Interpt.
Traditional economies answer the economic questions of what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom by relying on these.
What is custom and tradition?
People respond to these in predictable manners.
This economic system is often times confused as a system of government…
Communism
Supply is from the perspective of whom.
What is the supplier/producer ?
What is the abbreviation to analyze the market structures of any industry/
N , S , E , C
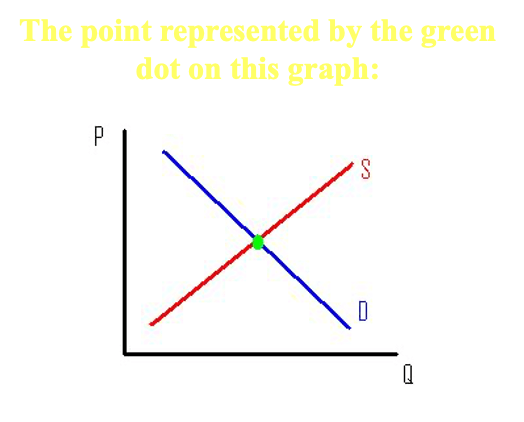
What is equilibrium
The single largest economic system today.
What is Mixed Market Economy?
Because we have unlimited wants and desires and limited resources we are forced to make .
What are trade-offs?
This term can be described as anything that can be used physically monetarily, or laboriously to help a business.
What is capital?
This factor can change market demand by changing the amount of money consumers make.
What is income?
In this market structure the top 4 producers control the industry and have some price control
What is an oligopoly
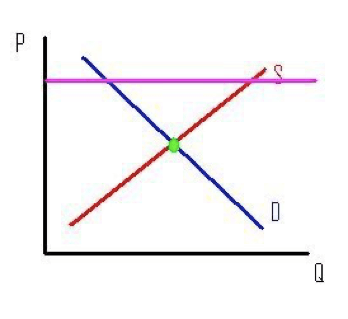
A surplus will drive the price _____ by _____
Down by sales
Command economies answer the economic questions of what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom by relying on this group of people.
What are the decisions of a powerful rule or central government?
When we make a decision, our next best choice is represented best as.
What is opportunity cost?
This term describes political philosophy and movement encompassing a wide range of economic and social systems which are characterized by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership.
What is socialism?
Tariffs, sin tax’s, and subsidies are all examples of this shifter.
What is government intervention
A farmers market is an example of this market structure
Perfect Competition
What is an example of a price ceiling?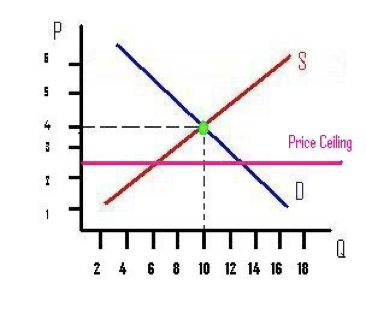
Rent Control / Pay Scales / Insurance Out of Pockets
Market economies answer the economic questions of what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom by relying on this group of people
What are producers and consumers?
Stonestown, Amazon, a Farmers Market all describe which economic principal
What is markets coordinate trade?
The mysterious force that coordinated markets was termed this by economist Adam Smith.
What is “the invisible hand?”
Supply may increase or decrease due to this change in the amount of money a supplier has to spend to make their product.
What is cost of inputs?
In a monopolistic competition companies vie (fight) for business (customers) through
different-ion
What is happening to the equilibrium price and quantity in the image?
Price and quantity increases
Of the six economic goals discussed in the textbook, market economies are the best at achieving these two.
What is economic efficiency and economic freedom?
This image best describes what.
What is the law of diminishing returns/utlilization?
Who is Karl Marx
This demand shifter moves the market demand by changing the price of goods consumers use in place of another good.
Price of Subsititute Goods
What are the 3 types of government monopolies?
What is - patents & copy right, licenses, and franchising(outsourcing)
What is shifting in this visual?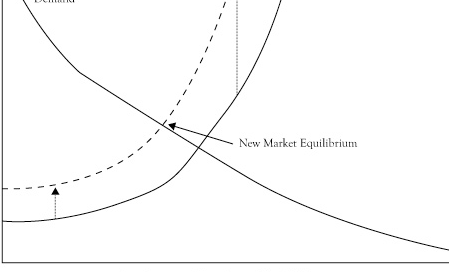
Supply is decreasing and quantity