Matter is anything that has _________ and __________.
mass; volume (or takes up space)
Which change produces a new substance, physical change or chemical change?
Chemical change
Density is the relationship between an object's ___ and ___.
Mass and density
What are the two main types of matter?
Pure substances and mixtures?
Which mixtures exhibit the Tyndall Effect? Be more specific than homogeneous and heterogeneous mixures.
Colloids and suspensions.
Describe the shape and volume of the three states of matter
Solid: definite shape and definite volume
Liquid: indefinite shape and definite volume
Gas: indefinite shape and indefinite volume
Define physical properties and list 5 physical properties.
Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the substance. Solubility, density, polarity, malleability, ductility, etc.
Find the density of an object that has a mass of 525 g and occupies a volume of 15.0 mL.
35.0 g/mL
What are the two types of pure substances? Define and give an example of each.
Element - pure substance made up of only one kind of atom (ex: Hydrogen, Oxygen, etc.)
Compounds - pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in set ratios (ex: NaCl, H2O, CO2)
True or False: When substance form mixtures, the substances do not retain their original properties.
False, they do.
Describe the kinetic energy of all three states of matter.
Solid - low KE, liquid - medium KE, gas - high KE
Define chemical properties and list the 4 that we've gone over.
Chemical properties describe matter based on its ability to change into new matter that has different properties. Ex: Toxicity, Reactivity, Oxidation state, and Flammability.
One side of a cube measures 4 cm long. The cube’s mass is 250 g. Find the density of the cube.
4 g/cm3
What are the two types of mixtures? Define and give an example of each.
Homogeneous mixtures - Mixture of two or more substances physically combined that appears uniform throughout (ex: solutions and colloids; salt water and milk)
Heterogeneous mixture - mixture of two or more substances physically combined that does NOT appear uniform. You can see the different parts. (ex: suspensions; salad dressing, cereal, etc.)
List 3 ways to increase the solubility of a solid
Stir it, shake it, heat it, crush it.
What is happening at parts 2 and 4?

Part 2 is a solid and a liquid, part 4 is a liquid and a gas. The substance is undergoing a phase change and the heat being added is used to help overcome that phase change.
Give 4 examples of physical changes.
Tearing a paper, crushing a can, changing state (ice melting, water freezing), dissolving salt in water, etc.
The density of copper is 8.96 g/mL. The sample of copper you have has a volume of 2.40 mL. Find the mass of the sample.
21.5 g
Solution - small particles, evenly distributed, does not scatter light. Ex: salt water, sugar in water
Colloids - medium particles, evenly distributed, DOES scatter light, can be opaque. Ex: milk, fog
Suspensions - large particles, particles settle, DOES scatter light, can be opaque, must shake! Ex: salad dressing, pulpy orange juice
What approximate mass of NaNO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 10 oC?
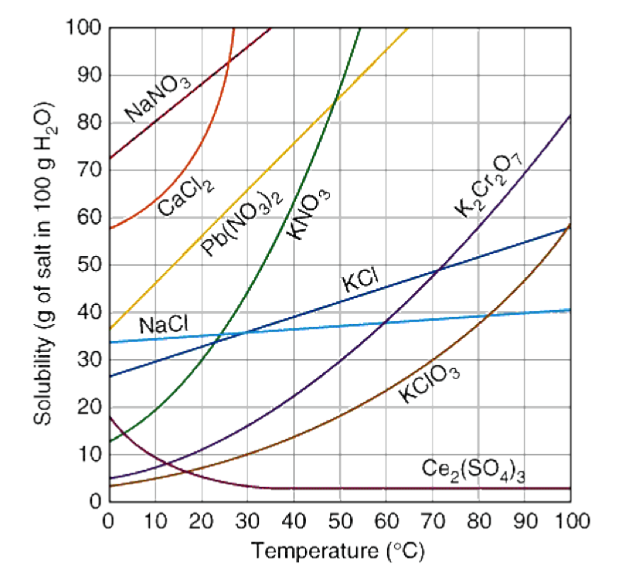
80 g
What is the melting point and the boiling point of this substance?

Melting: 0 oC
Boiling: 100 oC
Give 4 signs of a chemical change
Change in color, Change in odor, Production of gas (fizzing/foaming), Heat given off (exothermic), Heat taken in (endothermic), Light created, Sound produced, Precipitate forms
Water’s density is 1 g/mL. What would happen to a solid object with a density that is less than water when it is placed in water?
It would float.
Classify solutions even further and define each, using the words "solute" and "solvent" in your answer
Unsaturated: a solution that contains less solute than can be dissolved in the solvent. The solvent is capable of dissolving more solute if added.
Saturated: a solution containing as much solute as the solvent is capable of dissolving. Any additional solute added will collect at the bottom.
Supersaturated: a solution containing a greater solute than the solvent can hold. This occurs when a saturated solution is carefully cooled.
If you want to dissolve 40 g of KCl at 50 oC, will the solution be unsaturated or saturated?
Unsaturated