This is the name for a prediction that states there is no difference between two groups of data, and the experimental observations are due to chance.
What is the null hypothesis?
This is the acronym used to remember the essential elements in living things.
What is CHOPN?
This element forms the backbone of most organic molecules, and can form long chains as well as rings with single or double bonds.
What is carbon?
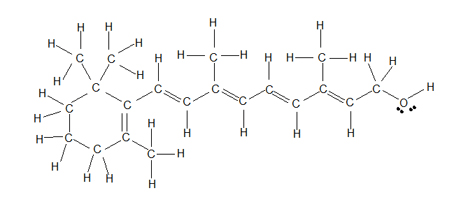
This level of protein structure occurs when a chain of amino acids coils and folds due to hydrogen bonding.
What is secondary?
This is the formula used to determine the number of electrons that each shell around a nucleus can hold.
What is 2n2?
This is the name for something that does not change throughout the experiment?
What is a constant or controlled variable?
This is the type of bond that typically occurs between a metal and a nonmetal.
What is ionic?
The glucose molecules in the image below represent repeating units also known as this:
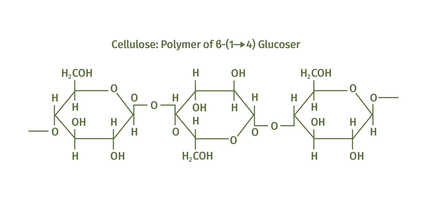
What is a monomer?
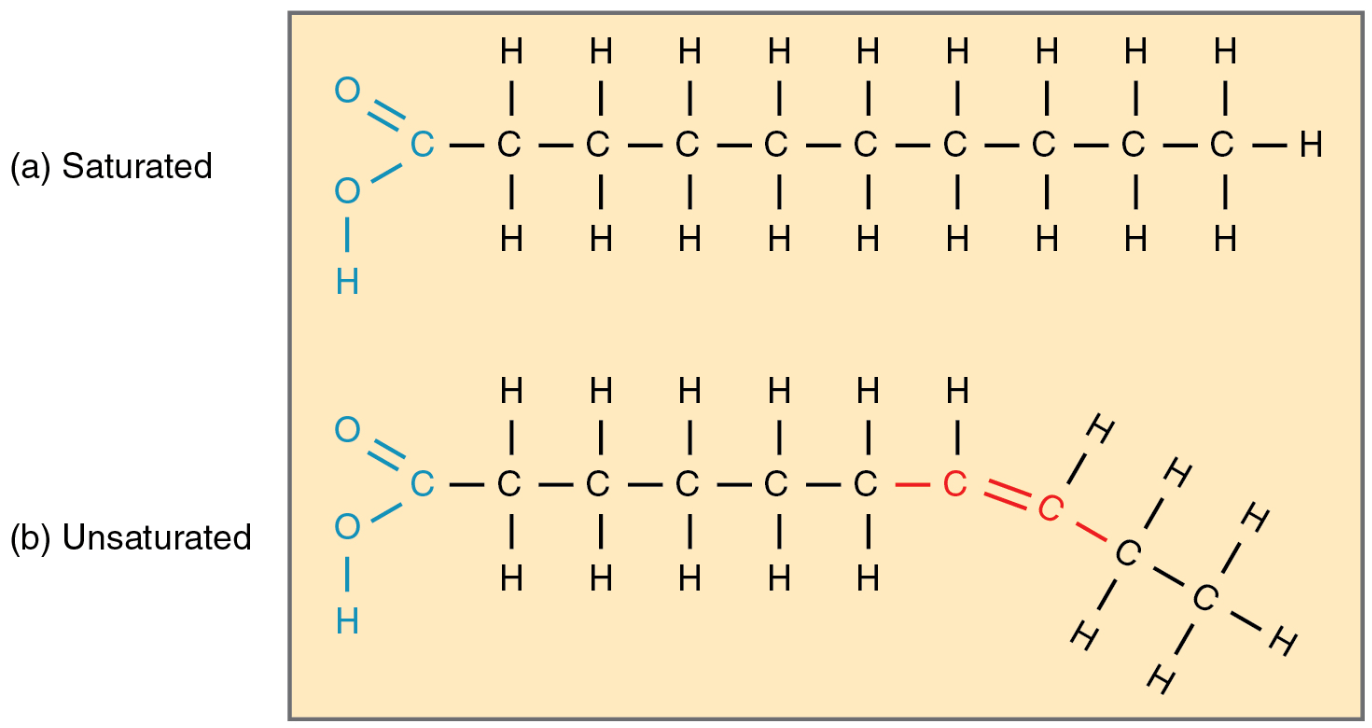
This type of bond is present in an unsaturated fatty acid within a lipid.
