Thinking
Thinking
The mental frameworks that guide our thinking
Schema
The term that refers to things being put into memory
Encoding
This part of memory has a potentially infinite duration and capacity
Long term memory
This refers to the phenomenon where most info is forgotten soon after the event but the amount forgotten levels off over time
Forgetting curve
This decision making process has a single correct sets of steps that should be followed every time
Algorithm
Convergence and retinal disparity
Binocular depth cues
This effect suggests that studying a little each day is better than cramming for a test
The spacing effect
This refers to memory retrieval done without cues
Recall
Intelligence tests should be _____ in order to useful
standardized; valid; reliable
"A flipped a coin and got heads 4 times. That means tails is only getting more and more likely." What fallacy is this?
Gambler's fallacy
The mental shortcuts or "rules of thumb" that allow us to make decisions quickly that are "good enough"
Heuristics
The process by which synaptic connections between neurons become stronger with frequent activation
Long term potentiation
This refers to the degenerative disease that affects memory. It is more typical in older people
Alzheimer's Disease
This kind of interference involves new info covering old info.
Retroactive interference
"I found other people who also remember the Fruit of the Loom logo having a cornucopia. I must be right!" What bias is this?
Confirmation bias
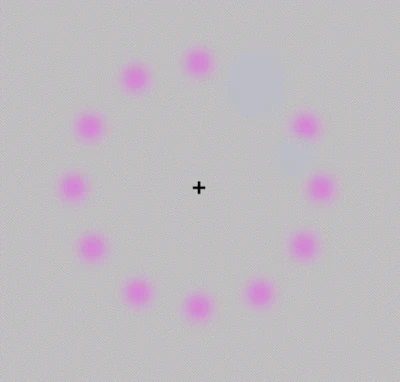 the rapid succession of stationary images that gives the illusion of movement
the rapid succession of stationary images that gives the illusion of movement
phi phenomenon
This effect describes the fact that the start and end of a list are more memorable than the middle of the list
Serial position effect
This refers to a kind of memory that is easier to retrieve when you are in the same environment where the memory was encoded (ex. it is easier to remember Psych info in this classroom specifically)
Context-dependent memory
Name any two of the intelligence theorists covered in class.
Galton; Gardner; Sternberg; Spearman
This memory model includes the central executive, phonological loop, and visuospatial sketchpad.
Working memory model
The changing of a schema to allow new information
Accommodation
Remembering that I need to leave right after school for an appointment is what kind of memory?
Prospective memory
This is a proposed cause behind infantile amnesia.
Memory areas (hippocampus) underdeveloped
Sigmund Freud believed memories were repressed in order to...
save ourselves from pain
Mr. Wetzel's favorite color.
Purple