Which structure, carpel or stamen, represents the female reproductive part, and which represents the male reproductive part of a flower?
Male: Stamen (Filament & Anther)
Female: Carpel (Stigma, style, ovary)
Define Megasporangia and Microsporangia.
Megasporangia are structures that produce megaspores (female spores, leading to female gametophytes), while microsporangia produce microspores (male spores, leading to male gametophytes).
Define an apical meristem and axillary bud.
Apical meristem and an axillary bud is their location and function: the apical meristem is at the tip of a shoot or root, driving primary growth, while axillary buds are located in the leaf axils and can form lateral branches or flowers.
True or false: Secondary growth only occurs in woody plants.
True: Secondary growth creates the parts of a plant we typically refer to as "wood".
Name a form of asexual reproduction.
Budding
Fragmentation
Spores/seeds
What is the purpose of an ovule in an Angiosperm?
It is the organ within the plant that produces and houses egg cells. After fertilization, the ovule becomes the fruit, seed, or seeds of the plant.
What are the two types of cones that Gymnosperms carry?
Male cones, which produce pollen, and female cones, which house ovules and develop into seeds.
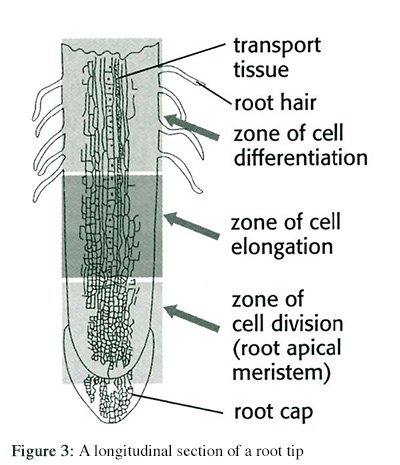
What is the significance root hairs in plants?
They are finger-like extensions, that form near the root tip. They dramatically increase the surface area of roots, enabling more efficient absorption of water and nutrients from the soil.
What are names of the two lateral meristems?
Cork cambium: produces the periderm (bark)
Vascular cambium: produces new vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) that contribute to the plant's thickness.
What is the difference between the vascular tissue xylem and phloem.
Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots upward, while phloem transports sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
What type of relationship do flowering plants and their pollinators have?
Mutualistic relationship, where plants benefit from pollen transfer for reproduction, and pollinators benefit by obtaining food (nectar and pollen).
Why are Gymnosperms referred to as "naked seeds"?
Seeds that are not enclosed within a protective covering (like a fruit) and are exposed, a characteristic of gymnosperms (like conifers) in contrast to angiosperms (flowering plants) where seeds are enclosed in fruits.
What layers make up the dermal tissue system in non-woody plants?
Consists of the epidermis with a waxy coating called the cuticle that prevents water loss from the epidermis.
True or False: All plants have lateral meristems, but only some plants have lateral meristems creating secondary growth.
True: While all plants have the potential for lateral meristems, not all plants utilize them to produce secondary growth.
What are the 3 types of plant cells.
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
What is the difference between a Eudicot and a Monocot Angiosperm?
Monocots have one cotyledon (mono = one; cotyledon = seed leaf), while eudicots have two
(eu = true; di = two; cotyledon = seed leaf).
Can you explain the significance of pollen and seeds in the reproductive cycle of gymnosperms.
Pollen, carrying the male gametes, is crucial for fertilization, while seeds, containing the developing embryo, are the key to dispersal and the next generation's survival.
Where are these zones located on a plant: Zone of elongation, Zone of differentiation, Zone of cell division.
True or false: Plants that do preform secondary growth do it simultaneously with primary growth.
True: 1 & 2 growth occur simultaneously just in different regions of the plant.
Name a evolutionary advantage seeds have over spores.
- Seeds can remain dormant for days to years until conditions are favorable for germination
- They have a supply of stored food
- They may be transported long distances by wind or animals
Explain the significance of double fertilization in angiosperms.
It ensures both the formation of the embryo (a diploid zygote) and the endosperm (a triploid tissue that nourishes the developing embryo), leading to successful seed development and plant survival.
Name the 4 phyla of Gymnosperms
Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, Ginkgophyta, and Gnetophyta
The 3 primary meristems Protoderm, Ground meristem, and procambium. Give rise to what type of tissue.
Protoderm --> dermal tissue, Ground meristem
--> ground tissue, and procambium --> vascular tissue.
In woody plants the tissue periderm (bark) replaces what layer that was created during primary growth?
Periderm (secondary tissue derived from the cork cambium) replaces the epidermis.
Explain the concept of Alternation of Generations
Life cycle characteristic of plants, where organisms alternate between a multicellular, haploid (n) gametophyte stage and a multicellular, diploid (2n) sporophyte stage.