The half-life of chrominum-51 is 28 days. If the sample contained 510 grams, how much chromium would remain after 56 days?
127.5 grams
A common ancestor is not a single individual or link in the chain, but instead represents a population of individuals from which the animal descended from with modifications.
What were the push and pull factors for humans migrating out of Africa?
Push Factors: climate change, exhausted food supply, drought, lack of resources
Pull Factors: new technology, want for exploration, language and communication advancements
What are the three types of adaptations?
1. Structural: involving body of organism
2. Physiological: related to biochemistry and interactions within the body
3. Behavioral: having to do with actions
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is how a cell makes a copy of itself!
First, the cell gets ready by copying all its DNA — that’s like making a backup of its instruction book. Then, it lines everything up neatly in the middle, splits the copies apart, and finally divides into two new cells.
Now there are two identical cells instead of one — just like twins!
How to calculate field of view?
mag. 1 x diameter 1 = mag. 2 x diameter 2
A trait that is shared by all members of a clade and only members of that clade.
What is the spatial scale of the Great Migration?
People started in Africa and moved to Asia, and later Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and Australia. Finally they went to Europe and the North American, and ultimately South America.
What does the acronym of "Dumb Kids Playing Catch On Freeways Get Smashed" stand for?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
A cell with a diploid number of 78 undergoes meiosis, how many chromosomes are in each daughter cell?
39 daughter cells
The field of view is 675 μm and a starfish ray takes up 3/4 of you view. What is the average size of one starfish ray?
506 μm
Which graph is gradualism and which is punctuated equilibrium? 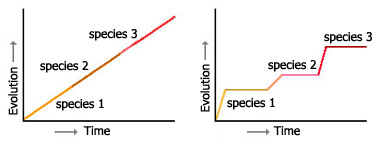
Graph 1 is gradualism (slow change over time) and graph 2 is punctuated equilibrium (long periods of little change, then sudden speciation events).
What is the temporal scale of the Great Migration?
People started in Africa 200,000 years ago and began to spread to other locations approximately 50,000-60,000 years ago. 40,000 years ago they moved to Europe and 15,000 years ago they traveled to North America.
What are the 6 kingdoms?
1. Plantae
2. Animalia
3. Fungi
4. Eubacteria
5. Protista
6. Archaebacteria
What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis?
1 diploid cells to 2 haploid cells to 4 haploid cells
Diameter of field for the following in micrometers is:
3,400 μm
What is morphology?
Physical and structural traits
In what order did hominids evolve in?
A. afarensis: 3.9 - 2.9 mya
A. africanus: 3.6 - 3.5 mya
H. habilis: 2.4 - 1.65 mya
A. boisei: 2.3 - 1.2 mya
H. erectus: 1.8 mya - 300,000 years ago
H. neaderthalensis: 400,000 - 40,000 years ago
H. sapiens: 50,000 - 60,000 years ago
What is taxonomy?
The modern science of grouping living organisms based on
- structural, genetic, and biochemical similarities and differences
- cellular organization
- evidence from evolutionary relationships
The illustration below represents what stage of meiosis?
Metaphase 1
Suppose a piece of bone 1/32 of its original carbon-14 activity. How many years ago would that creature have lived?
28,650 years ago
What is the difference between radial and bilateral symmetry?
Radial is identical body halves around the central axis
Bilateral is two sides as left and right, mirroring each other
What are differences between early hominid skulls and modern hominid skulls?
- no sagittal crest
- reduced maxillary prognathism (slope of face)
- bigger cranium
- change in position of foramen magnum (bipedal)
What are the 3 criteria to be considered evolutionary adaptation?
1. genetically passed onto the next generation (heritable traits)
2. to be functional for a specific environmental factor (fits a niche)
3. contributes to an advantage for that species (fitness)
What are the 10 facts about Human Variation?
1. human groups distinguish themselves principally, culturally
2. human biological variation is continues, not discrete
3. clustering populations is arbitrary
4. populations are biologically real, not races
5. populations also have a constructed component
6. there is much more vairation within groups than between them
7. people are similar to those nearby and different from those faraway
8. racial classification is historical and political and does not reflect natural biological patterns
9. humans have little genetic variation
10. racial issues are social-political-economic, not biological