What is Crude Death Rate?
Number of deaths per 1000 people a year
Explain the DTM.
Explain Relocation diffusion
is the spread of cultural traits through migration.
Ex. Migrants bring their music, food, fashion, religion, and language with them.
Many migrants open restaurants, and their food becomes popular within the native-
born culture.
Examples: Mexican food in the United States, Indian food in Great Britain
What is doubling time?
the amount of time it takes for the population of a region to double.
What is a population pyramid?
It is used to evaluate the make up of a country's population
What is Crude Birth Rate?
Number of Births a year per one thousand people.
Explain the ETM
Explain Thomas Malthus's Theory.
BONUS TRIPLE POINTS IF CORRECT*
The theory states that food production will not be able to keep up with growth in the human population, resulting in disease, famine, war, and calamity.
DTM is characterize by which 3 main factors?
CBR, CDR, NIR/RNI
Which age group is considered independent group (working)
15-64
What is Emigration?
Movement away from a location
1800s
Explain Population Policies.
A population policy is a set of measures taken by a State to modify the way its population is changing
Decline in CDR is usually a result of ....
improvement technology and healthcare
What is the dependency ratio and how do we calculate it?
number of people in a dependent age group ÷number of people in the working-age group, x 100
How is Physiological Density different from Arithmetic Density?
Arithmetic density, also known as real density, is very simply the total number of people divided by the total land area. Physiological density is the number of people per unit area of arable land
Which ETM stage describes the causes of death relating to poor sanitary conditions?
Stage 1
At what TFR (Total Fertility Rate) does a population needs to be to maintain their Stationary Population Level (SPL)
TFR of 2.1
Low growth is characterized by....
High CBR and High CDR leading to low RNI/NIR
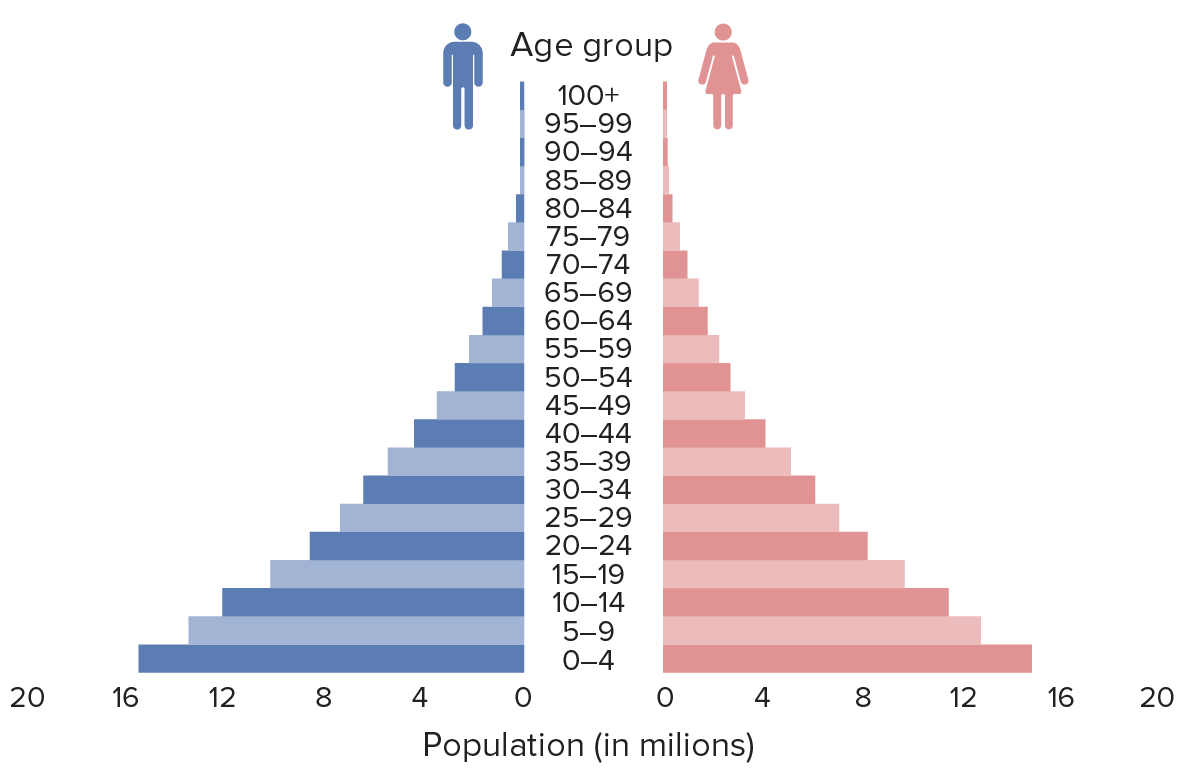
What stage would this be considered? Why?
