Angiosperms are vascular plants with seeds. What are their other 2 defining characteristics?
Flowers & Fruit
What are the areas where leaves attach to the stem?
Nodes
What type of Branching allows the stem to grow from its terminal bud to lengthen the stem?
Monopodial
What are petals?
Modified Leaves
Which seed is monocot and which seed is dicots in the image below?

Bean: dicot
Cereal gran: monocot
What are the flowers of an angiosperm?
The reproductive structures
What are the two types of branching angiosperms can have?
Dichotomous & Axillary (lateral)
Do angiosperms have to be either sympodial or monopodial?
No, they can be both
What do sepals do for a flower?
Protects & supports the flower
Which stem is monocot and which stem is dicot in the image below?
2nd: dicot
Does and annual or perennial grow for many years and often flowers annually?
Perennial
What type of branching is shown in the picture below?
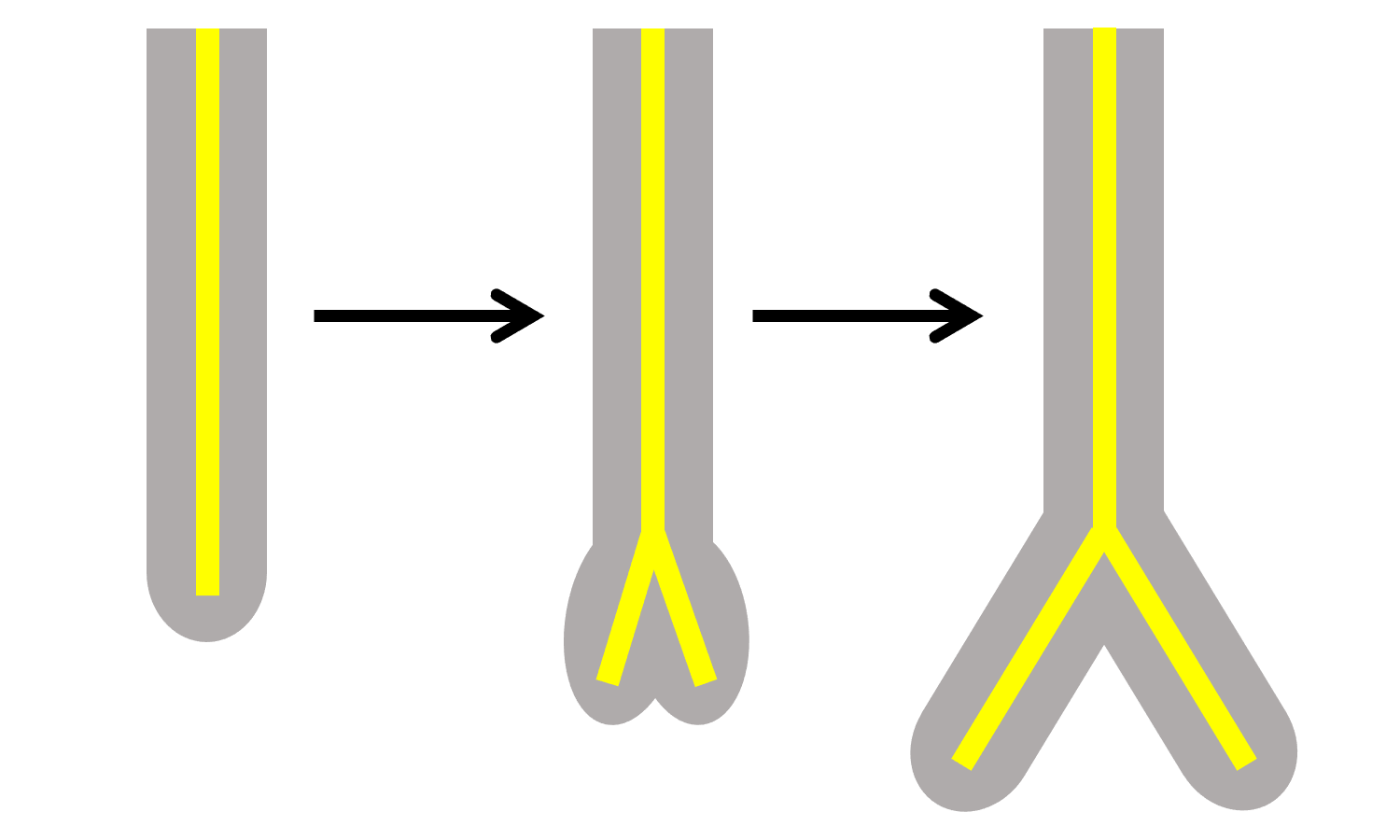
Dichotomous
What are the 3 basic parts of a leaf?
Blade, Petiole, & Stipule
Once a flower is pollinated and the ovules are fertilized, what does the ovule grow into?
Fruit
Which leaf is a monocot and which is a dicot in the image below?