What is a double bond?
This is supported by a massive body of evidence, but can never become a law.
This is the manipulated value in an experiment.
What is the independent variable?
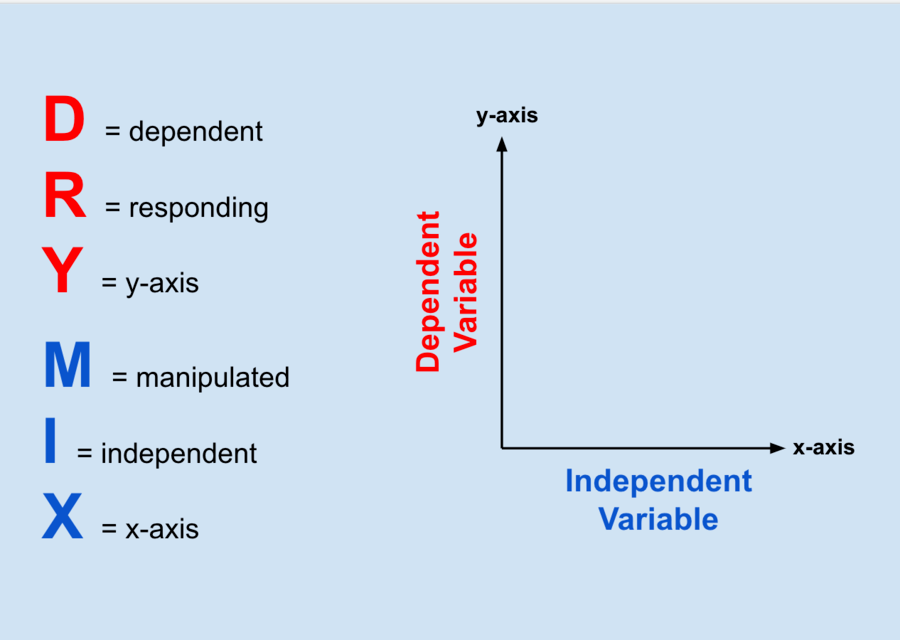
This type of bond is responsible for causing water molecules to form a crystalline structure when cooled, due to the fact that the water molecules move slowly.
What is hydrogen bond?
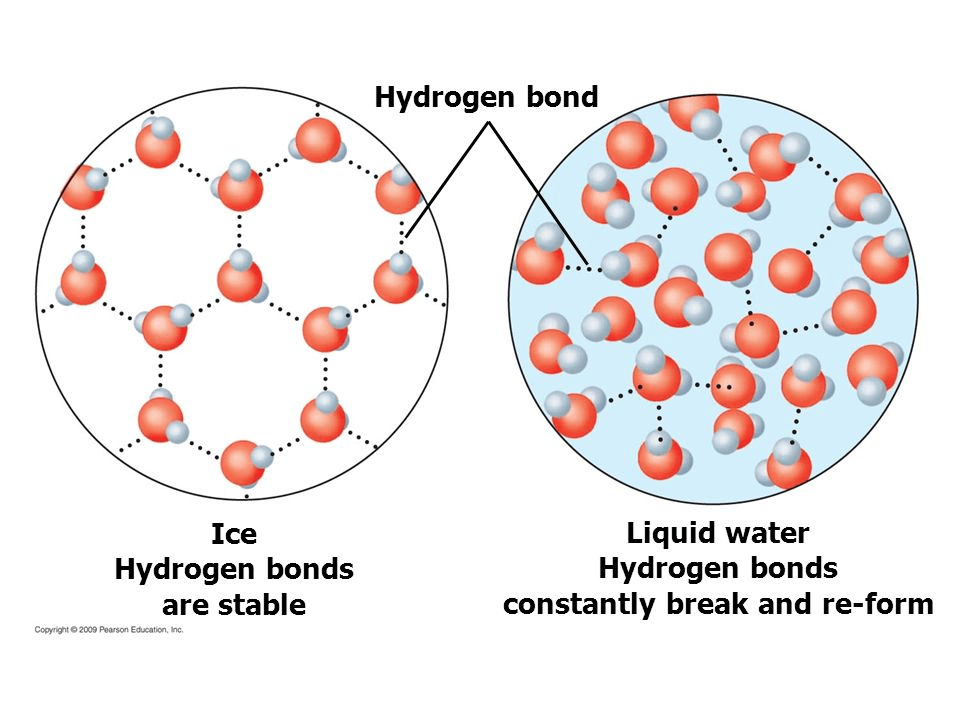
This is the chemical formula for the carboxyl group.
