Definition of mutualism and an example
Both organisms benefit from each other
Three groups of protists
Plant-like, fungi-like, and animal-like
Cell membrane definition
Outer barrier that separates a cell from its environment
Example of herbivory
Giraffe eating a tree
They are unicellular and lack cell walls, do not have plant structures
Definition of parasitism and an example
One organism benefits, the other organism is harmed
Characteristics of animal-like
Heterotroph
Unicellular
Eukaryote
Asexual Reproduction
Example of carnivory
Lion eating a zebra
Is Eutrophication good or bad for the environment? Why?
Eutrophication is bad for the environment because if it happens, ecosystems will perish, taking animals and fish dying too.
Definition of commensalism and an example
One organism benefits, the other organism is neutral (not harmed or benefitting)
Characteristics of protists
Single-celled eukaryotic organisms, neither plants nor animals nor fungi
How do you spell DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Two types of competition and their definitions
Interspecies - Competition occurs between members of DIFFERENT species for resources
Intraspecies - Competition occurs between members of the SAME species for resources
Draw a Flagellate, how do they move? Where are they located?
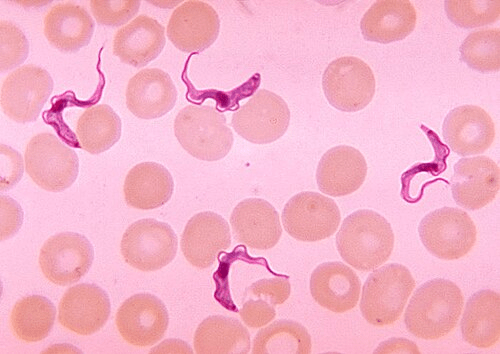
They use flagellums, found in bloodstreams
Definition of neutralism and an example
Both organisms are unaffected
Characteristics of plant-like
Autotroph
Most are unicellular - some algae is multicellular (these are the only multicellular protists)
DO NOT have a cell wall (this differentiates them from plants)
