What is the energy of motion called?
Kinetic energy.
What type of energy transformation occurs when a battery powers a flashlight? (
Chemical energy to light energy (and thermal energy).
What is the process called when heat moves through direct contact?
Conduction.
What do we call materials that allow electricity to flow easily?
Conductors.
Define kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion.
Name two types of potential energy.
Gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, nuclear energy, chemical energy.
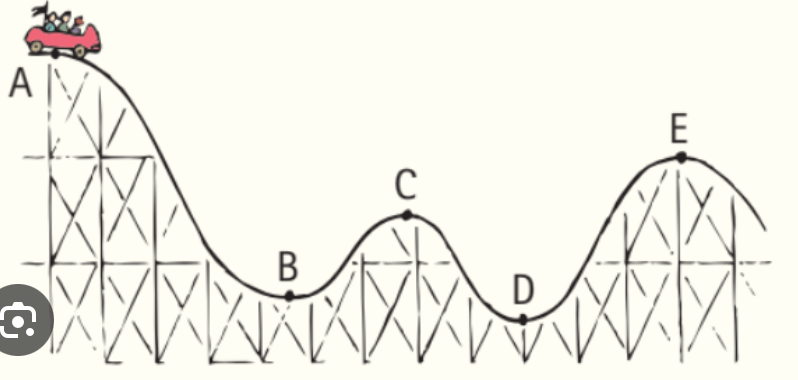 Describe the energy transformation that occurs in a roller coaster at the top of a hill.
Describe the energy transformation that occurs in a roller coaster at the top of a hill.
At the top of a hill, potential energy is at its maximum, and as it descends, that potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
Name the method of heat transfer that occurs through liquids and gases.
Convection.
Describe conduction in terms of electricity.
Conduction refers to the transfer of electric charge through direct contact between materials; electrons move from one material to another.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy of an object due to its position or condition.
Explain the relationship between potential energy and height.
The potential energy of an object increases as its height increases, as it has more energy stored due to its position.
Give an example of a scenario where potential energy is converted to kinetic energy.
Answers vary. ex A falling apple converts its potential energy (when it is high) to kinetic energy (as it falls).
How does radiation transfer heat?
Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves without needing a medium (e.g., heat from the sun).
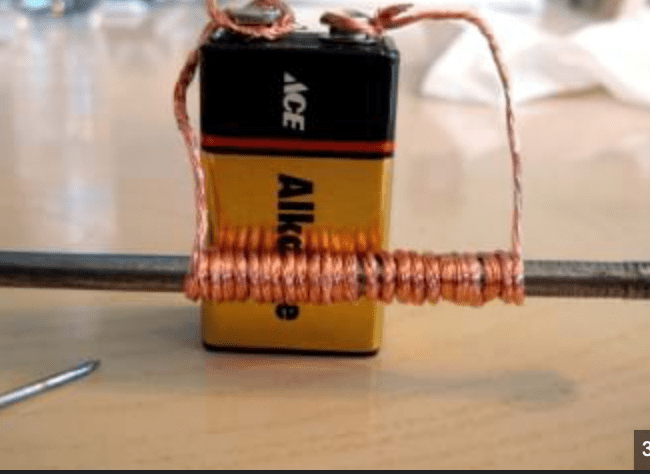 How does an electromagnet work and what does it produce?
How does an electromagnet work and what does it produce?
An electromagnet uses electric current to generate a magnetic field.
Describe thermal energy.
Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of particles in a substance, related to temperature.
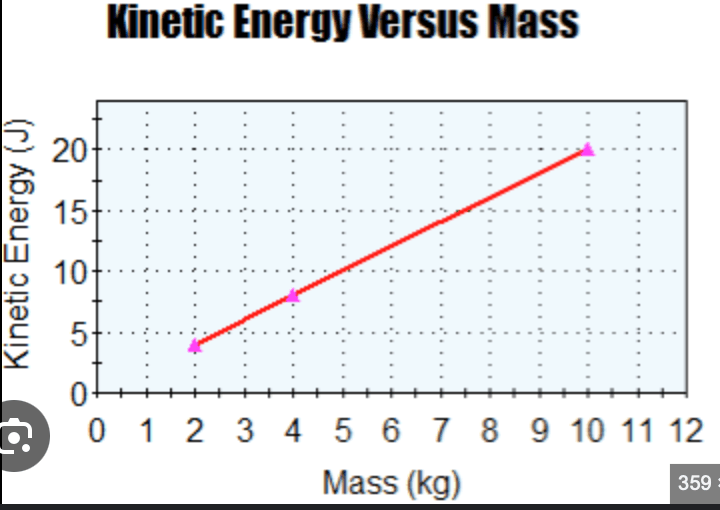
Given a graph that shows the relationship between kinetic energy and Mass for an object of constant speed, describe how the kinetic energy changes as mass increases. KE = 1/2 mv²
As mass increases, the kinetic energy increases as well, following the formula KE = 1/2 mv².