What is -COOH?
Changes in pH, temperature, or the genetic code can cause a protein to do this.
What is denature?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
What is the maximum number of bonds an element of nitrogen can make with other atoms?
What is three?
This is the name for the practice of stating a generalization based on a number of specific observations.
What is inductive reasoning?
When this attraction is greater than this other attraction, there is a formation of a concave meniscus of water in a graduated cylinder. (Your answer should be in the form 'what is _______ is strong than ______?')
What is cohesion is greater than adhesion? 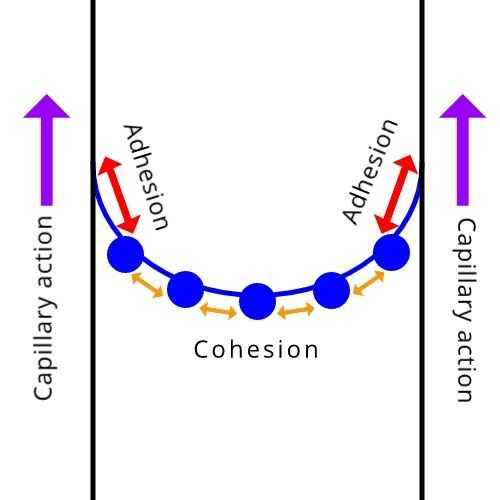
This type of reaction breaks the bonds in a polymer by adding water, where one -H of the water bonds to one monomer and the remaining -OH attaches to the other monomer.
What is hydrolysis?
This would be the complementary strand of DNA for the following strand:
5' - TCGGCAATC - 3'.
What is:
3' - AGCCGTTAG - 5' ?
This is the name of the sugar in the nucleotide below, named so because it lacks an extra oxygen atom on the 2nd carbon, which would have made it a hydroxyl group.
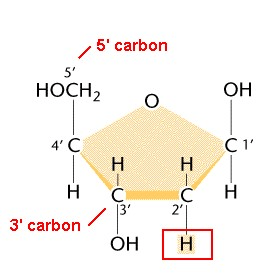
What is deoxyribose?
This is the name for a group that is exposed to a treatment known to produce the expected effect. If it does not, there may be something wrong with the experimental procedure.
What is a positive control?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
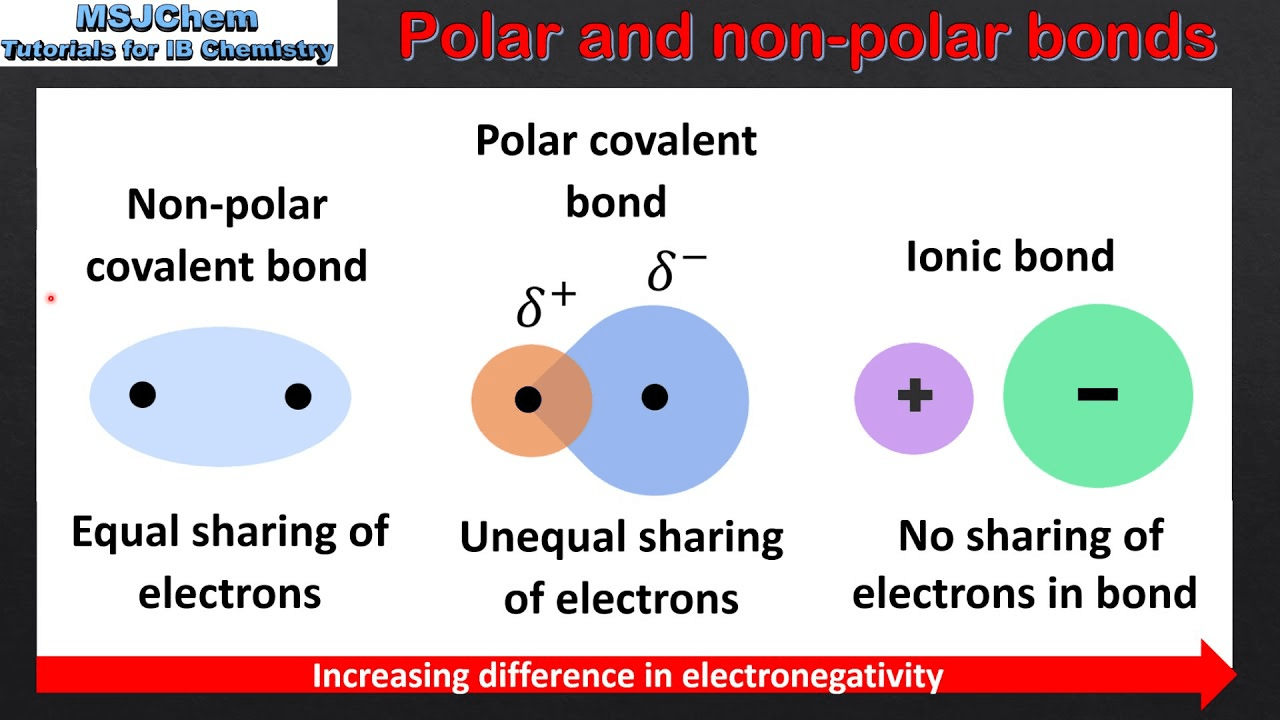
This is what causes the hydrogen of one atom to have a partial positive charge and the electronegative atom to have a partial negative charge.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!