All have chlorophyll (pigment to absorb sunlight to make energy, like plants)
Vacuole definition, are they in animal cells?
storage for usually liquid, yes but they are smaller than vacuoles seen in plant cells
Explain how symbiosis, predation and competition are different. Why are they considered different interactions.
Symbiosis they are both still alive
Predation one will always die
Competition one can die
Draw a euglenoid, how do they move?
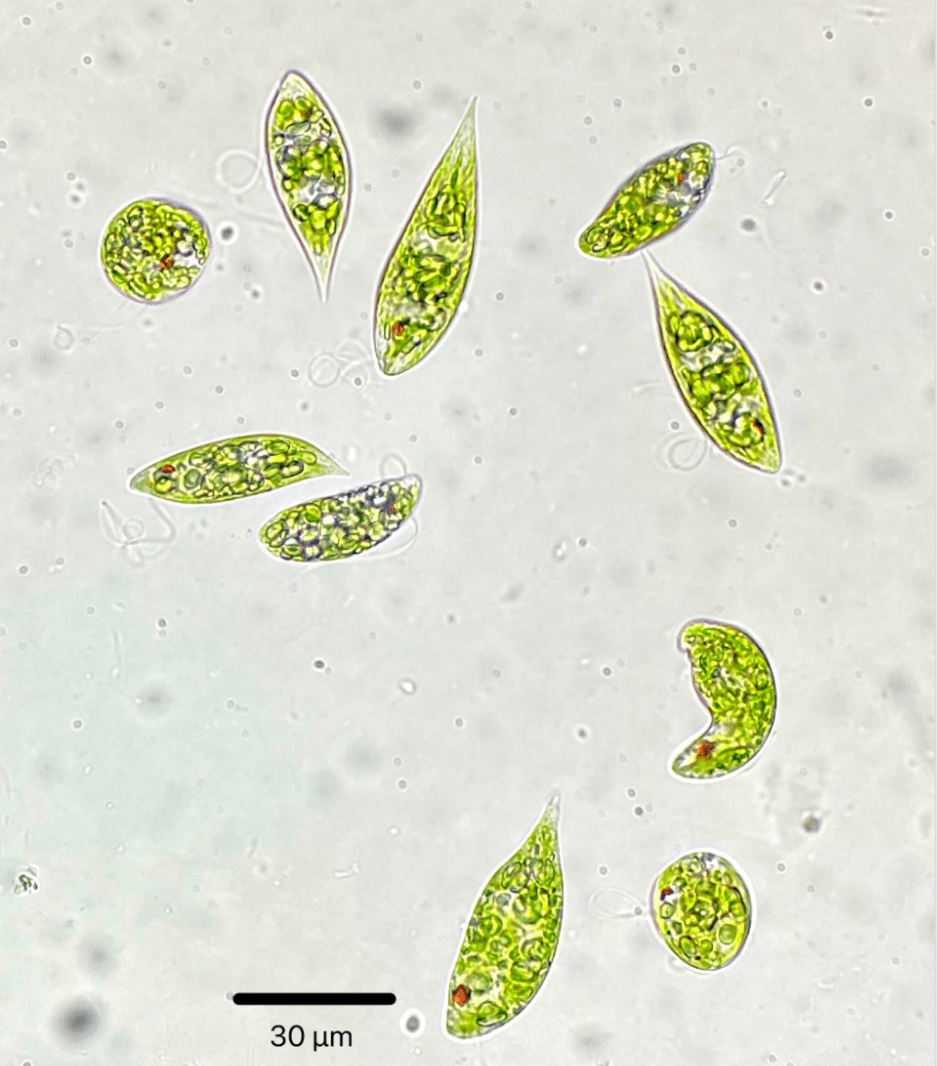
They use flagellums
Fig tree and fig wasp example, what type of symbiotic relationship is it
Mutualism, The fig tree provides a protected habitat for the wasps to lay eggs and raise their young, while the fig wasp pollinates the fig's internal flowers, helping the fig to produce seeds and reproduce.
How do Amoebas move around
Pseudopods
What do lysosomes do?
They break down large molecules into smaller molecules
Double Jeopardy
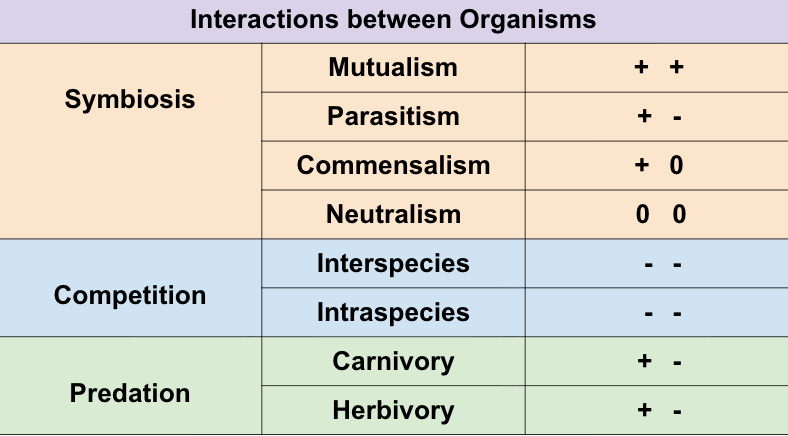
Create the chart from all 8 interactions. Label species 1 and species 2. Create a key
Describe Eutrophication using all the steps.
1. Nutrient load up: Excessive nutrients from fertilizers are flushed from the land into rivers or lakes by rainwater. 2. Plants flourish: These pollutants cause aquatic plant growth of algae, duckweed and other plants 3. Algae blooms, oxygen is depleted: algae blooms, preventing sunlight reaching other plants. The plants die and oxygen in the water is depleted. 4. Decomposition further depletes oxygen: Dead plants are broken down by bacterial decomposers using even more oxygen in water. 5. Death of the Ecosystem: Oxygen levels reach a point where no life is possible. Fish and other organisms die.