Stage 1. High CBR and High CDR
What is Antinatalist?
policies are designed to curb population growth by discouraging citizens from having children.
What is the difference between Pandemic and Endemic?
BONUS DOUBLE POINTS IF CORRECT*
A pandemic is a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease over a whole country or the world at a particular time.
An endemic means a disease is spreading in a community at the normal or expected level.
What is Neo-Malthusian?
school of thought claims that Earth’s resources (Not just food) can only support a finite population.
Advocate for programs and policies designed to control population growth, so they would be most likely to support a program that limits family size to two children.
What are some consequences of an aging population?
An increase in global life expectancy, coupled with decreased fertility rates, is the main reason for the aging population in most countries.
Increase life expectancy. Decrease fertility rates.
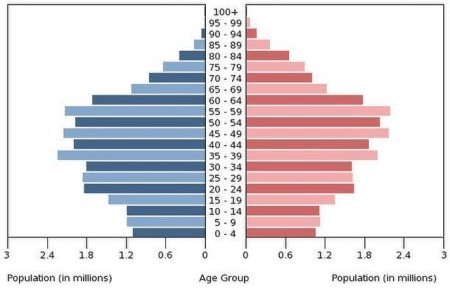
What stage on the DTM would this fall under. Would this population most likely need an anti-natalist or pro-natalist policy?
Stage 5. Pro-Natlist, because the population is declining.
What is Brain Drain?
Loss of trained or educated people to the lure of another country
Which stage in the ETM model is affected by diseases that are related to crowding in cities?
Stage 2
What do critics of the Malthusian Theory believe?
They believe that Thomas Malthus did not account for the improvement in technology which would add to growth of food yield.
What are some population policies?
Antinatalist policies-are designed to curb population growth by discouraging citizens from having children.
Pronatalist policies-encourage births and aim to accelerate population growth.
Examples are welcome
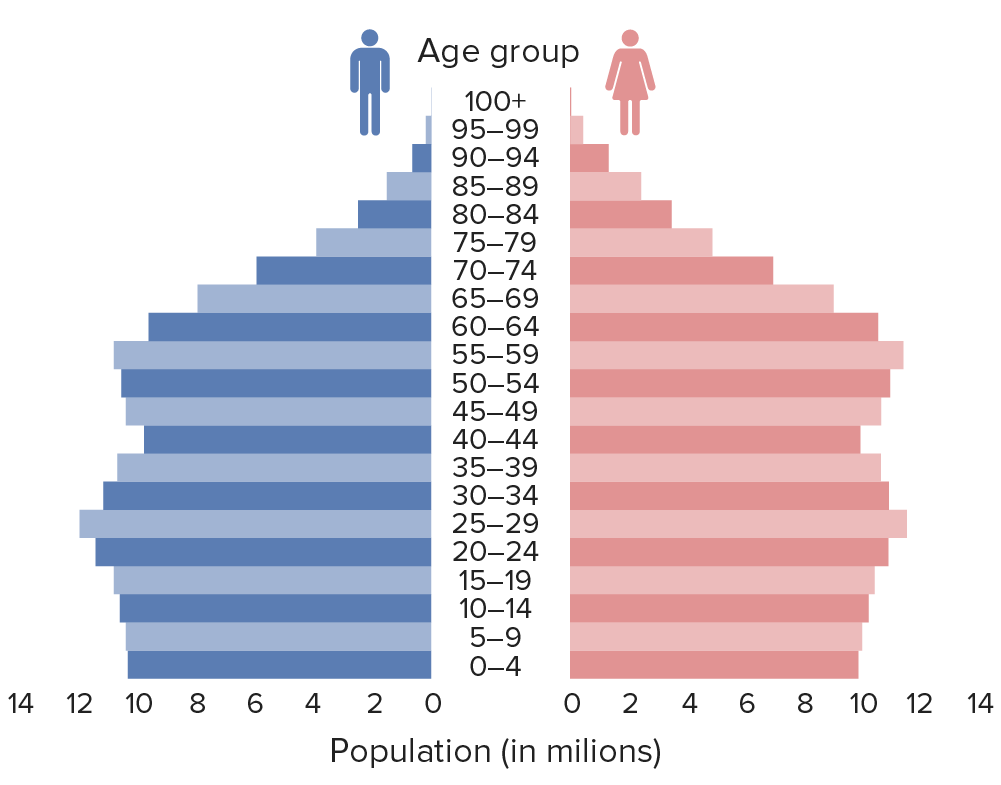
Which cause of death on the ETM would a population like this most likely be experiencing?
