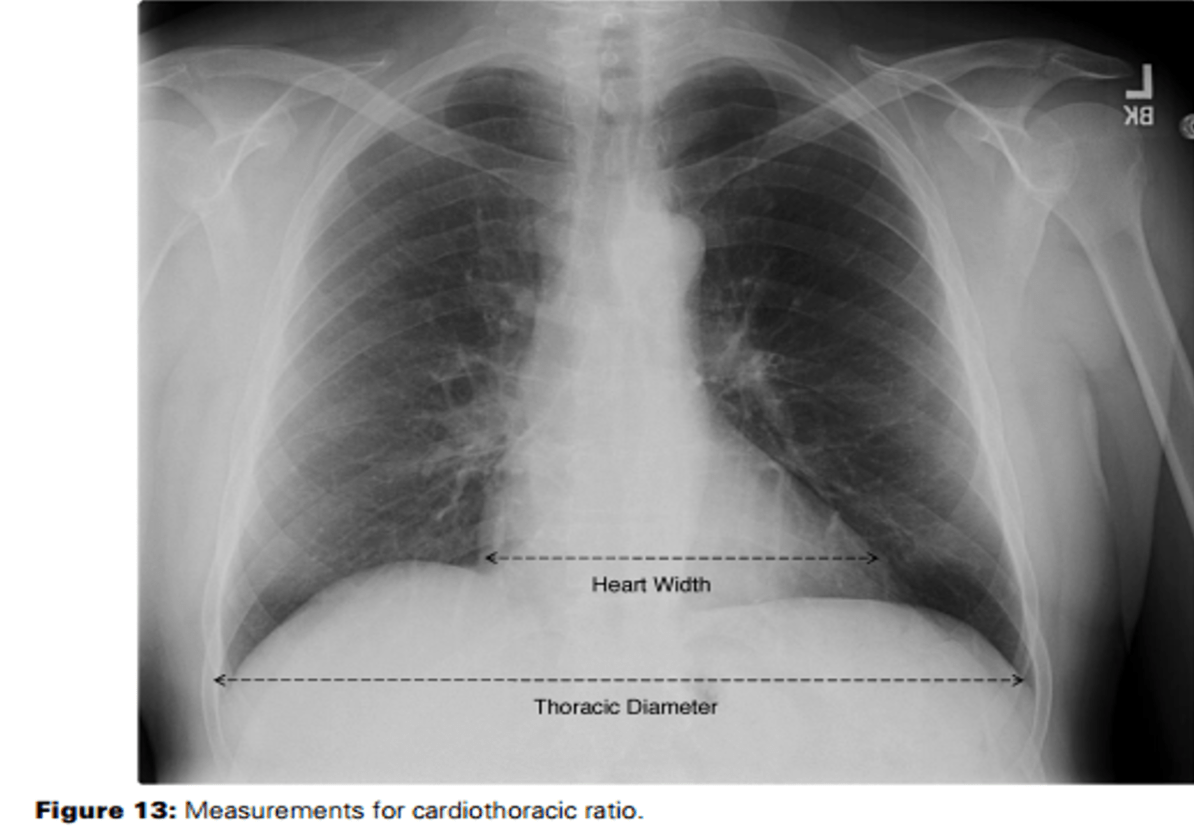
Less than 1:2 or 50%
The cardiothoracic ratio is determined by measuring the horizontal width of the heart and dividing that width by the widest interval of the thorax.
The PA view provides the most accurate estimation of heart size.
What transducer array configuration has a flat footprint that contains piezoelectric crystals in parallel?
Linear array transducer
This configuration produces an image that’s the same width as the transducer, which allows for a geometrically accurate representation on the screen. These transducers generally operate in the higher frequency range and are best for vascular access.
What is the first radiographic sign of pulmonary edema?
