This principle describes the influence of the internal factors of emotion, past experiences, and expectations.
What is top-down processing?
This step-by-step process guarantees a correct solution.
What is an algorithm?
These are the three major processes involved in remembering information.
What are encoding, storage, and retrieval?
You can remember the password to your first email account, but not your current work email.
What is proactive interference?
This factor of intelligence is determined by dividing mental age by chronical age; today, this coefficient is most used to place students into specialized academic programs.
What is Intelligence Quotient (IQ)?

The World Wildlife Foundation represents this Gestalt principle of visual perception.
What is Closure?
This shortcut in problem-solving saves time, but may lead to biased and/or inaccurate solutions or judgments.
What are heuristics?
This memory technique walks individuals through their home, where each room is associated with a piece of information to be remembered.
What is the method of loci?
What is retroactive interference?
Intelligence assessments must adhere to consistent procedures and environments.
What is standardization?
This Gestalt principle is often represented by this image of a vase. Or are these faces?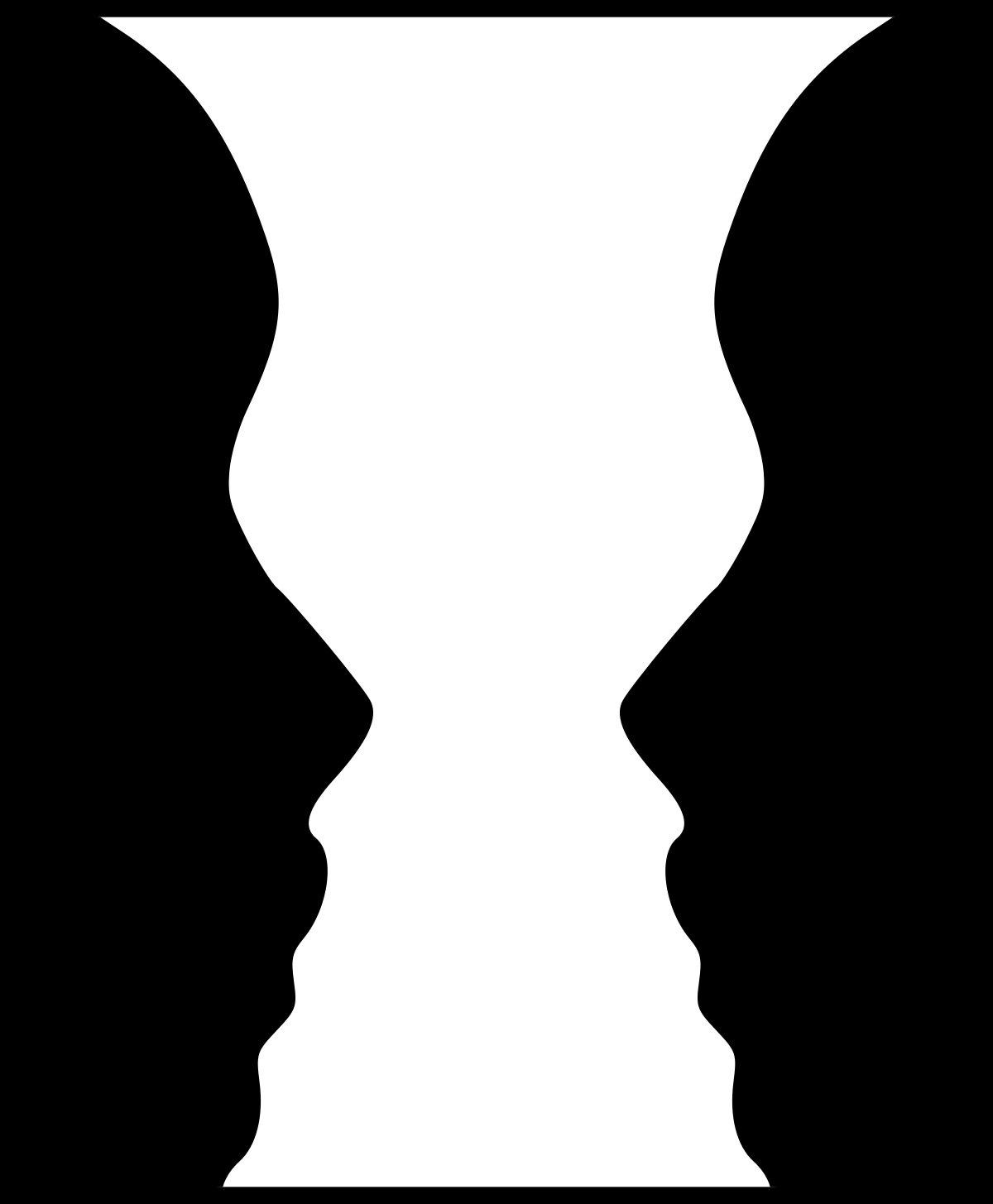
What is Figure-Ground?
This psychological phenomenon occurs when an individual is influenced by their exposure to a related stimulus.
What is priming?
"My very energetic mother just served us nachos" and "Please excuse my dear Aunt Sally" are examples of this memory trick.
What are mnemonics?
E.P. can give you turn by turn directions from his childhood home to the grocery store, but cannot remember what street he currently lives on.
What is Anterograde Amnesia?
IQ scores across much of the world have generally increasedo ver time, often due to societal factors like higher socioeconomic statuses and access to better nutrition and advanced health care.
What is the Flynn Effect?
This concept allows our brains to interpret visual stimuli as three-dimensional.
What is retinal or binocular disparity?
This bias occurs when information is presented in a specific manner meant to elicit a desired effect.
What is framing?
This memory system is critical to the memory process, but is limited in both capacity and duration.
What is sensory memory?
M.B. cannot remember anything from before her car accident.
What is Retrograde Amnesia?
The belief that intelligence is malleable, or flexible.
What is growth mindset?
Relative size, interposition, texture gradient, linear pespective, and relative height are all examples of this type of perception of depth within the environment.
What are monocular cues?
After three years majoring in Political Science, you find that you have much more interest in Psychology; however, you only have a year left in your degree program, and decide that it is too late to change your major. You have succumbed to this psychological principle.
What is sunk-cost fallacy?
The process of retrieving and reproducing information without any memory cues.
What is recall?
This temporary inability to retrieve a word from memory, despite having a strong feeling of knowing the word.
What is the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon?
Achievement tests that accurately measure how much an individual knows have this.
What is validity?