All matter is made of these.
What are atoms?
In 1869 and 1871, this Russian chemist published and then revised a table using known patterns.
Who is Dmitri Mendeleev?
Atomic radius ________ from the right to the left and ___________ from the top to the bottom of the periodic table.
What is increases, increases?
Atoms form these so that they can become more stable.
What are chemical bonds?
This is one method is used to determine the subscript values for an ionic compound.
What is the crisscross method?
Atoms that have the same number of protons, so they are atoms of the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons.
What are isotopes?
The rows of the periodic table are called ___________, and the columns are called _________ .
What are periods and groups?
One of these form when an atom gains an electron.
What is an anion?
These compounds break apart easily in water, but do not easily break apart when not in water.
What are ionic compounds?
This is a group of atoms that work together to form an ion.
What are polyatomic ions?
To find the atomic mass of all bromine atoms, multiply the mass of each isotope by its relative _________.
What is abundance?
The strength of the force between two charged particles depends on the charge of the particles and the distance between them.
What is Coulomb's Law?
Saying that all ions in main group 1 have a +1 charge and all ions in main group 6 have a -2 charge refers to this.
What is their common ion charge?
When a nitrogen atom bonds with another atom/s, it has to form this many bonds in order to satisfy this rule.
What is 3 bonds ; octet rule?
The prefix naming is used only to determine the name of these compounds. Be careful, don't add "mono" if there is only one of the first atom involved in the compound.
What are molecular/covalent compounds?
This is still used as a model of the atom because it is a simplified picture that can still explain many important atomic properties.
What is the Bohr Model?
This can be calculated by subtracting the number of inner shielding electrons from the number of protons.
What is the effective nuclear charge?
This is why atoms with a larger atomic radius have a lower ionization energy.
What is a reduced attraction from the nucleus due to increased distances to the electrons?
This type of bond forms when atoms share electrons, but not completely equally.
What is a polar covalent bond?
These are the two types of Van der Waals forces. Underline the intermolecular force that every, single compound has.
What are London Dispersion and Dipole interactions.
The type of energy released from an atom when its electrons fall from excited state back to ground state.
What is a light/radiant energy?
Core electrons are closer to the nucleus and experience a greater force of attraction. The outermost electrons, the valence electrons, experience this effect from by the inner, core, electrons.
What is the shielding effect?
Put these elements in order of INCREASING electronegativities (smallest to largest):
Ca, S, O, Al, Mg
What is: Ca, Mg, Al, S, O?
These are the 3 ways/clues to determine whether or not a compound is polar or non-polar.
What is:
1. an asymmetrical shape
2. If there is one or more lone pairs of electrons
3. A large electronegativity difference between atoms
Which elements would form an ionic bond with Sodium?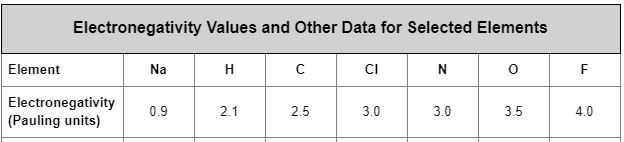
What are: Cl, N, O, F