Bones and joints are associated with this system
Skeletal
This plane divides the body into left and right portions.
sagittal
Define Proximal and Distal
Proximal- Closer to the attachment point or trunk
Distal- Farther from the attachment point or trunk
Which life function does your skin provide?
Maintaining boundaries
Define Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy=the organs and their locations
Physiology=Function
One of the functions of this system is to produce heat
Muscular
Which plane was the following x-ray taken?
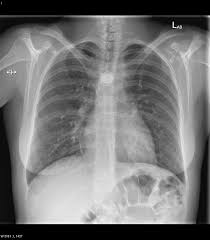
Frontal or coronal
Use the correct anatomical directional term: Your Heart lies _____ to your ribcage?
Posterior or Dorsal or Deep
The process od removing waste from the body
Excretion
The thoracic cavity houses which organs?
lungs, heart
what is the function(s) of the endocrine system?
Secretes chemical messenger, hormones, between body parts, maintain proper growth, reproduction, and metabolism
This plane divides the body into superior and inferior portions
Transverse
Use the correct anatomical directional term: Your neck is _____ to your chest
Superior
Which survival need is required for cellular respiration?
Oxygen
Reproduction can occur at two organizational levels
cell and organism
Define Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain a steady internal environment.
The following x-ray was taken along which plane?

Sagittal
Your ears are ____ to your nose.
Lateral
This survival need accounts for 60-80% of our body weight
Water
Which organ system is responsible for fast reactions like reflexes?
Nervous
Give an example of one type of homeostasis in the human body
body temp
insulin
Compare and contrast: Parasagittal and Midsagittal
Midsagittal divdes the body into equal left and right halves (through the midline)
Parasagittal does not pass through the midline
Your ankle is ________to your knee
Distal or inferior
Which survival need would be affected by traveling to higher elevations?
Atmospheric pressure
Put the following terms in order from smallest to largest.
Lung, carbohydrate, oxygen, nervous system, blood
oxygen, carbohydrate, blood, lung, nervous system