A measure of how applicable the results of a study are to a larger group of people or situations
Generalizability
The only research method that allows a cause-and-effect relationship to be established.
Experiment
Bias from people’s responding in ways they presume a researcher expects or wishes
Social Desirability Bias
Numerical data that allow one to generalize - to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
Inferential Statistics
Reviews research proposals, prior to the start of the study, to ensure that the study complies with all applicable federal regulations and institutional policies.
Institutional Review Board
A definition of a variable or condition in terms of the specific operation, procedures, or observable behaviors.
Operational Definition
An experimenter wants to see how sleep deprivation impacts test scores. The experimenter has one group that gets a full night sleep (8 hours for this study), and then varies the hours of sleep that other participants get. Then participants take a test. What is the independent variable?
Manipulates hours of sleep
You look at a ________ when studying a correlation.
Scatterplot
Measures of Central Tendency
Mean
Median
Mode
The process of giving participants in a completed research project a fuller explanation of the study in which they participated than was possible before or during the research.
Debriefing
This kind of sample reflects the characteristics of the population. Representative, unbiased sampling is critical for internally and externally valid results.
Representative sample
In an experiment, a variable that potentially has an effect on the outcome, but is not accounted for or eliminated.
Confounding Variable
Name the 6 types of non-experimental research
Case Study
Meta-analysis
Naturalistic Observation
Correlation
Survey
Statistics
This shows how spread out the data is
Standard Deviation
List at least 3 ethical guidelines
Informed consent
Informed assent
Protection from harm
Confidentiality
Debriefing
Deception
A flawed sampling process that produces and unrepresentative sample.
Sampling Bias
The experimenter may treat participants differently and influence their behavior according to the research hypothesis.
Experimenter Bias
An undiscovered causative variable
The third variable
What is the standard deviation?

2 inches
What ethical guideline was violated?
A person was asked to be part of an experiment where they would be locked in a room. They were food and water deprived and when they complained they got shocked. Afterwards, they were let go back into the general public without a word.
Informed consent
No protection from harm
No debrief
Give an example of overconfidence
Answers will vary
You must be able to ________ an experiment to know it is has strong validity or reliability.
Replicate
What is regression towards the mean?
The tendency for extremely high or extremely low scores to become more moderate (i.e., closer to the mean) upon retesting over time.
This is a ______ skew, which means the mean will be (higher)(lower) in the distribution
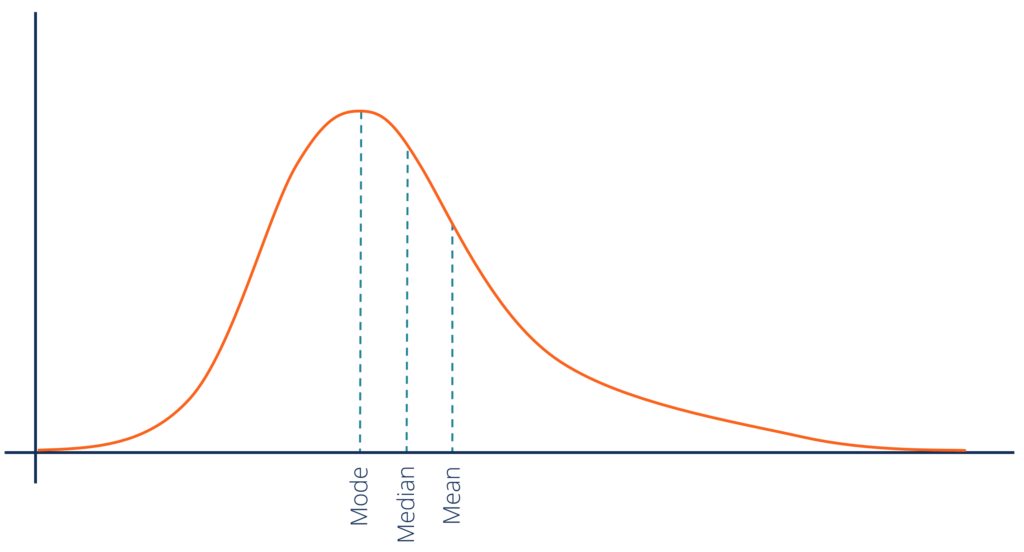
Positive
Higher
Would this pass the institutional review board?
Dr. Wendell Johnson of the University of Iowa and his graduate assistant, Mary Tutor are interested if stuttering is a learned behavior. They believe that if young children receive negative feedback regarding their speech patterns, they will develop speech disorders such as stuttering.
Dr. Johnson and Ms. Tutor have gathered orphan children to serve as their participant group. They have been given a baseline assessment of their speaking abilities to identify stutterers and “normal” speakers. Twelve children were identified as normal speakers. In one part of the experimental procedure, six “normal” speakers will be told that their speech is not normal at all, that they are beginning to stutter and that they must correct this immediately. They will be belittled for every mistake. The other six “normally speaking” orphans will be treated as such and given compliments. After a sufficient period of therapy, both groups will be retested and the data will be compared to the original baseline results.
Dr. Johnson and Ms. Tudor feel that they will gain a better understanding of the role that reinforcement and punishment plays in the development of speech. They hope their experiment will lead to new speech therapy methods and eventually a cure for stuttering. If it can be learned, it can be unlearned.