These are large molecules made from repeating smaller units called monomers.
What are macromolecules?
The monomers of carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides?
A process that changes one set of chemicals into another by breaking and forming new bonds.
What is a Chemical Reaction?
Determine the type of macromolecule that enzymes are.
What are proteins?
This is the name for the individual small subunits that join together to make a larger macromolecule.
What is a monomer?
This type of protein speeds up chemical reactions but is not used up.
What is an enzyme?
This is the amount of energy that must be absorbed to start any chemical reaction.
What is Activation Energy?
Label the three parts of the enzyme-substrate complex.
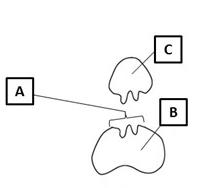
A. Active Site
B. Enzyme
C. Substrate
Glucose, fructose, and galactose are examples of these simple sugar monomers for carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides?
A type of lipid that is the main structural component of the cell membrane.
What is a phospholipid?
Catalysts speed up a reaction by doing this to the required activation energy.
What is... decreases (or lower) it?
Determine what enzymes do to chemical reactions in the body
What is... speed them up?
This macromolecule provides insulation and protection around organs for long-term energy storage
What are lipids?
True or False. True or False: Lipids mix easily with water.
What is false?
Determine the reactants and products in the equation below.
6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is...
Reactants: 6CO2 + 6H2O
Products:C6H12O6 + 6O2
What happens to the substrates during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction (a type of chemical reaction)?
What is... converted into products?
Determine what each macromolecule is based on the photos below:
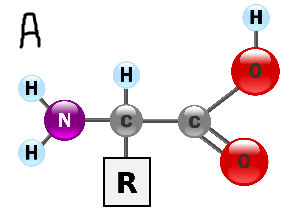
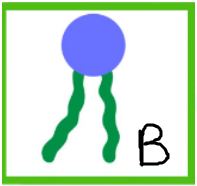
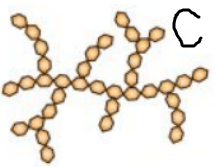
What is...
A. Proteins
B. Lipids
C. Carbohydrates
D. Nucleic Acids
Write the elements found in each macromolecule.
What is...
Carbohydrates: CHO
Lipids: CHO
Nucleic Acids: CHONP
Proteins: CHONPS
When baking soda is mixed with vinegar, bubbles are formed. Those bubbles are made of this gas.
What is carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Too much heat or a pH outside the optimal range can cause an enzyme to lose its shape and function, a process known as this.
What is Denaturation?