List the three subatomic particles in an atom, their location, their charges
Proton / In the nucleus / +
Neutron / In the nucleus / 0
Electron / Outside the nucleus / -
Why is water polar?
Oxygen is slightly negative (due to a high electronegativity level) and water is slightly positive (due to a low electronegativity level)
Define
-Solvent
-Solute
-Solution
-Solvent: The dissolver
-Solute: The dissolved
-Solution: The mixture
What section of the ocean has the highest concentration of gas?
The top layer (~200 m)
-Due to turbulence, wave movement, and photosynthesis
What is the equation for density?
density = mass / volume
What is covalent vs ionic bond?
Covalent: shares electrons / nonmetal + nonmetal
Ionic: transfer electrons / metal + nonmetal
As water freezes to ice, what happens to its density and why?
Density goes down due to water molecules forming a crystalized structure containing air pockets between
What are the three methods for measuring pH?
Litmus, universal, probe
How does pressure affect solubility and why?
↑Pressure = ↑Solubility
Why: The higher the pressure = the more the particles are pushed together = the easier it is to break apart the gas
What is the abrupt change in salinity called?
AND
What is the abrupt change in temperature called?
Halocline
Thermocline
How does the speed and composition of particles change as a substance changes from a solid, to a liquid, to a gas
Liquid- Particles are able to move against each other and move faster
Gas- Particles are far away from each other and move faster
Why can water break down covalent AND ions?
Covalent because water is a covalent bond
Ions because it has a slight charge
How does each factor affect the salinity of water?
-Evaporation
-Precipitation
-Runoff
Evaporation: Raises salinity due to fresh water leaving and salt particles staying
Precipitation and runoff: Lowers salinity due to fresh water being added
How does salinity affect solubility and why?
↑Salinity = ↓Solubility
Why: The saltier the water = the more particles = the salt blocks water from bonding with gas