Cephalization
1st stage is cephalization – redistribution of vascular markings to the upper lung
2nd stage includes peribronchial cuffing and Kerley A and B lines
3rd stage includes alveolar edema, pleural effusion, and increased cardiac size
What are some ways that an iodinated contrast reaction may present?
Type I: acute <1 hour. Signs include pruritus, urticaria, bronchospasm, dyspnea, hypotension, laryngeal edema, cardiovascular collapse
Delayed reactions: >1 hour after administration. Signs include rash, pruritus, gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment is supportive.
Patients with a history of reactions can be pretreated with prednisolone 50 mg, 12 and 2 hours before procedure and 50 mg diphenhydramine immediately prior to procedure.
What determines the vertical placement of structures on the ultrasound screen?
Time delay
How long it takes for the echo to return to the transducer
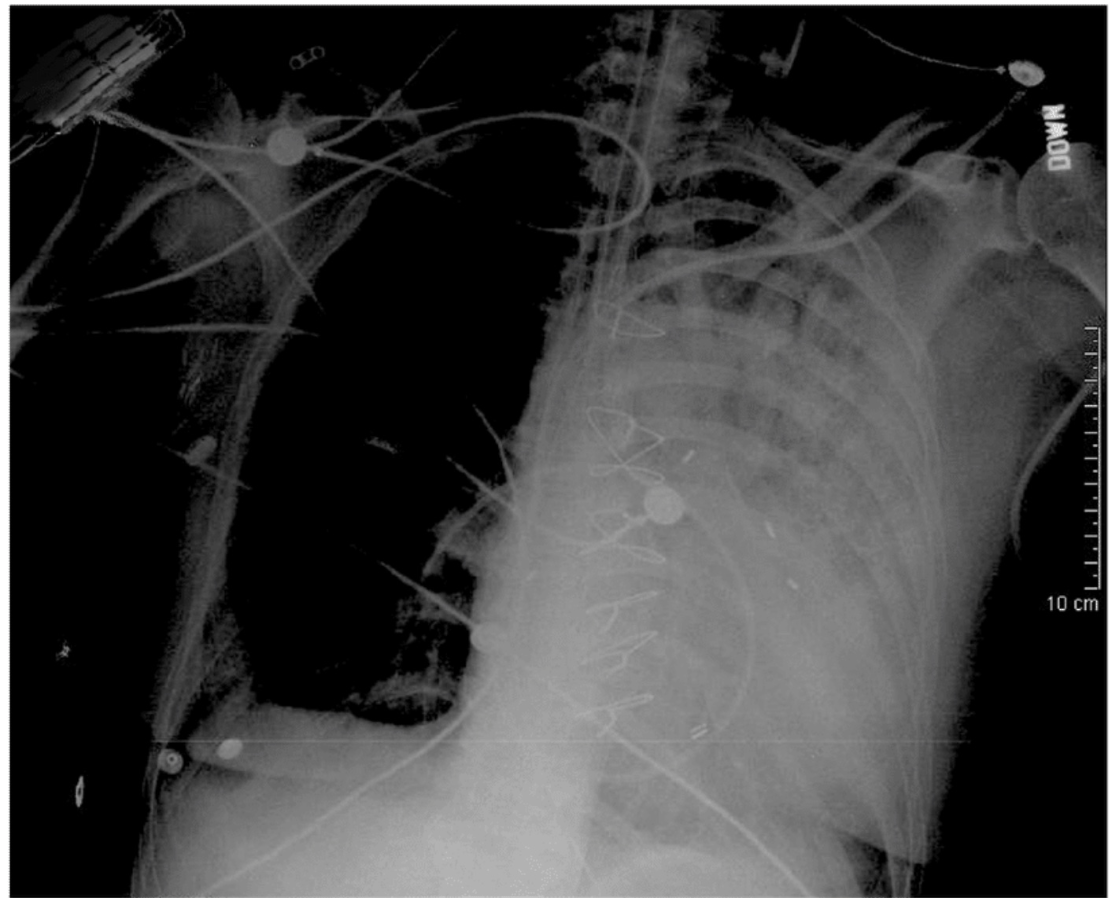
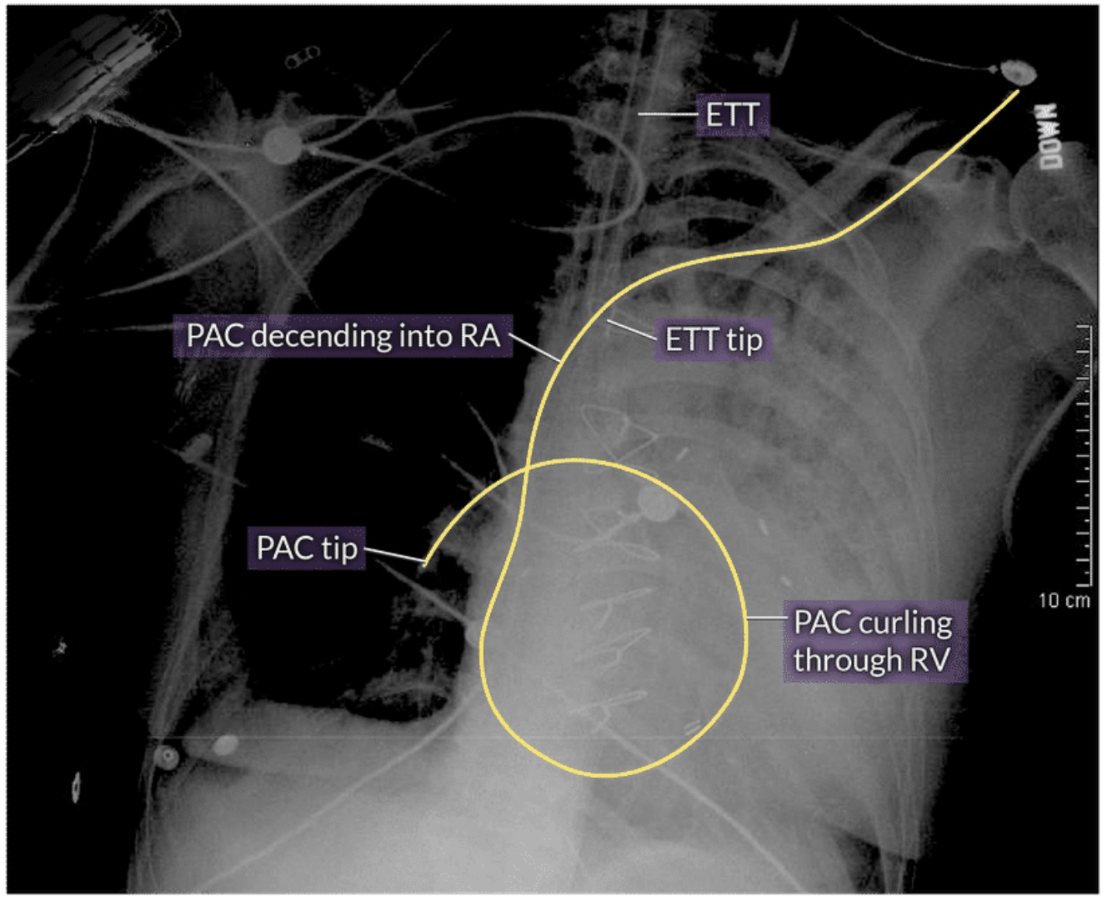
Identify the 2 appliances in this chest X-ray
PAC and ETT
A PAC should be visualized coursing from the SVC to RA to RV to PA in West’s zone 3
Which setting on the ultrasound machine is used to adjust the strength of the returning echoes displayed on the screen?
Gain
Adjusting gain can increase or decrease the brightness on the screen but it does not change the relative contrast of the anatomy.
