This type of map emphasizes spatial phenomena by showing areas shaded or patterned in proportion to a statistical variable.

Choropleth Map
The unique combination of physical and human features that give a location its identity.
Place
The physical gap or distance between two objects.
Space
The system that determines absolute location using satellites.
GPS (Global Positioning System)
The way humans use the natural environment to meet their needs, such as farming near rivers. There are 5 categories.
Land use
This projection distorts size but preserves shape, often making Greenland look larger than Africa.
Mercator Map
A region defined by one or more common characteristics, such as language or climate.
Formal Region
The frequency with which something occurs in a given space.
Density
The system that stores, analyzes, and displays geographic data in layers.
GIS (Geographic Information System)
The belief that physical environment causes or strongly shapes human social development.
Environmental Determinism
A map that represents phenomena with symbols sized according to value.
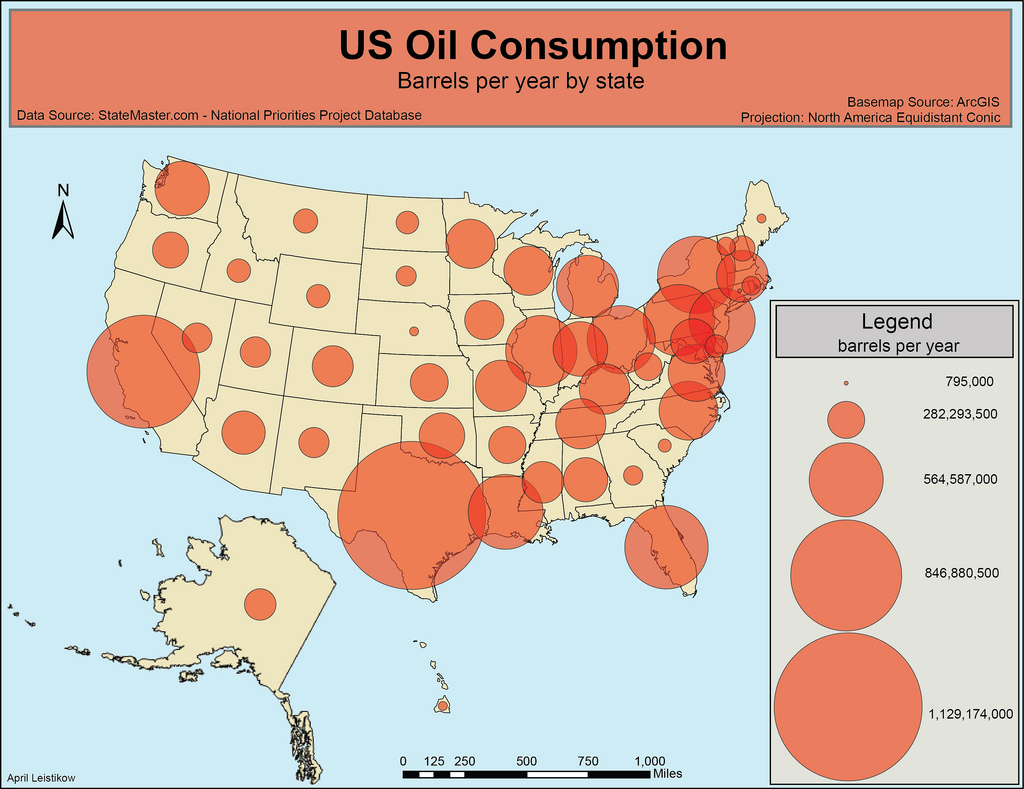
Proportional Symbol Map
A region organized around a central node, like a metropolitan area.
Functional Region
Describe the spatial pattern of hispanic people in the US.
