When water molecules are attracted to other molecules
cohesion
A source of fast energy
carbohydrates
Enzymes end in these 3 letter
ase
Source of electrical spark in earths early atmosphere
lightning
Fats are ______.
lipids
Capillary actions works together with ______ & ______.
Cohesion and Adhesion
The singular unit that build up a polymer/macromolecule
Monomer
enzymes _______ chemical reactions
speed up
What activity led to increased levels of ammonia, methane, water vapor, and hydrogen in the atmosphere.
volcanic eruptions
The connection between the oxygen of one water molecule and the hydrogen another water molecule
hydrogen bond
Water is able to withstand rapid temperature change
high specific heat
Nucleic acid
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by ________
Lowering the activation energy
How were the oceans formed during earths early time
earth cooled, condensation led to water vapor becoming liquid water
Enzyme act as a _____.
catalyst
Ice _____ when frozen, because of this ice ____ in water.
expands/floats
Makes up the cell membrane
Lipids
What happens to enzymes when the conditions (temperature and pH) are changed
Enzyme is denatured, becomes inactive, stops working
The product of the miller urey experiment was
Organic molecules-Amino acids
Water is able to act in different ways because it is ______. (hint: positive and negative)
Polar
Cooling off through sweating is a benefit due to this property of water
Heat of vaporization
What is the name of each structure

1. Top left: Carbohydrate
2. Top right: Lipid
3. Bottom left: Nucleic Acid
4. Bottom right: Protein
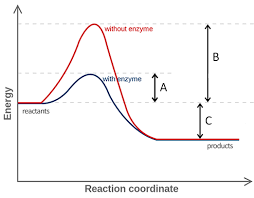
draw the activation energy graph correctly on the board. make sure to label reactants, products, reaction without enzyme, reaction with enzyme.
Name the 4 gasses that filled earths early atmosphere.
To get all points you must name all gasses. You will need to write down all 4 and submit on a paper. Partial credit will be provided.
1. Methane
2. Ammonia
3. Water Vapor
4. Hydrogen
What are the monomers of each macromolecule
Carbohydrate- Monosaccharide
Lipid- Triglyceride
Protein- Amino Acid
Nucleic Acid- Nucleotide