Elements on the PT are arranged in order of increasing...
atomic number
CH4
carbon tetrahydride
Ammonium Sulfide
(NH4+)2S
What is a Bohr model / what does it show?
Protons, neutrons and electrons in the proper orbitals for an element
What is this image showing?
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Lithium, Aluminum and Vanadium are all classified as...
metals
Al2O3
aluminum oxide
Cadmium Sulfate
CdSO4-2
Remember Cadmium is always a +2 charge
What is an ion?
An element that has gained or lost electrons and has taken on a charge.
If an element emits a RED flame, describe what each of the following would be:
FREQUENCY
ENERGY
WAVELENGTH
FREQUENCY - LOW
ENERGY - LOW
WAVELENGTH - LONG
Nonmetals such as Nitrogen and Oxygen tend to form _______ which are negatively charged ions.
anions
Li2SO3-2
Lithium sulfite
Zinc Chloride
ZnCl2
Remember Zinc is always a +2 charge
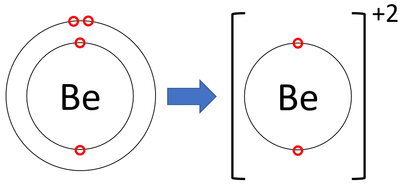
Draw the Bohr model for an ION of Beryllium and indicate its charge.
If an element emits a BLUE-PURPLE flame, describe what the following would be:
FREQUENCY
ENERGY
WAVELENGTH
FREQUENCY - HIGH
ENERGY - HIGH
WAVELENGTH - SHORT
Metals tend to form ______ which are positively charged ions.
cations
FeF3
Iron (III) Fluoride
Sodium Carbonate
Na2CO3-2
Draw a Bohr model of Nitrogen and indicate its charge.

Describe what happens when an unstable electron is exposed to heat (like we saw in the flame lab).
The electron starts to gain energy and moves to a different energy level away from the nucleus, which emits light in the process of falling back toward the nucleus.
This classification of elements tend to have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
metalloids
Mg(CN)2
Magnesium Cyanide
Strontium Chromate
SrCrO4-2
Draw a Bohr model of Neon and indicate its charge.

Why did Potassium emit a purple/pink flame in our experiment?
Potassium had more energy levels, also called orbitals, to jump.