Some ultrasound machines also have a time gain compensation feature which allows you to adjust the gain in the near or far field.
What is this patient's primary problem?
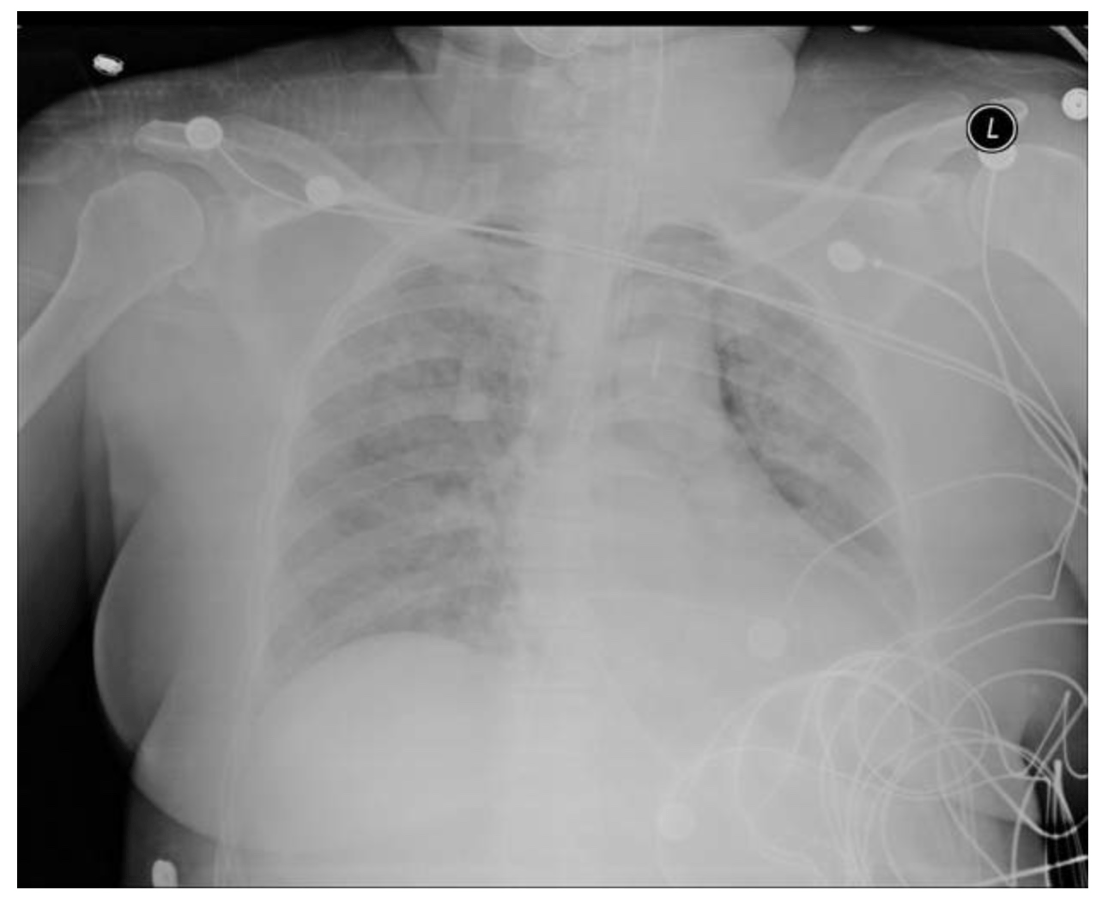
This patient has complete alveolar consolidation secondary to either cardiogenic pulmonary edema or acute respiratory distress syndrome.
What is the largest risk factor for contrast induced nephropathy?
Preexisting renal insufficiency
Contrast-induced nephropathy is the leading cause of hospital-acquired acute renal failure. High osmolality agents present higher risk than low osmolality.
Usually self-limiting and resolves within 2 weeks, however some may require dialysis.
Prevention is aimed at adequate hydration.