What type of cell contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles?
Eukaryotic cells.
Which organelle contains enzymes that help digest cellular waste and break down macromolecules?
The lysosome.
Draw a graphic organizer about cell transport including types of transport (passive and active) and types of solutions
Draw how a cell would look like in each phase: Interphase, early prophase, late prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase

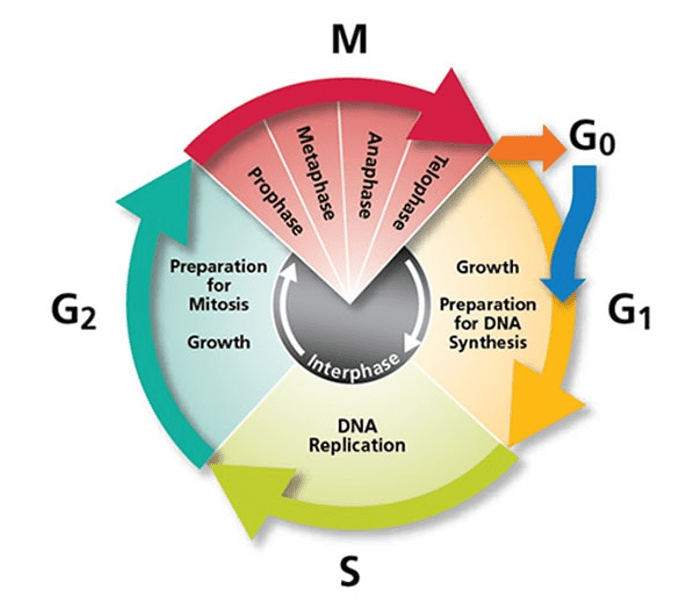
Make a diagram of the cell cycle in a circle and add the regulation centers
Draw a prokaryote cell

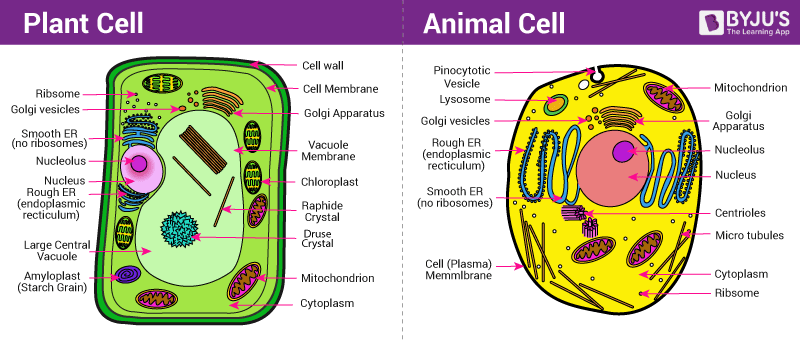
Draw an animal and plant cell with al the organelles
What is the main difference between how small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and large, polar molecules like glucose cross the cell membrane?
Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer due to their size and polarity, while large, polar molecules like glucose require transport proteins for facilitated diffusion or active transport.
Which phase of the cell cycle is the longest, and why does a cell spend most of its time in this phase?
Interphase. The cell spends most of its time in this phase because it is growing, performing normal cellular functions, and replicating DNA to prepare for division.
Compare the role of the G1 checkpoint and the G2 checkpoint in ensuring cell cycle accuracy.
The G1 checkpoint ensures the cell has adequate nutrients, size, and undamaged DNA before proceeding to DNA replication. The G2 checkpoint verifies that DNA replication was completed correctly and that there is no DNA damage before the cell enters mitosis.
What are the three main principles of the cell theory?
- All living things are made of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms.
- All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Which organelle is found in both plant and animal cells but is significantly larger in plant cells, and why is it larger in plants?
The vacuole. It is larger in plants because it stores water, nutrients, and waste and helps maintain turgor pressure for structural support.
Compare and contrast endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of their mechanisms and purposes in maintaining homeostasis.
