or Melt Down📉
or Melt Down📉
(💧Particles Edition🧊)
✨Energy✨
😤
👻
What happens to the particles in a solid when it melts?
They are no longer locked together, and can slide freely around each other.
Name the three most common states of matter on Earth.
Solid, Liquid, and Gas.
What is the direction that energy will flow in this diagram?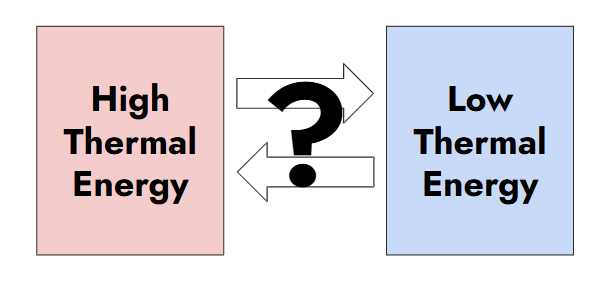
In a chemical reaction, what are the starting substances called?
Reactants.
What does “conservation of mass” mean?
Matter is not created or destroyed, or atoms are not added or lost in a chemical reaction.
What a liquid turns into a gas, what do we call that process?
Boiling, Evaporation, aka: Vaporization
Which state of matter has an unchanging shape and volume?
Solid.
When you hold an ice cube, why does your hand feel cold?
The thermal energy from your hand is flowing into the ice cube.
What are the substances formed after the reaction called?
Products.
In this reaction, A + B → AB, what must be true about the number of atoms before and after?
The amount of A and B as reactants must equal the amount of A and B produced as the product AB.
The amount of atoms before and after will be the same.
What phase change occurs when a gas turns back into a liquid?
Condensation.
Why can liquids flow, but solids can't?
Liquid particles can move freely around each other, but solid particles are locked in place.
In an endothermic process, what happens to the motion of particles?
Energy is absorbed, so particles will move faster.
Identify the reactants and products in this reaction: Hydrogen + Oxygen -> Water
Reactants: Hydrogen + Oxygen
Product: Water
Why does a burning candle seem to “lose” mass even though it follows conservation of mass?
The reaction of burning a candle turns some of the candle into gases, which float away and appear to be lost.
Dry ice skipping the liquid stage and turning into gas is called what?
Sublimation.
What happens to particles movement as temperature decreases.
They move slower and may start to stick together.
In an exothermic process, what happens to the motion of particles?
Energy is released, so particles move slower.
Identify the reactants and products in CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Reactant: CaCO₃
Products: CaO + CO₂
How can you prove mass is conserved in a reaction?
Measure the mass of reactants and products and observe that they are the same.
During boiling, why doesn't temperature increase once the liquid starts bubbling?
That energy is going toward the liquid particles breaking free into gas particles.
Why can gases be squished, but liquids and solids cannot?
Gas particles are far apart, so there is room left to be squished closer. Liquid and solid particles are already close together and cannot be squished closer.
What is the main difference between endothermic and exothermic processes?
Whether energy is absorbed or released by the process.
In the equation Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂ , explain what happens to the zinc, hydrogen, and chlorine atoms during the reaction.
The atoms are rearranged, with the hydrogen and chlorine breaking apart, two chlorine bond with a zinc, and two hydrogens bond with each other.
Explain how the Law of Conservation of Mass connects to Coefficients in chemical equations.
Ex: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
The coefficients tell you how many molecules are needed as reactants and how many are produced as products in order for the equation to be balanced.
In other words, its lets the amount of atoms before and after to be the same.