What is a Guest Worker?
Citizens of poor countries who obtain jobs (low skilled) that local residents won't accept.
A country can still have a growing population even if life expectancy is not very high. This is called __________________
Demographic Momentum
Explain the J-Curve when talking about population from the beginning of time until the 20th century.
The world was at a very moderate/gradual growth rate until improvement in technology and health dropped the CDR cause a huge population growth around the world.
What causes reduced fertility rates across the world?
The social structure, women rights, religious beliefs, economic prosperity, education, and urbanization within each country are likely to affect birth rates as well as abortion rates.
When one group cause a strain on the independent (working) group to provide and support that group, it is called ____________________
What is a high dependency ratio?
Distance Decay
the decline of an activity or function the further you are out from its original point.
Recite the following stages in the CORRECT STAGE ORDER (1-5) according to the DTM Model.
High Growth
Low Growth
Moderate Growth
Negative Growth
Low Growth
1. Low Growth
2. High Growth
3. Moderate Growth
4. Low Growth
5. Negative Growth
Explain Ravenstein's Laws (Name at least 2/3)
Most migration is for economic reasons (job opportunities, resources)
Most migration goes from rural to urban
- Migration increases as industries develop
What is Population Aging and how is it determined?
Population aging refers to changes in the age composition of a population such that there is an increase in the proportion of older persons.
Low CDR, Low CDR, High life expectancy
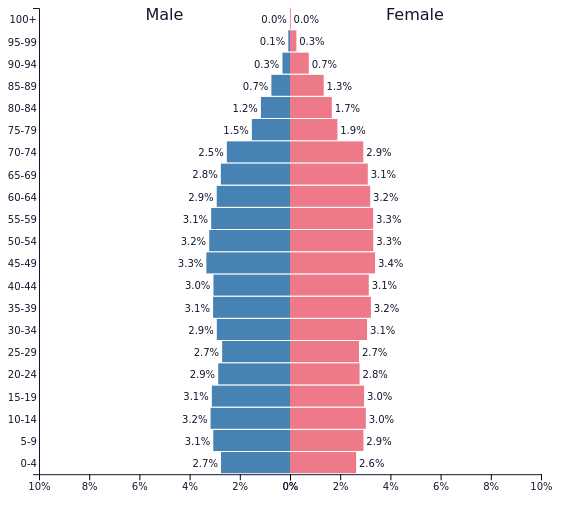
What stage would this country be considered? Extra 500pts if you can guess which European country this is.
Stage 4, France