The oral cavity is indicated by this letter.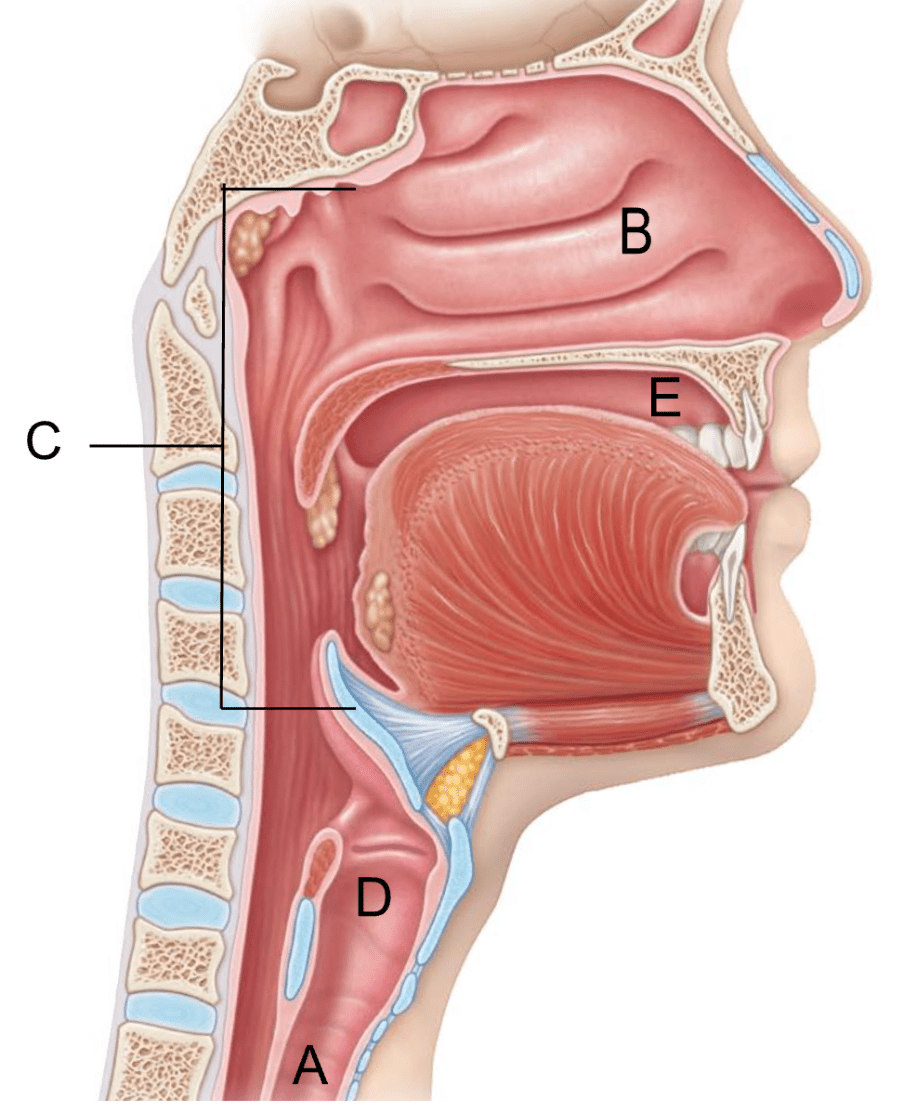
E
Hyperventilation can lead to all of the following except:
A) faster than normal heart beat
B) pain or tightness in the chest
C) dizziness
D) fainting
E) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood
E) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood
Protects the superior opening of the larynx during swallowing
Epiglottis
Rigid airway reinforced with C-rings of hyaline cartilage
Trachea
The pharynx is indicated by this letter. 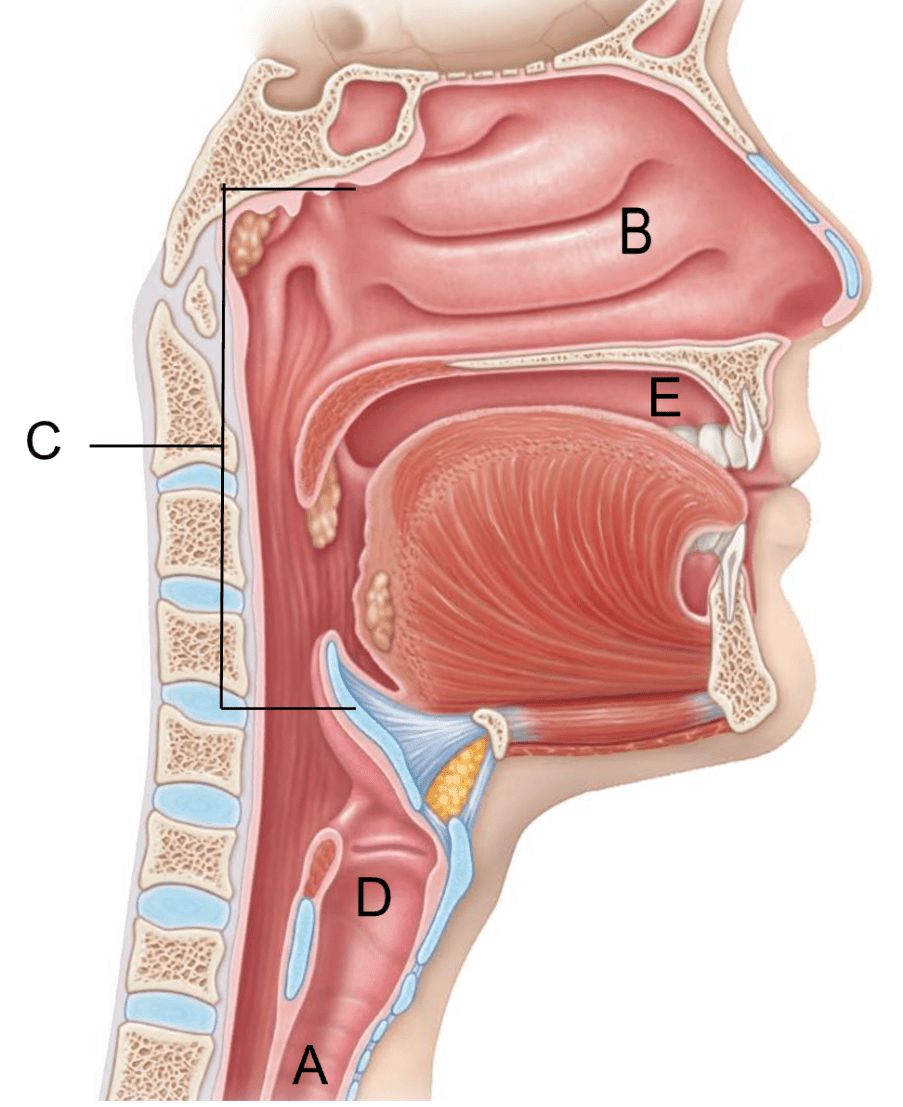
C
The respiratory rate in adults is ____________.