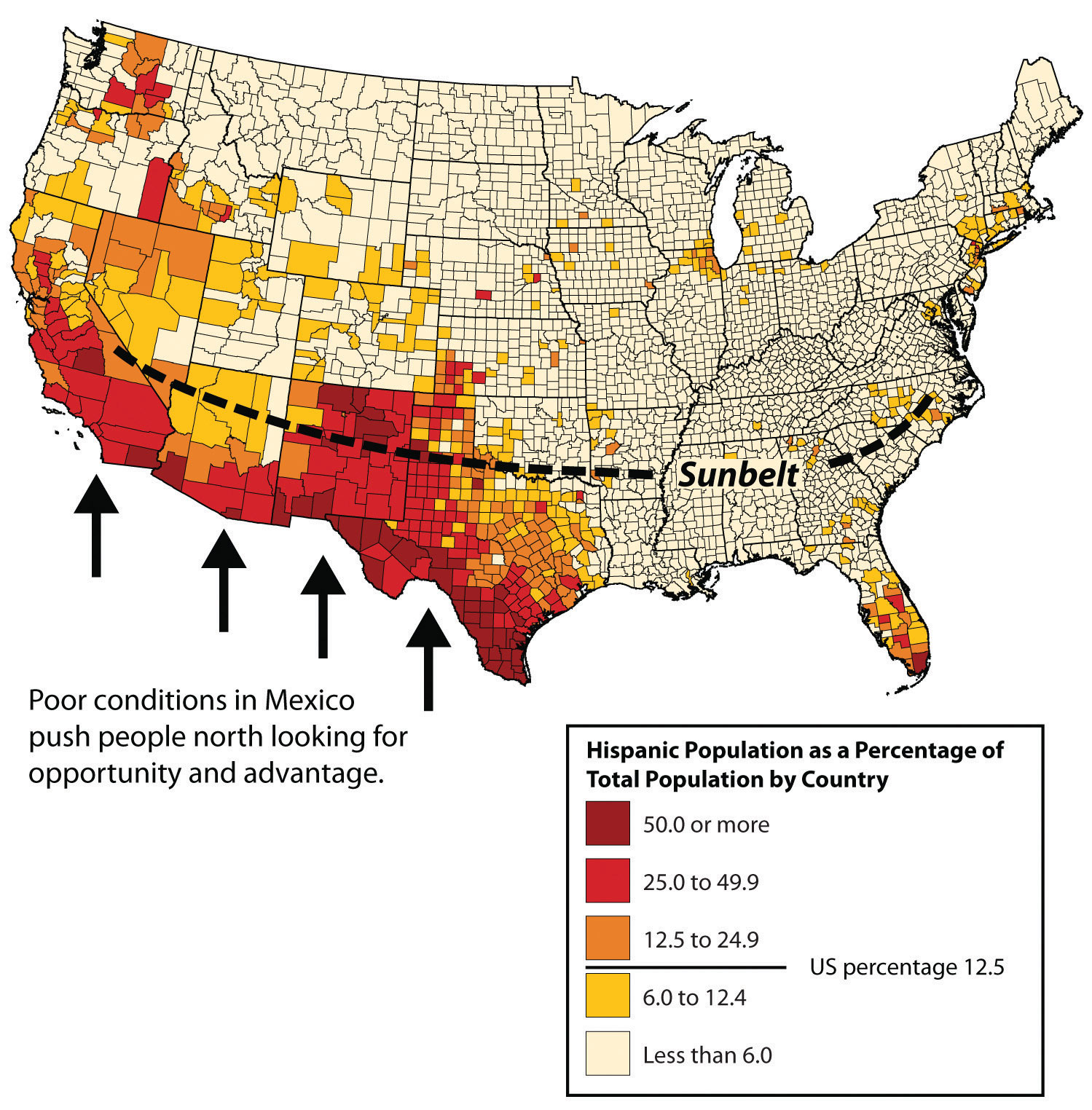
Dispersed though most of the midwest, southeast, and northeast.
Clustered around the Southeast of the US
The science of mapmaking.
Cartography
The relationship between the portion of Earth studied and Earth as a whole.
Scale
This projection balances distortion by creating equal-area divisions, often used in classrooms today.
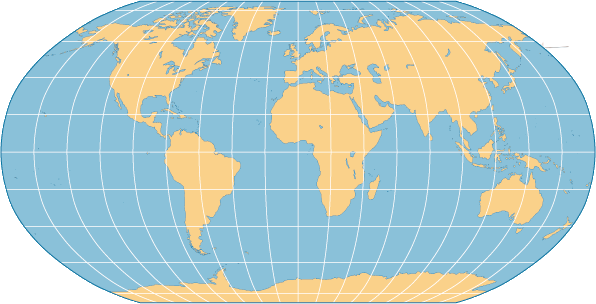
Robinson Projection
A region defined by people’s subjective views, like “the South” or “the Middle East.”
Perceptual / Vernacular Region
Describe the spatial pattern of settlements in the image.
Linear pattern
The imaginary lines used to measure distance north or south of the equator.
Latitude
The way in which we analyze data and understand patterns depending on how much of the Earth we are analyzing.
Scale of Analysis
A map that connects places of equal value, like elevation or temperature.

Isoline Map
The given name for a place.
Toponym
The geometric arrangement of objects in space, such as linear, centralized, or random.
Pattern
The statement that “all maps lie flat and all maps lie” refers to this unavoidable mapmaking problem.
Distortion
The idea that humans can adapt and modify the environment around them to suit our needs.
Possibilism