The site of protein synthesis
What is the ribosome?
A biological catalyst
What is an enzyme?
The center of an atom
What is the nucleus?
1. The type of bonding where electrons are transferred from...
2. The type of bonding where electrons are shared between...
1. What is ionic bonding?
2. What is covalent bonding?
NOT A QUESTION
Name two energy stores.
kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, thermal (or internal), magnetic, electrostatic, and nuclear
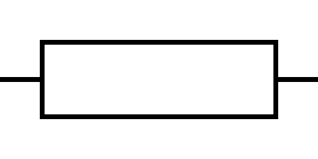
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor?
NOT A QUESTION
Name the 4 types of pathogen
Bacteria, virus, fungi, protist.
mass/volume= ?
density
The movement of water from dilute to concentrated solution.
What is osmosis?
Protease
Lipase
Amylase
Which enzyme breaks down protein, lipids, starch?
An atom with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is an isotope?
NOT A QUESTION?
Why do Ionic substances have a high boiling and melting point?
Many strong electrostatic forces of attraction which require lots of energy to overcome.
The energy required to heat 1kg of a substance by 1 degree celsius.
What is specific heat capacity?
Is the same in all parts of a series circuit but is shared between the branches of a parallel circuit.
How does current behave in series and parallel?
Not being able to catch a disease once you have had it before.
What does it mean to be immune?
A helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons)
What is an Alpha particle?
This type of cell contains a nucleus, mitochondria etc
What is a eukaryote/eukaryotic cell?
It has to pump blood around the entire body, not just to the lungs and back.
Why is the left side of the heart bigger/stronger?
Reactivity increases as you go down because ...
(bonus points for explanation)
What is the reactivity in group 1 (or 2)?
NOT A QUESTION
Name two covalent structures
Small molecule, giant covalent.
Watts, Joules, Kilograms
What are the units for power, energy and mass?
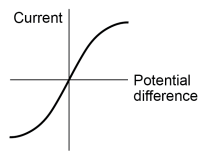
Draw the I/V graph for a filament lamp.
A dead/weakened version of a pathogen.
What is a vaccine?
Can be stopped by a thin sheet of aluminium.
What can stop beta radiation?
NOT A QUESTION
What are the stage of the cell cycle?
Growth, mitosis, cytokinesis (will accept decriptions)
NOT A QUESTION
How are malignant and benign tumours different?
Malignant- can form secondary tumours, made of cancerous cells
Benign - can not form secondary tumours, not made of cancerous cells
Solid spheres, plum pudding, nuclear, planetary
What are the models of the atom?
(bonus points if you can describe two)
Is harder than a pure metal because it has different sized atoms that distort the layers so they cannot slide over one another.
Why are alloys hard?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one store to another.
What is the law of conservation of energy?
Brown wire, blue wire, green and yellow wire.
What colour is the live, neutral, Earth wire? (right order needed)
NOT A QUESTION
What are the steps of drug testing
Cells and tissues, animals, healthy people, patients.
NOT A QUESTION
How is irradiation different to contamination?
Irradiation is the exposure of an object to radiation, while contamination is the presence of radioactive material on or within an object
NOT A QUESTION
How are the lungs and intestines adapted for diffusion? (at least two)
Thin walls, large surface area, rich blood supply
1. The movement of water through the xylem
2. The movement of sugars through the pholoem
1. What is transpiration?
2. What is translocation?
He left gaps for undiscovered elements and put all similar elements in the same group.
What did Mendeleev do in his periodic table?
Diamond has 4 bonds per carbon but graphite only has 3, leaving one electron per carbon delocalised so it can...
Why can graphite conduct electricity but diamond can't?
NOT A QUESTION
Why can no energy transfer be 100% efficient?
Some energy always dissipated to the surroundings (usually as thermal energy.)
NOT A QUESTION
What is the purpose of s step up transformer?
Increase potential difference, this reduces resistance so less energy is lost as heat when carried through cables.
NOT A QUESTION
How does a vaccine work?
Dead/weakened injected
WBC make antibodies
memory cells
antibodies made quicker on re-infection.