Which macromolecule is the fastest source of energy for cells?
Carbohydrates
What type of (macro)molecule are enzymes?
Proteins
Which organelle is known as the “powerhouse of the cell”?
Mitochondria
Which type of cell has chloroplasts?
Plant Cell
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells
What are the building blocks (monomers) of proteins?
Amino acids
What is the name of the part of the enzyme where the substrate binds?
Active Site
Which organelle packages and ships proteins?
Golgi apparatus
Name ONE structure found in plant cells but NOT animal cells.
Cell wall, chloroplast, or large central vacuole
Which type of cell is smaller and simpler?
Prokaryotic Cells
Which macromolecule stores long-term energy and provides insulation?
Lipids
What happens to enzyme activity if the temperature gets too high?
2 Part Answer!!!!!
The enzyme denatures and the reaction rate decreases
What is the job of the plasma membrane and what school comparison is made? (Have to get both)
Controls what enters and leaves the cell, Old Man Rob
Why do plant cells need a large central vacuole?
To store water, nutrients, waste, and maintain turgor pressure
What type of DNA do prokaryotic cells have?
Single circular DNA
Name the macromolecule that stores and transmits genetic information AND list its two types.
Nucleic acids — DNA and RNA
Why is an enzyme described as “specific”?
Its shape only allows it to bind to a specific substrate (lock-and-key model)
Which organelles work together to make and transport proteins?
Ribosomes and Rough ER make proteins, Golgi Apparatus ships them where they need to go
Why do animal cells not need chloroplasts?
Animals do not perform photosynthesis; they obtain energy by consuming food
Name TWO structures found in BOTH prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
DNA, ribosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm
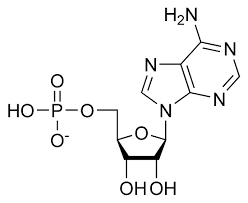
Identify this structure:
Nucleic Acid
Explain how pH and temperature BOTH affect enzyme activity.
Enzymes have both an optimal pH and temperature. When the optimal pH or temp isn't met or is exceeded, the rate of reaction becomes skewed
Muscle cells contain many more mitochondria than skin cells.
What does this tell you about the function of mitochondria and the energy needs of different cells?
Mitochondria produce ATP through cellular respiration, and cells with higher energy demands (like muscle cells) contain more mitochondria to meet those energy needs.
Why can plant cells survive without consuming food, but animal cells cannot?
Plant cells contain chloroplasts that perform photosynthesis to make glucose, while animal cells lack chloroplasts and must obtain energy by consuming food.
Explain why prokaryotic cells are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and are less complex, allowing them to function efficiently at a smaller size.