What six elements are most common in the human body?
CHNOPS
(Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur)
Organ system responsible for the transport of oxygen into the bod and carbon dioxide out of the body.
What is the respiratory system?
The study of how muscle contracts is the study of _________.
What is physiology?
Any change to a variable is called the _____.
What is a stimulus?
This directional term describes the position of the muscles relative to the skin.
What is deep?
Identify the four macromolecules that make up cells.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids
The organ system that produces blood cells and stores inorganic salts such as calcium phosphate.
What is the skeletal system?
Arrange the following terms related to negative feedback in order as they operate to maintain homeostasis.
1-control center 2-effector 3-receptor 4-response 5-stimulus
What is 5, 3, 1, 2, 4?
Describe a positive feedback loop and give TWO examples.
A positive feedback loop occurs when the original stimulus is amplified. Examples include:
1.) Labor contractions
2.) Milk production
3.) Blood clotting
The elbow is _________ to the wrist.
What is proximal?
The organ system responsible for the production of vitamin D.
What is the integumentary system?
Survival needs:
Nutrients, Oxygen, Water, Temperature, Atmospheric Pressure
The pathway used when the hypothalamus triggers the blood vessels to constrict to help increase body temperature is the _____.
What is the efferent pathway?
This term describe when someone is lying face down.
What is prone?
List the nine levels of organization from least complex to most complex starting with atom and ending with organism.
Atom --> Molecule --> Macromolecule --> Organelle --> Cell --> Tissue --> Organ --> Organ System --> Organism
The organ system responsible for removing metabolic waste from the blood and helping to maintain the body's water and salt concentration.
What is the urinary system?
The heart is __________ to the lungs.
What is intermediate?
Identify and describe TWO different receptors found in the body that help maintain homeostasis.
Thermoreceptor - detects changes in temperature
Chemoreceptor - detects changes in levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, calcium, etc.
This directional term describes the position of your eyes relative to the upper part of your nose
What is lateral?
Identify the 4 different types of tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscular and Nervous
The slow acting control system that uses chemical messengers to regulate and control body.
What is the endocrine system?
A.) cranial
B. ) abdominopelvic
C.) thoracic
D.) spinal
E.) none of these
Describe the role of the effectors when the blood sugar is high.
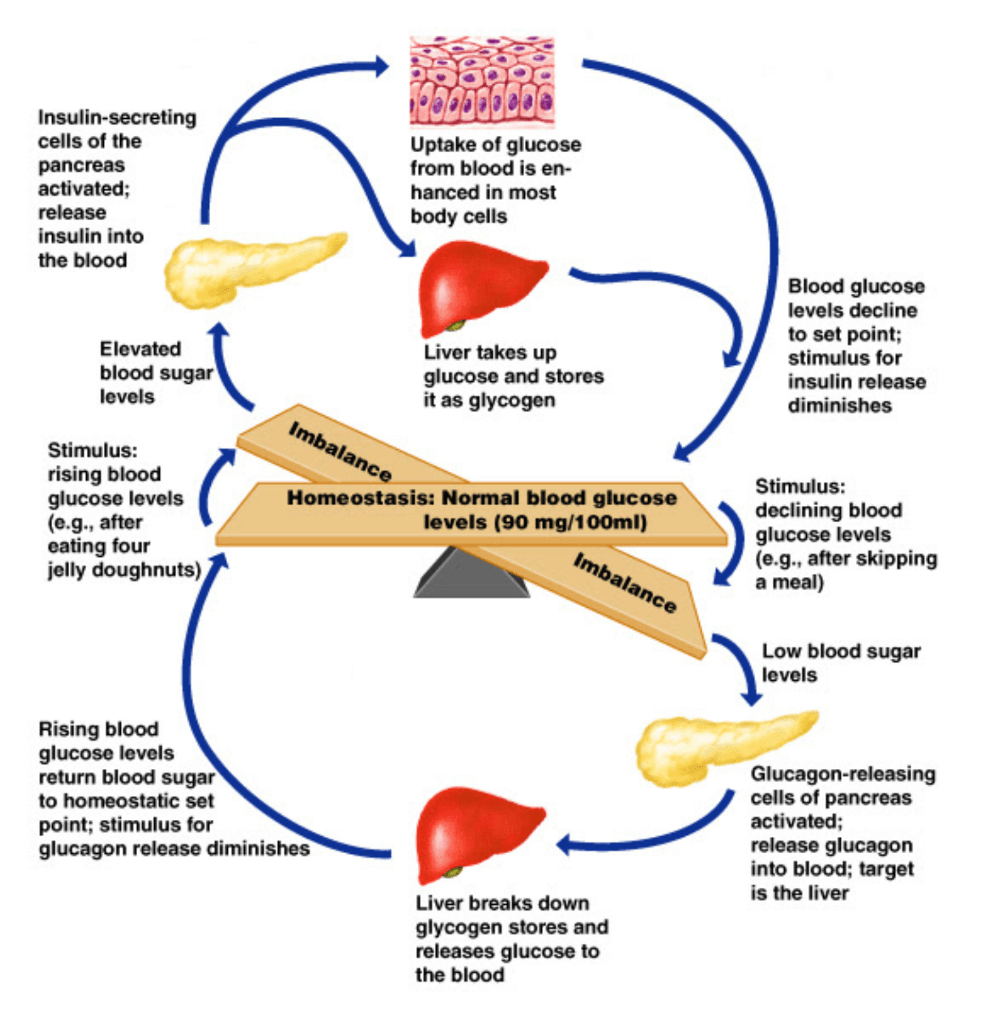
The pancreas releases insulin
Insulin causes body cells to take up glucose
Insulin causes the liver to take up glucose and store the glucose as glycogen.