What energy transformation happens when you strike a match?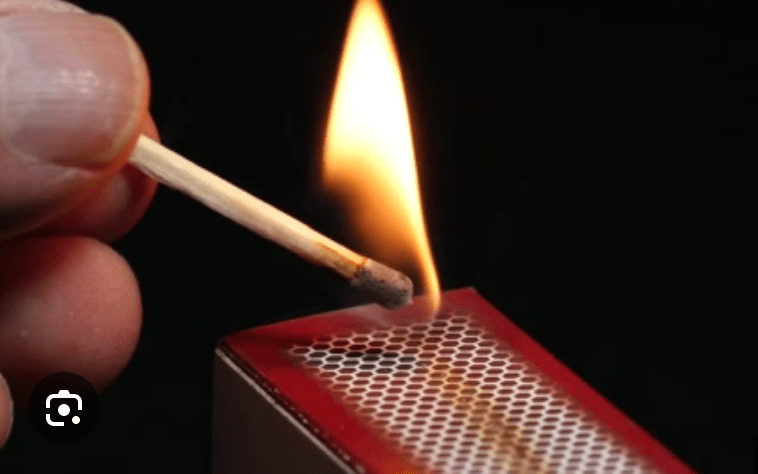
When you strike a match, chemical energy is transformed into heat energy and light energy.
What effect does heat transfer have on molecular (particle) motion? (think about what happens to their energy, temperature, and movement)
Heat transfer causes molecules to move faster, increasing their energy and temperature.
Identify a factor that affects the strength of an electromagnet.
The number of wire turns affects the strength of an electromagnet; more turns result in a stronger magnetic field.
What is an insulator?
An insulator is a material that resists the flow of electricity or heat.
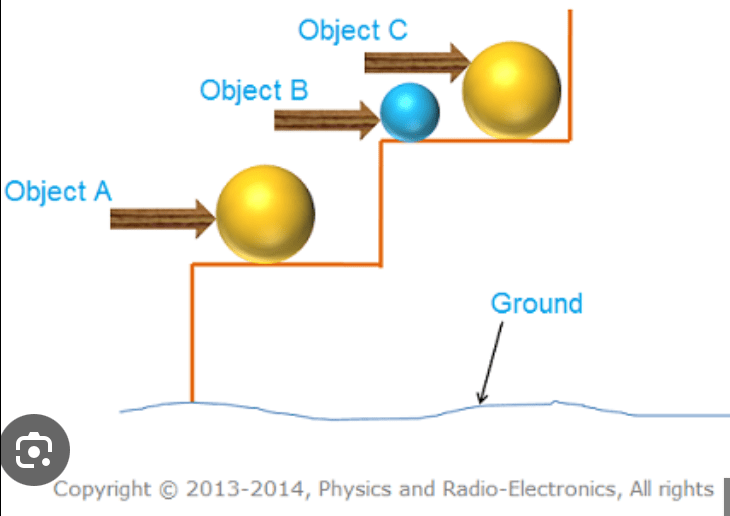
Analyze the illustration showing three objects at different heights. Explain how the potential energy of objects B and A compares to C and what factors influence their potential energy.
The object at a greater height has higher potential energy due to its position so A<C (C >A)and due to having less mass the PE of B < C (C >B). Potential energy is determined by the mass of the object and height following the formula PE = mgh
Explain the transformation of energy in a pendulum swing. (Include an illustration)
In a pendulum swing, potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as it swings down and then back to potential energy as it swings up.
Explain or illustrate how convection currents work in heating a room.
Convection currents work by heating air or liquid, causing it to rise, cool down, and then sink, creating a circulating pattern.
Explain how friction can produce static electricity.
Friction can cause static electricity by transferring electrons from one object to another, resulting in charged objects.
Define the law of conservation of energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.