What are the three major branches of geography?
Physical geography: deals with natural features of the planet ( mountains, coasts, fauna) and the elements that act on and affect it, such as climate and currents
Human Geography: study of different people of the world, their communities and cultures, and their relations across space and place
Regional geography: identifying and defining different regions of the world and studying their unique characteristics, such as their human and natural elements
What is the solar system composed of?
Celestial bodies such as the star, planets, and satellites
What do you call the movement of Earth as it turns on its own axis, once every 24 hours?
Rotation
What are geographic coordinates?
It is a network of imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that are drawn on globes or maps.
What is the science of studying and making maps?
Cartography
What are the main tools used for representing and analysing our planet’s geography?
Geographic Information Technologies
What is the galaxy a combination of?
It is a combination of planets, stars, gas clouds and cosmic dust.
What do you call the movement of Earth around the Sun on an elliptical orbit?
Revolution
What divides our planet into two equal halves of hemispheres?
Equator
What is the result of projecting a 3D image into a flat surface?
Projection
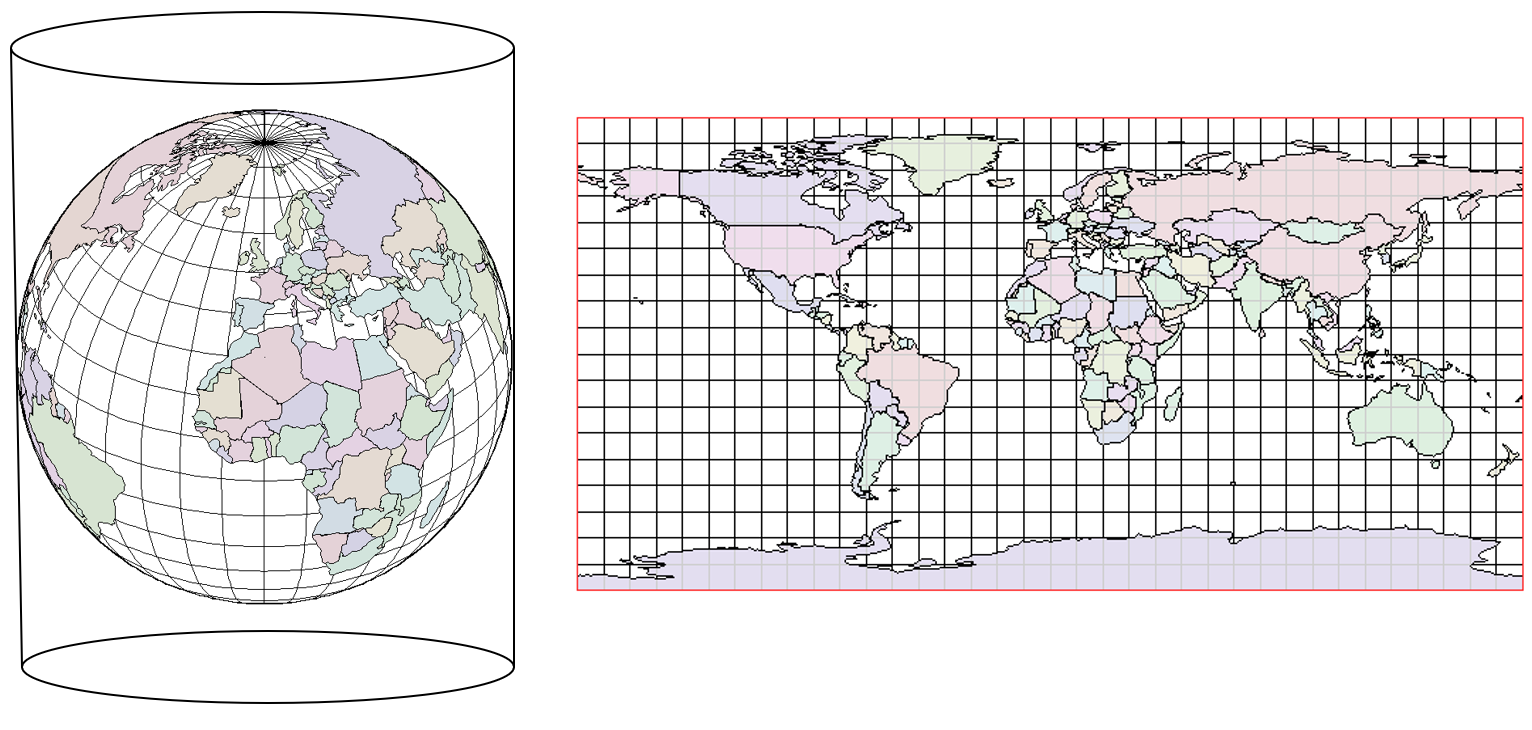
- Cylindrical Projection:
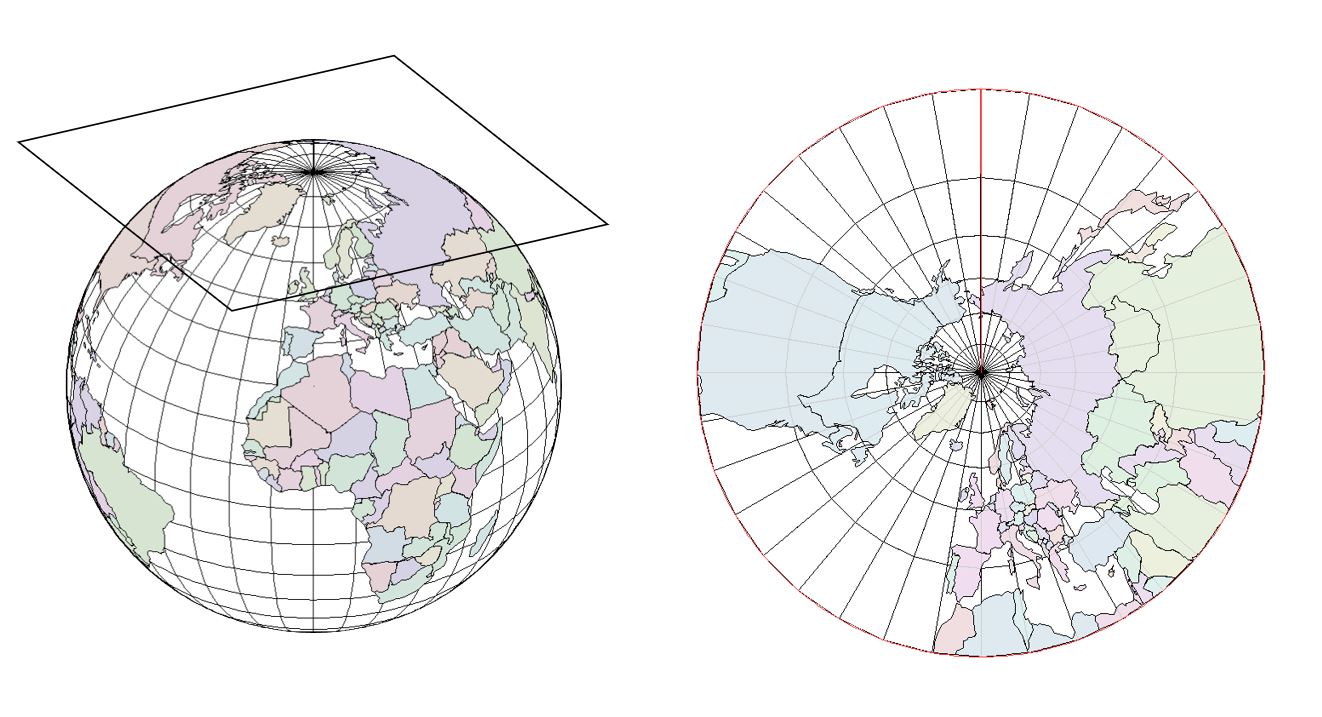
- Conical Projection
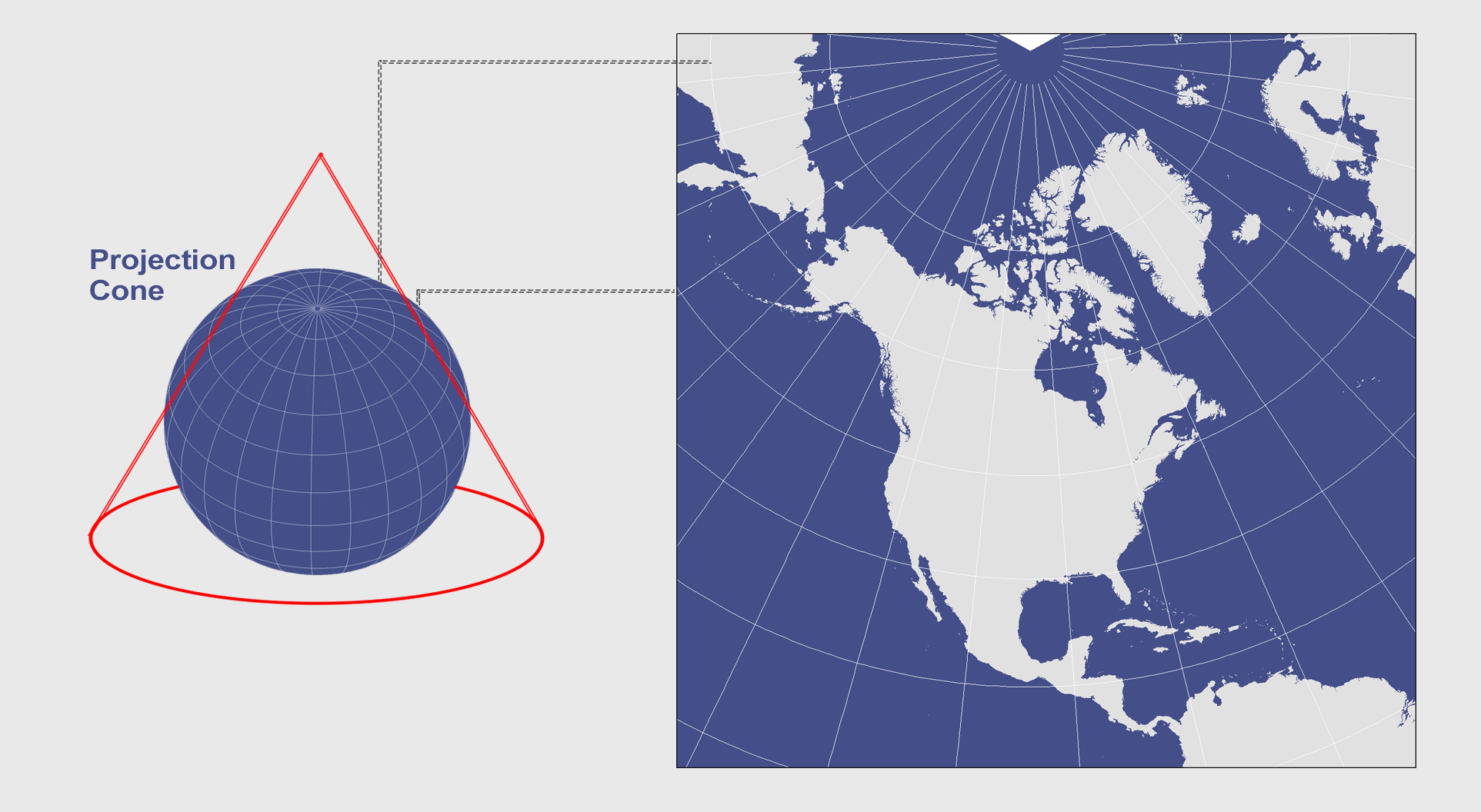
- Planar Projection
What is this digital map or plan that is a scale representation of a particular area showing physical or other features of a country?
Digital Cartography
What is the shape of the Earth?
Almost perfect sphere but is slightly flattened on both North and South poles
What do you call the year with 366 days?
Leap year
What are these imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the Equator?
Parallels
What is the true representation of the whole or part of an area on a flat surface?
Map
Types of Maps:
Topographic Maps
/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)
Thematic Map

What tool is used to obtain geographic information by scanning an area using digital equipment such as satellites and cameras?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
What is a celestial body?
It is a natural object located outside the Earth’s atmosphere
How many days and hours does it take to complete one full revolution?
365 days and 6 hours
What is the angular distance between any point on Earth and the Equator?
Latitude
Note: Angular distance - measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds

What represent smaller areas than other maps, such as cities or towns?
Street Maps
Why is studying Geography important?
Be able to interpret and use maps to navigate and/or recognise key area features
Identify different climatic features and understand climate trends
Understand phenomena such as rain, snow, waves, tides, and earthquakes
Recognise physical characteristics of different regions and economic development in those regios
Understand how regional populations have developed and are distributed
What is the basis of the existence of life on Earth? Give one.
Distance from the sun: creates proper temperature for its inhabitants
Presence of abundant water: Appearances of the first forms of life supporting the essentials for survival
Existence of an atmosphere: protects life from dangerous solar radiation
What are the cardinal points in the context of Geography?
North, South, East, and West
What is the angular distance between any point on the Earth and the prime meridian/Greenwich meridian?
Longitude

What is a Scale?
- It is the ratio between the size of an area represented on the map and the real size of an area
- It can be expressed numerically or geographically