The shaking an trembling that results from movement of rock beneath Earth's surface
Earthquake
Which fault has the same stucture as a normal fault but the blocks move in the reverse direction?
reverse fault
How many types of seismic waves are there? Name them
3 - P waves, S waves, Surface waves
The block of rock that lies above a fault is called what?
hanging wall
A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch is called a(n)
anticline
a large area of flat land elevated high above sea level
plateau
In a strike-slip fault, the rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other sideways with little what?
up or down motion
What does a seismogram use to record the drum's vibrations?
pen
Which of the following can cause damage days or months after a large earthquake?
aftershock
t/f: With the range of data available, geologists cannot predict exactly where or when earthquakes will happen
true
Name the 3 types of faults
Normal, reverse, strike-slip
in a normal fault, the part of the fault that lies below the other part is called what?
footwall
What is a modified Mercalli scale?
rates the amount of shaking which is rated by people's observations without using any instruments. How strongly people feel the shaking
The rating system that estimates the total energy released by an earthquake is called....
moment magnitude scale
The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock breaks under stress and triggers an earthquake is called the
focus
An instrument that records and measures an earthquake's seismic waves
seismograph
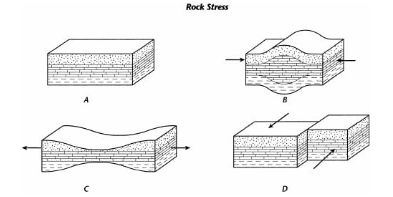
What kind of stress is happening at B, C, D?
B: compression
C: tension
D: Shearing
What is the difference between and anticline and syncline?
Both are fold in rock but Anticline arches upward and syncline bends downward
The type of seismic waves that arrive at the surface first and move by compressing and expanding the ground like an accordion are called
P waves - Primary waves
What kind of risk is shown on the map and how is this risk determined?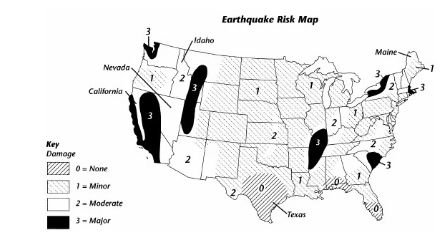
The map shows the risk damage from earthquakes. Geologists determine earthquakes risk by locating where faults are active and where past earthquakes have occured.
Name the three types of stress and tell me what they do
Tension; plates pulling apart
compression: plates coming together
shearing: two plates slip past each other
Which type of stress produces reverse faults?
Compression
The seismic waves that produce the most sever ground movements
surface waves
t/f: the squeezing together of rocks by stress is called shearing.
false; compression
how do California and Nevada compare in possible severity of earthquake damage?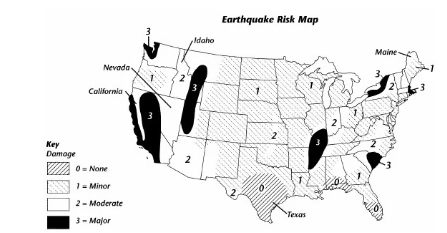
both states could suffer earthquakes causing moderate to major damage