What is polar colavent bond?
A peptide bond forms when this functional group of one amino acid interacts with the carboxyl group of another amino acid.
What is the amino group? (-NH2)
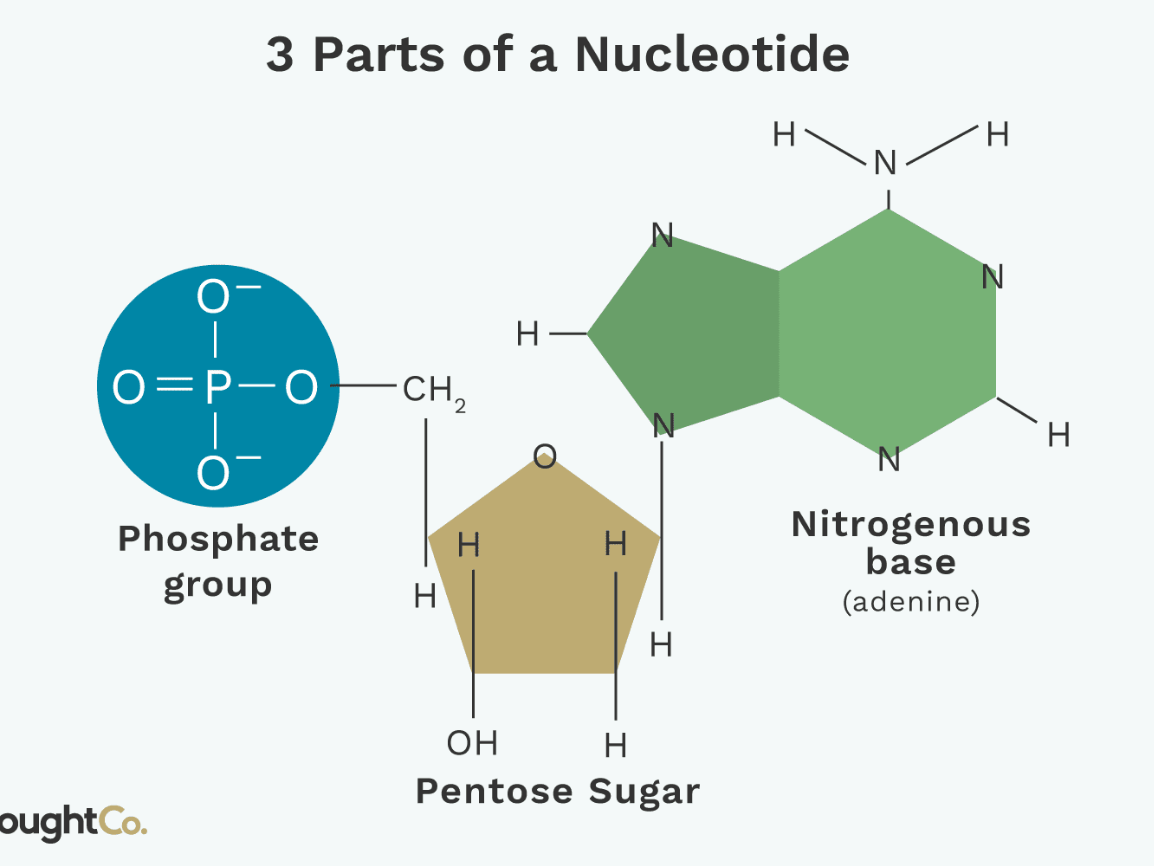
A nucleotide contains these three parts in its structure.
What is a (5' carbon) sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
This is the name for a positively charged ion.
What is a cation?