Drilling a hole in the skull in attempts to "release evil spirits", relieve headaches, sickness, etc.
What is Trepination
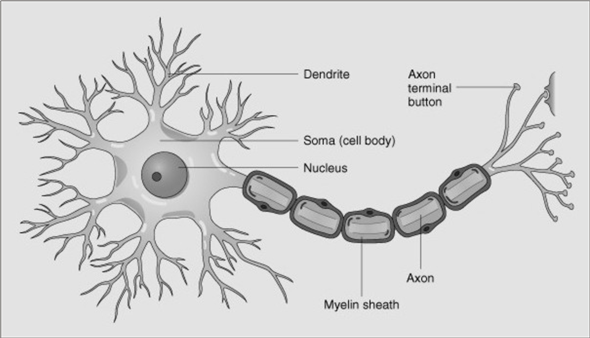
Describe the structure of a neuron.
What is -60 mV
*Between -50 to -80 mV
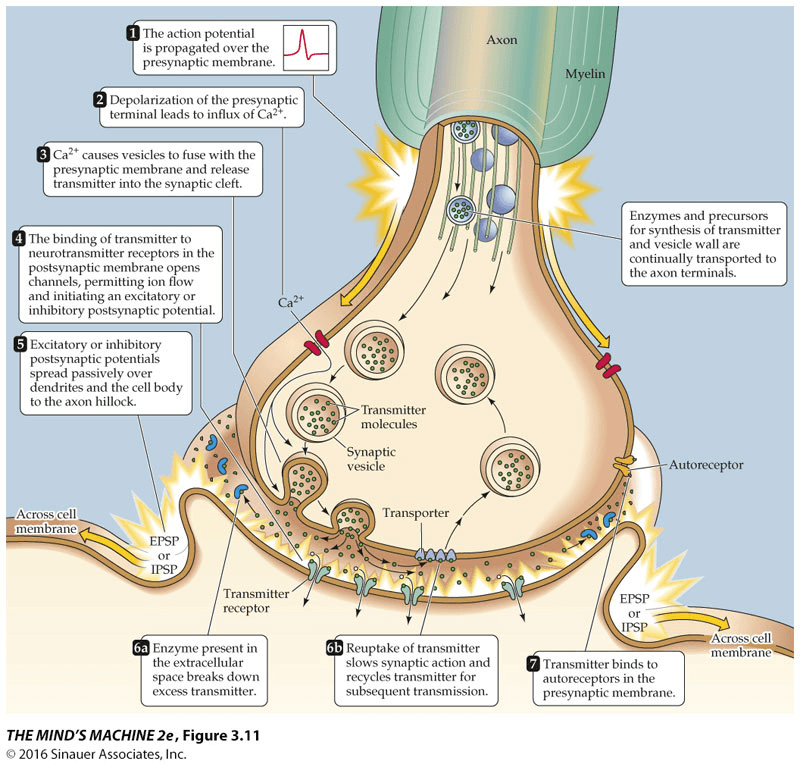
Demonstrate the steps for synaptic transmission.
Detects temperature and pain
What are Free Nerve Endings
He was the physician to the Roman gladiators.
Who is Galen
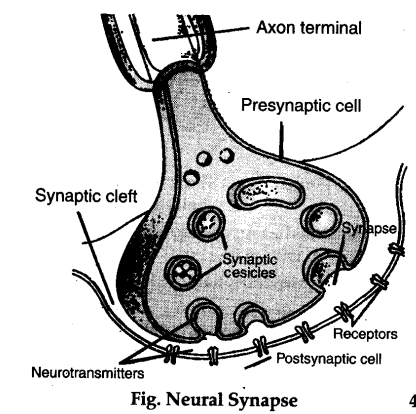
Draw and/or explain the structure of a synapse.
State the cations and anions discussed in the chapter.
Cations: K+, Ca2+, Na+
Anions: Cl-, Proteins-
This NT is transmitted in the forebrain. It activates 2 receptor types: nicotinic and muscarinic. Linked to Alzheimer's Disease.