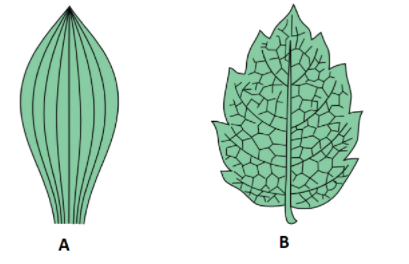
A: monocot
B: dicot
What are the two basic root types of an angiosperm?
Primary & Secondary
What type of branching is shown in the image below?
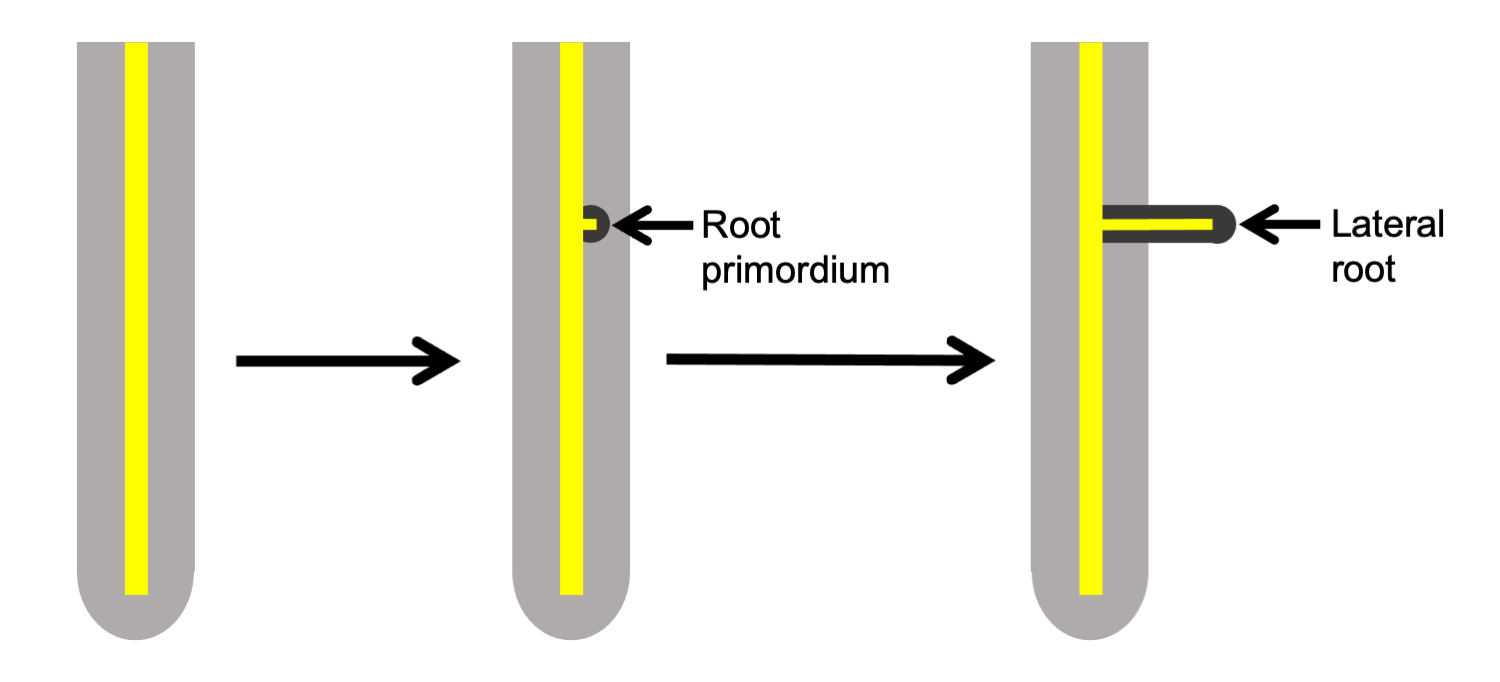
Axillary
What are the four main parts of a flower?
Stamen, Pistil, Petals, & Sepal
What is the male reproductive structure of a flower, and what is it made of?
Stamen: Anthers
Which flower is a monocot and which is a dicot in the image below?