12-18 respirations per minute
Which tonsil is located in the oropharynx at the end of the soft palate:
Palatine Tonsils
The type of tissue lining the alveoli is _____ epithelium.
Simple Squamous
The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by there two structures
Both the hard and soft palate
When oxygen enters the respiratory system, the next structure to which it travels immediately upon leaving the trachea is _________.
Main (primary) left and right bronchus
The portion of the pharynx continuous with the mouth is termed the _________.
Oropharynx
Define the role of respiratory surfactant:
Respiratory surfactant is a complex mixture of lipids and proteins that lines the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs) and reduces surface tension, preventing them from collapsing and making breathing easier
Air from the nasal cavity enters the superior portion of the pharynx called the _______________.
Nasopharynx
The gas exchange that occurs between blood and tissue cells in the capillaries is called _________.
Internal respiration
Most of the respiratory passage surface is lined with _____.
A) pseudostratified epithelium
B) simple columnar cells
C) stratified squamous cells
D) simple squamous epithelium
A) pseudostratified epithelium
How many alveoli are there in an average adult lung?
300,000,000
The respiratory conducting passageways perform all of the following functions EXCEPT:
A) allow air to reach the lungs
B) purify air
C) humidify air
D) exchange gasses
E) warm incoming air
D) exchange gasses
Air moving in AND out of the lungs is called:
A) internal respiration
B) inspiration
C) pulmonary ventilation
D) expiration
E) external respiration
C) pulmonary ventilation
When you inhale, air flows through respiratory structures in which sequence?
A) alveolus - bronchiole - bronchus - trachea - larynx - pharynx - nasal cavity
B) nasal cavity - pharynx - larynx - trachea - bronchus - bronchiole - alveolus
C) nasal cavity - alveolus - bronchiole - bronchus - trachea - larynx - pharynx
D) bronchus - trachea - larynx - pharynx - nasal cavity - alveolus - bronchiole
B) nasal cavity - pharynx - larynx - trachea - bronchus - bronchiole - alveolus
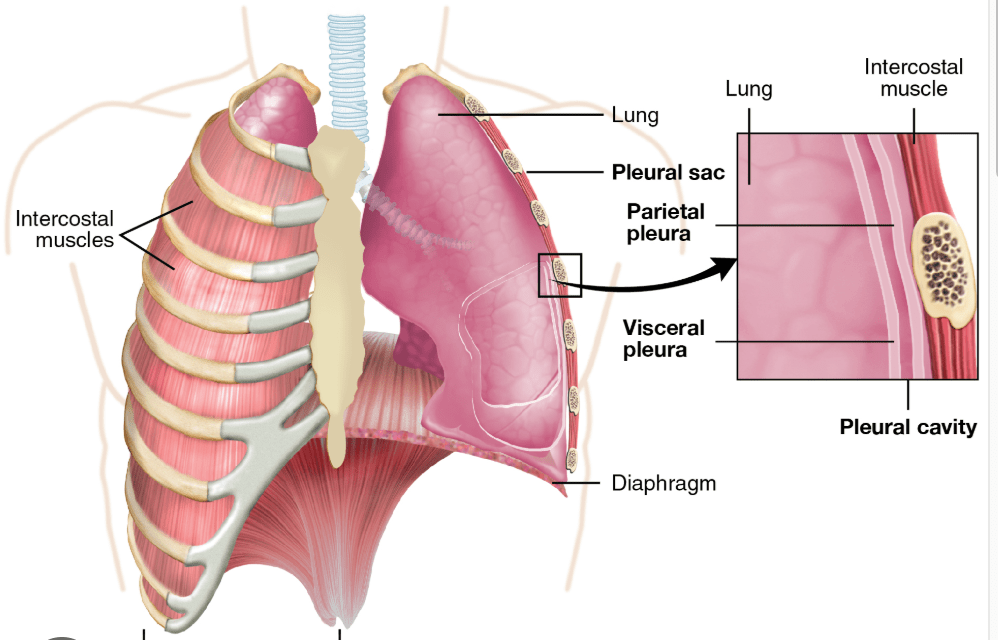
The pleural cavity is the space between the lung's visceral pleural and _____.
Parietal Pleural