What is Acetylcholine (ACh)
This states that each nerve input to the brain reports a particular type of information. Ex: pain from your knee travels along a different pathway than pain from your elbow.
What are Labeled Lines
This is the live dissection on animals.
What is Vivisection
Layer of fatty insulation surrounding axons; allows AP to travel faster.
What is Myelin
Describe the Sodium-Potassium Pump
Pumps 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ pumped in. As K+ build up inside the cell, they also diffuse out through open ion channels. As negative charge builds up inside the cell, it exerts electrostatic pressure to pull K+ back in.
This NT runs on 2 pathways, is linked to Parkinson's Disease, and is released in response to positive reinforcement and reward.
What is Dopamine (DA)
___ receptors display adaptation while ___ receptors do not.
What are phasic and tonic receptors.
This was the first medical record.
What is the Edwin Smith Papyrus.
This type of glial cell stretches between neurons and blood vessels and forms the blood-brain barrier.
What are Astrocytes
A ___ is an increase in membrane potential, while a ___ is a decrease in membrane potential.
What is a Hyperpolarization and Depolarization
This is the main excitatory NT
What is Glutamate (GLU)
After the AP generated by touch enters the dorsal cord and ascends to the dorsal column, what happens next?
In the medulla, information passes on to a second neuron, which crosses the midline and is sent to the thalamus.
This refers to the pattern of growth/development of the nervous system over time.
What is Ontogeny
This brain region is responsible for touch and body sensation and spatial recognition. If damage occurs in this area, what can happen as a result?
This is the stimulus intensity needed to trigger an AP.
What is Threshold -40 mV
These opioid peptides are a product of the pituitary.
What are Vasopressin and Oxytocin
___ detects painful heat at lower temperatures (ex touching a hot coffee mug), responds to capsaicin and travels along C-fibers, while ___ detects high temperatures (heat that can scald/burn), do not respond to capsaicin, and travel along A-Delta fibers.
What are TRPV1 and TRMP3
Night vision among cats, dogs, rodents, etc.
Neurons across all species.
These are things that are similar across many types of animals due to evolution.
A bundle of axons that connects the two brain hemispheres.
What is the Corpus Callosum
Once the membrane potential reaches the Na+ equilibrium potential of +40 mV, what happens?
As the inside of the cell becomes more positive, voltage-gated K+ channels open.
If a ligand reduces the effectiveness of a NT, thus decreasing the likelyhood a message will be sent across the synapse, it is a ___.
What is an Antagonist
Pain info travels to the thalamus, and then to the cingulate cortex (pain perception) AND the S1, at the same time.
This refers to changing a behavior and looking at changes in body structure and/or function.
What is Behavioral Intervention
Damage to this brain region can result in Parkinson's Disease.
What is the Substantia Nigra
Describe the two refractory periods.
Absolute Refractory: no APs can be produced.
Relative Refractory: only strong stimulation can produce an AP.
This graphs the relationship between drug dose and the effect.
What is the Dose-Response Curve (DRC)
Information about body movements and position.
What is Proprioception
Provide an example of a positive correlation.
Ex: The more one studies the higher grade they will receive.
Higher temperatures during summer increases ice cream sales.
This connects the brain to the spinal cord and is responsible for essential tasks such as breathing and blinking.
What is the Medulla.
A ___ produces a small depolarization, making the cell LESS negative, while a ___ produces a small hyperpolarization, making the cell MORE negative.
What is an EPSP and IPSP
___ is the degree of attraction between ligand and receptor, while ___ is the ability of a BOUND ligand to ACTIVATE the receptor.
What is Binding Affinity and Efficacy.
Name the two proprioceptors and what their function is.
What are Intrafusal fibers (small fibers within a muscle spindle - responds to stretch) and Golgi Tendon Organs (receptors within tendons - responds to muscle tension)