Both endocytosis and exocytosis involve vesicles to transport materials across the cell membrane. Endocytosis brings substances into the cell, such as nutrients or pathogens for processing, while exocytosis expels waste or secretes materials like hormones. Both processes require energy (ATP) and help regulate the cell’s internal environment.
During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur, and why is this phase critical for maintaining genetic continuity?
DNA replication occurs during the S phase (synthesis phase). This phase is critical because it ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA after cell division.
Describe how cancer cells differ from normal cells in their behavior during the cell cycle.
Cancer cells bypass normal cell cycle regulation, dividing uncontrollably without responding to signals to stop. They can avoid apoptosis and often form tumors by continuing to grow even when there is no need.
Describe the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, with their DNA located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that houses DNA and membrane-bound organelles.
Why do plant cells have both mitochondria and chloroplasts, and how do their roles complement each other in energy production?
Chloroplasts capture light energy during photosynthesis to produce glucose, which serves as food. Mitochondria then use the glucose during cellular respiration to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. Together, they allow plants to produce and utilize energy efficiently.
Explain what would happen to a freshwater (hypotonic) protist, like an amoeba, if its contractile vacuole stopped functioning, and why.
The amoeba would likely burst because it lives in a hypotonic environment. Without the contractile vacuole to pump out excess water, water would continue to enter the cell by osmosis, causing it to swell and eventually lyse.
What would most likely happen if the spindle fibers failed to attach to chromosomes during mitosis?
The chromosomes would not be properly separated, leading to unequal distribution of DNA between the daughter cells. This could result in one cell with extra DNA and another with none.
How do carcinogens increase the risk of cancer at the cellular level?
Carcinogens cause mutations in DNA, which can disrupt genes that regulate the cell cycle, such as tumor suppressor genes or proto-oncogenes. This can lead to uncontrolled cell division.
Who was the scientist who first observed cells under a microscope, and what material did he examine?
Robert Hooke; he examined cork.
What's the process for protein production? Where does it start and where does it end? Specially if that protein has to GET OUT of the cell?
Protein production starts in the nucleus, where the DNA is transcribed. The transcript is then transported to the ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum creating the protein. The protein is packaged into vesicles and sent to the Golgi apparatus for modification and sorting. Finally, it is transported in vesicles to the cell membrane, where it is secreted out of the cell through exocytosis.
Explain the role of protein channels in facilitated diffusion and how this differs from simple diffusion.
Protein channels allow specific molecules to pass through the membrane without energy input, enabling facilitated diffusion. This differs from simple diffusion, which involves molecules passing directly through the phospholipid bilayer without the need for a protein channel.
Explain the difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through the formation of a cleavage furrow, where the membrane pinches inward. In plant cells, a cell plate forms in the center of the cell and eventually develops into a new cell wall.
A scientist observes cells that are dividing rapidly and forming a mass but not spreading to other tissues. What type of tumor is this, and how is it different from a malignant tumor?
This is a benign tumor. Unlike malignant tumors, benign tumors do not invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body (metastasize).
Explain how the DNA is organized differently in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
In prokaryotic cells, DNA is circular and floats freely in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is linear and enclosed within a nucleus.
Explain the role of vesicles in transporting proteins through the endomembrane system, and describe what would happen if vesicle formation was disrupted.
Vesicles transport proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and then to their final destinations, either within the cell or outside it. If vesicle formation was disrupted, proteins would not be efficiently transported, leading to a breakdown in protein processing, secretion, and cellular functions, which could harm cell survival.
Using the concept of osmosis, explain why grocery stores spray water over the produce. How might this change the appearance of the produce, and why would this change be beneficial to a store?
More water outside the cells, water goes inside and make cells swell. This ensures that the produce is plump and not dehydrated.
Stem cells are used in various medical treatments. How do stem cells differ from differentiated cells in terms of their function?
Stem cells do not have a specific function and can divide to produce more stem cells or differentiate into various specialized cell types. Differentiated cells have specific functions and cannot revert to a stem cell state.
What does the M checkpoint do?
Check for spindle fiber attachment