This directional term describes the position of your belly button relative to your spine.
What is anterior?
Describe the function of each of the four macromolecules.
Carbohydrates - short-term energy
Lipids - long-term energy
Proteins - make up structures and help make reactions happen
Nucleic acids - store the genetic code; help make proteints
The lymphatic system collects fluid from the tissues a returns the fluid to the blood. The lymphatic system also works with the immune system to help fight infection.
List THREE life functions.
Maintain Boundaries, Movement, Responsiveness, Digestion, Metabolism, Excretion, Growth, and Reproduction
Identify the effectors, when the calcium levels are 12 mg/100 mL.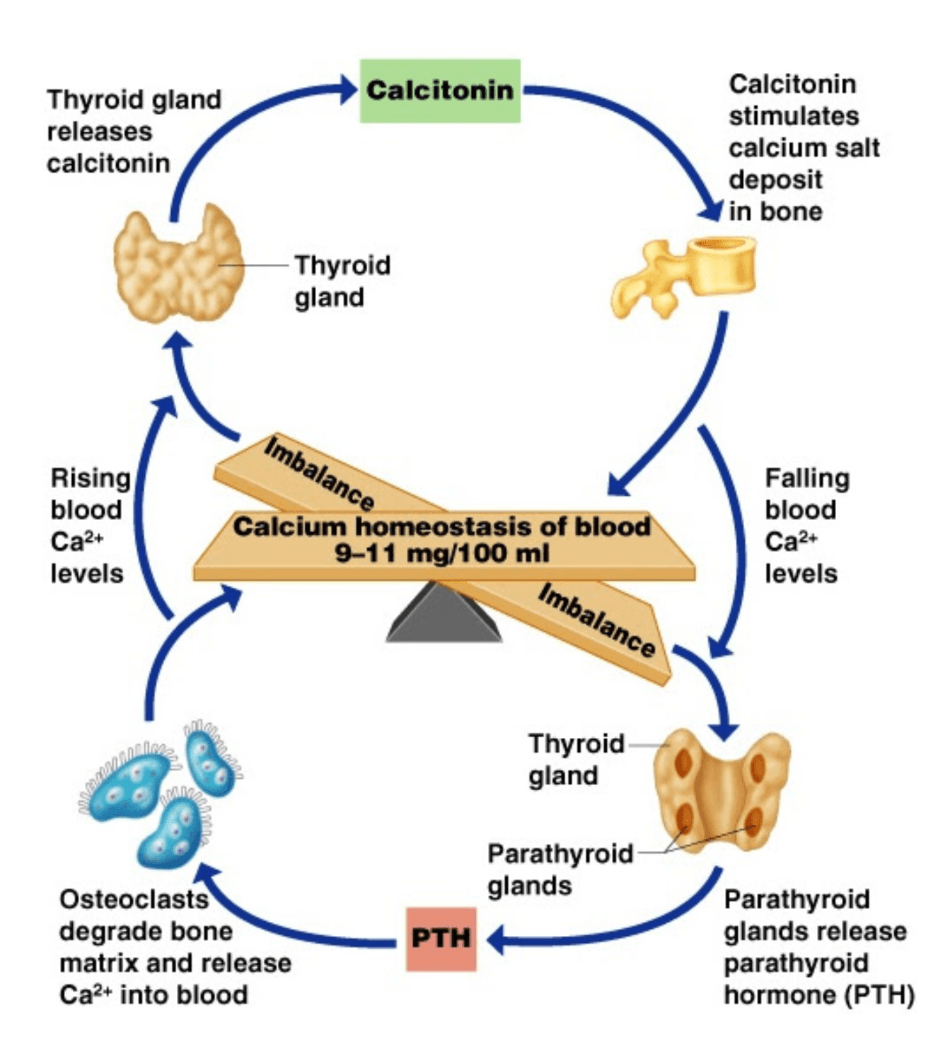
E: Thyroid Gland
R: Releases calcitonin
E: Bone cells
R: Take up calcium
This type of cut divides the body into anterior and posterior portions.
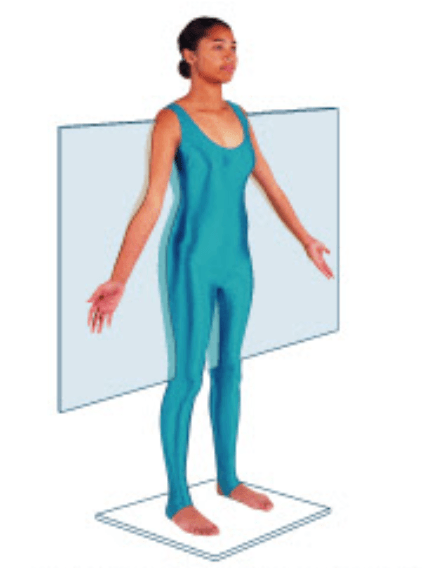
What is a coronal (or frontal) cut?