List at least two factors that can cause the temperature and salinity gradients to be mixed in the ocean.
Strong winds, waves, upwellings, currents
What are the five covalent bonds we talked about in class?
**Extra points if you get all the chemical formulas for them**
Water (H2O)
Oxygen (O2)
Glucose (C6H12O6)
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Explain how water dissolves sodium chloride
The partial positive hydrogen surrounds the negative chloride
The partial negative oxygen surrounds the positive sodium
How and why does salinity affect the freezing point of water?
Higher salinity causes water to freeze at a colder temperature due to salt particles blocking hydrogen bonds from occurring
How does temperature affect solubility and why?
↑Temperature = ↓Solubility
Why: The warmer the temperature = the faster the particles = the harder it is for the water molecule to "grab" the gas
How does each factor affect the density of water?
-Temperature
-Pressure
-Salinity
↑Temperature = ↓Density
↑Pressure = ↑Density
↑Salinity= ↑Density
What are the three ionic bonds we talked about in class?
**Extra points if you get all the chemical formulas for them**
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4)
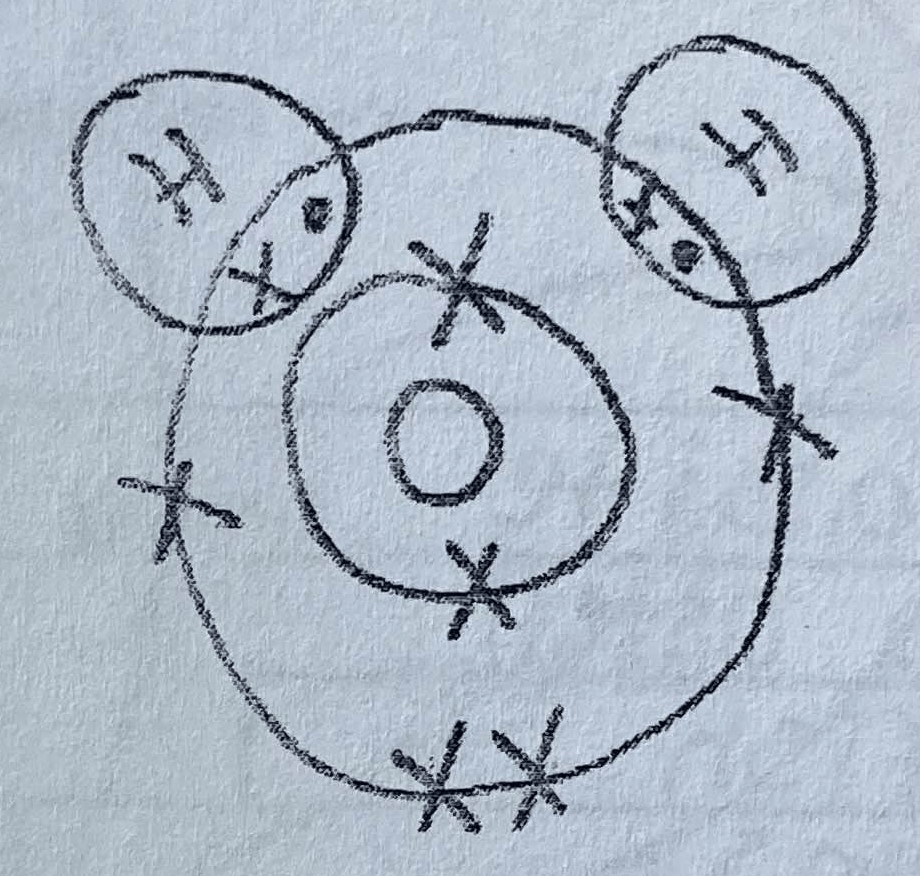
Draw a water molecule showing the sharing of electrons
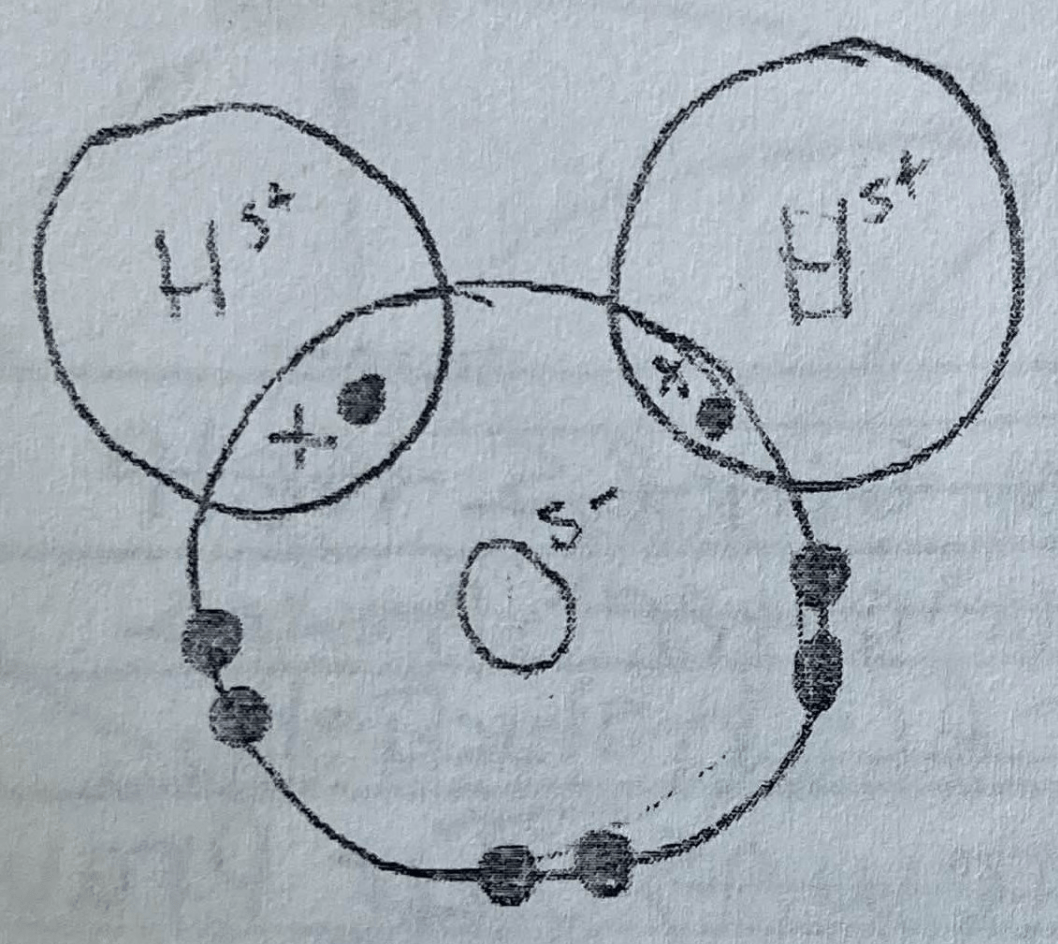
How does ocean acidification effect organisms that live in the ocean?
Causes organisms with shells / skeletons to not form correctly or dissolve easier
How does the concentration of oxygen change as you go from the surface to the deep ocean?
Highest at the surface (turbulence, wave movement, photosynthesis), decreases until you hit the oxygen minimum zone (no photosynthesis but respiration still occurring), increases slightly as you go deeper due to pressure
In a salinity gradient, where is the saltiest water and where is the freshest water located?
What is the one exception to this gradient rule?
Fresh on top (surface)
Salty on bottom (seabed)
One exception - tropical oceans due to high evaporation rates