Which organelle is responsible for ATP production in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondrion
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
Fatty acid tails
What transport process moves substances directly through the lipid bilayer without proteins or energy?
Simple diffusion
What term describes water movement across a selectively (semi) permeable membrane?
Osmosis
What is the term for how eukaryotic cells separate processes into different membrane-bound areas for efficiency?
Compartmentalization
Which organelle modifies, sorts, and ships proteins after they leave the rough ER?
Golgi apparatus
How do membrane proteins contribute to selective (semi) permeability?
They allow specific substances to cross the membrane.
What do we call the type of membrane protein that acts as a channel or carrier?
Transport Proteins
Through Osmosis, water wants to travel from areas of _________ solute concentration to areas of _________ solute concentration.
Low to High
Which Structure of the plant cell is labeled E?
The Large Central Vacuole
Which organelle is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
List at least 3 Cell Membrane Protein Functions:
Transport, Cell-Cell Recognition, Enzyme Activity, Signaling, Inter-cellular joining, Structural attachment
Compare facilitated diffusion and active transport in terms of energy use.
Facilitated diffusion does not use ATP; active transport does
If the water potential inside a bag is −0.4 and outside is 0, which way does water move?
Inside the bag
What cell structure contains digestive enzymes used for digestion of materials?
Lysosomes
Explain one structural difference between plant and animal cells and its functional significance.
Plant cells have a cell wall for structural support and protection; animal cells do not
Which of these molecules would diffuse through the plasma membrane faster: O₂, Na⁺, glucose, or H₂O? Provide at least 2 reasons.
O₂, because it is small and nonpolar
What transport process uses vesicles to move large materials out of the cell AND What transport process brings materials into the cell using vesicles?
Exocytosis - OUT
Endocytosis - IN
A cell is placed in an unknown solution and shows no net mass change. What can you conclude about the solution?
The solution is isotonic
When looking at this image, which cell would be most efficient at gaining nutrients through diffusion?
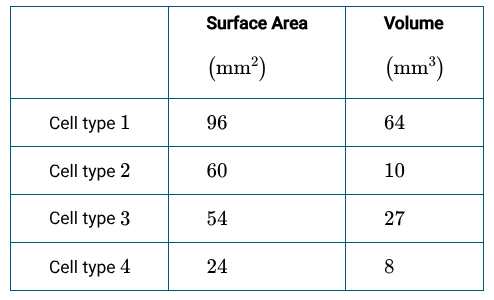
Cell 2
Why do cells have mitochondria with highly folded inner membranes?
The folds increase surface area for ATP-producing reactions
What is the primary function of carbohydrate chains attached to lipids or proteins in the cell membrane?
Cell recognition and/or signaling
Why does oxygen diffuses across the membrane more easily than glucose. (2 reasons)
Oxygen is small and nonpolar; glucose is large and polar
When a plant cell is in a hypotonic solution, the cell becomes firm. This is called?
Turgid
A dialysis tubing bag had an initial mass of 12.0 g. After being placed in distilled water for 30 minutes, its final mass was 14.4 g.
Calculate the percent change in mass of the dialysis tubing bag.
Based on your calculation, was the solution inside the tubing hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic relative to the surrounding solution?
1. 20%
2. The solution inside the dialysis tubing was hypertonic relative to the surrounding solution.