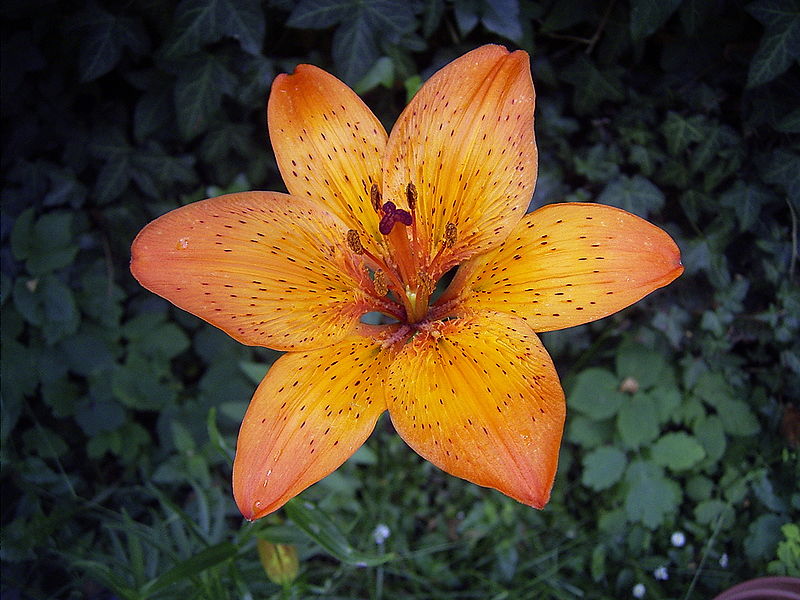
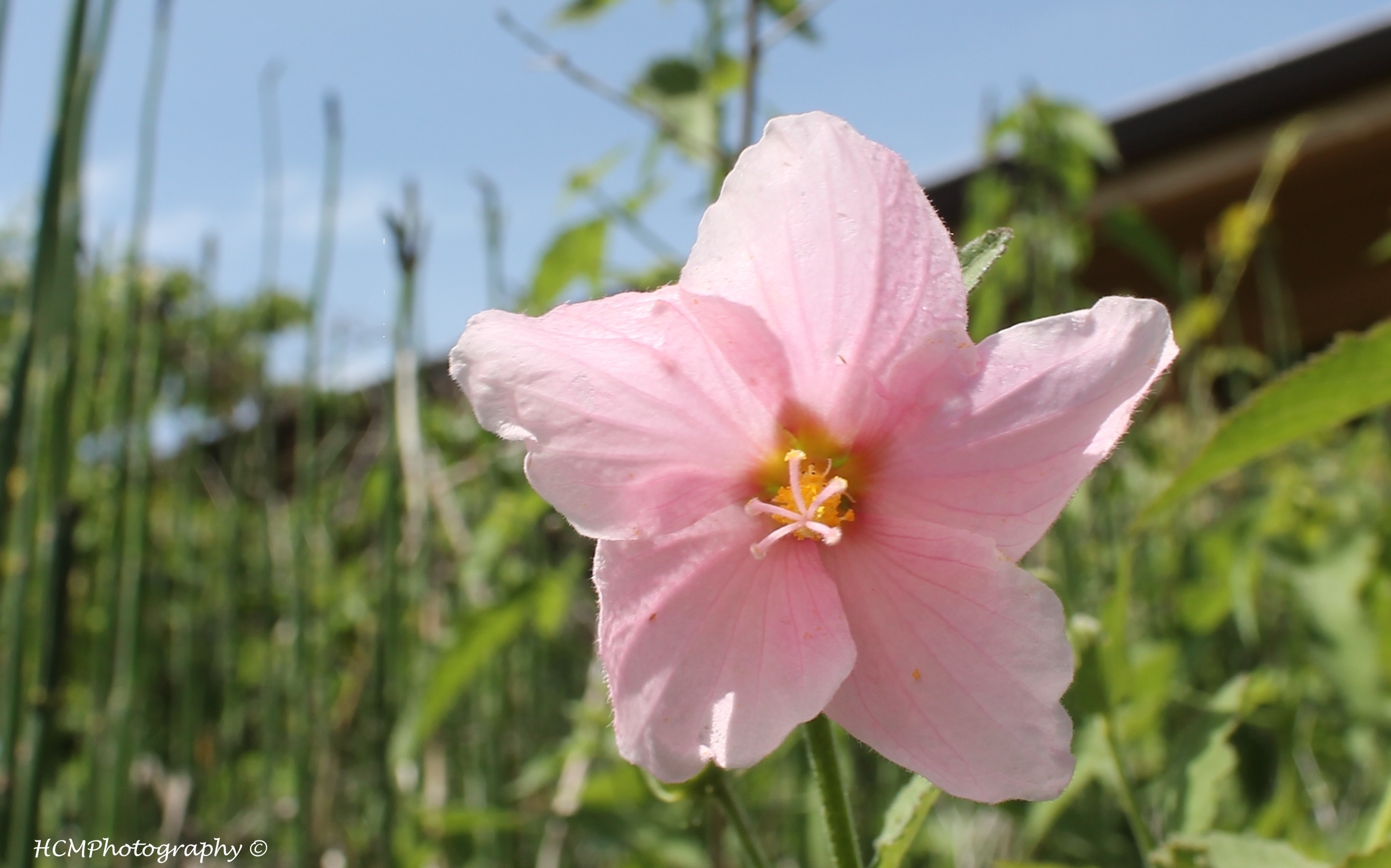


1st: monocot
2nd: dicot
What type of stems can angiosperms have?
Woody or Herbaceous
Is the image below monopodial or sympodial branching?
Sympodial
What is the female reproductive structure of a flower, and what is it made of?
Pistil: Stigma, Style, & Ovary
What is the purpose of the fruit?
Protect & disperse the seeds
Which root type is monocot and which is dicot in the image below?

Taproot: dicot
Fibrous root: monocot
