What are the 3 groups all amino acids have?
Amine, carboxylic acid, and side chain that varies.

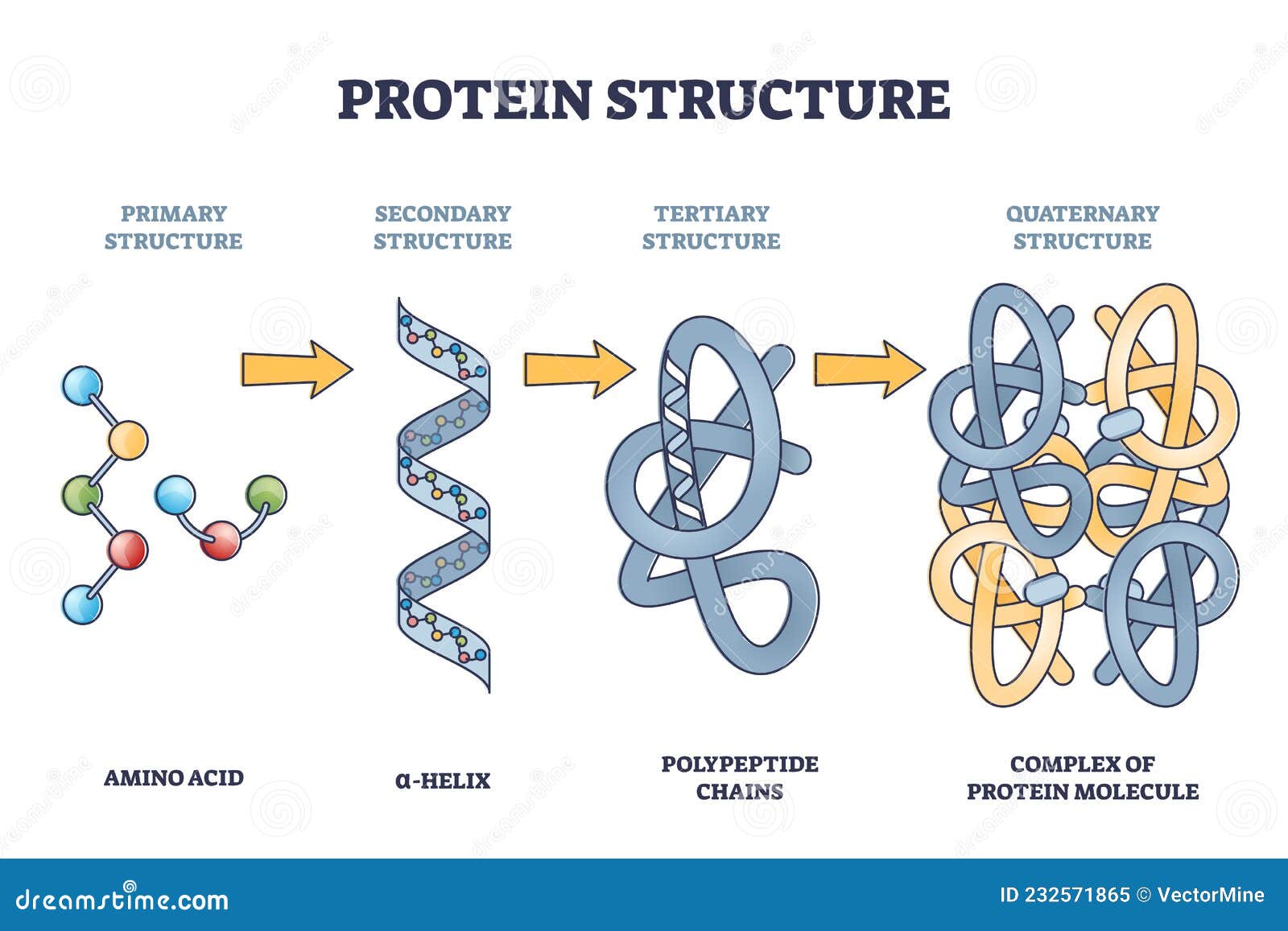
Describe the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
1. Primary Structure: The linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, held together by peptide bonds.
2. Secondary Structure: The local folding of the polypeptide chain into structures like alpha helices and beta sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
3. Tertiary Structure: The overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain, formed by interactions between side chains (R groups), such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, and hydrophobic interactions.
4. Quaternary Structure: The structure formed when two or more polypeptide chains (subunits) come together and function as one protein unit.
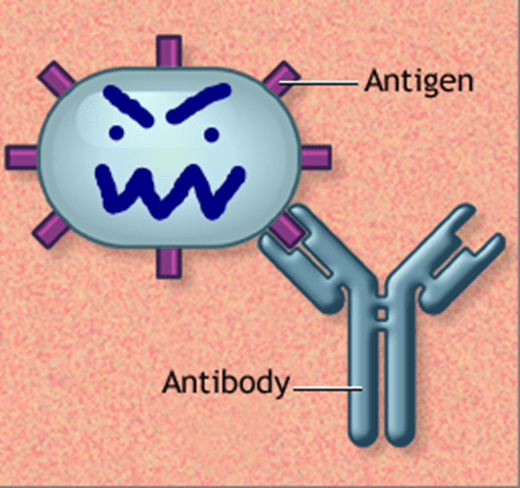
What is the difference between an antigen and an antibody?
An antigen is a foreign molecule (like part of a virus or bacteria) that triggers an immune response.
An antibody is a protein made by B cells that specifically binds to the antigen to help destroy or block it.
What is an oxidoreductase enzyme?
Oxidoreductases are enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, where electrons are transferred from one molecule to another.
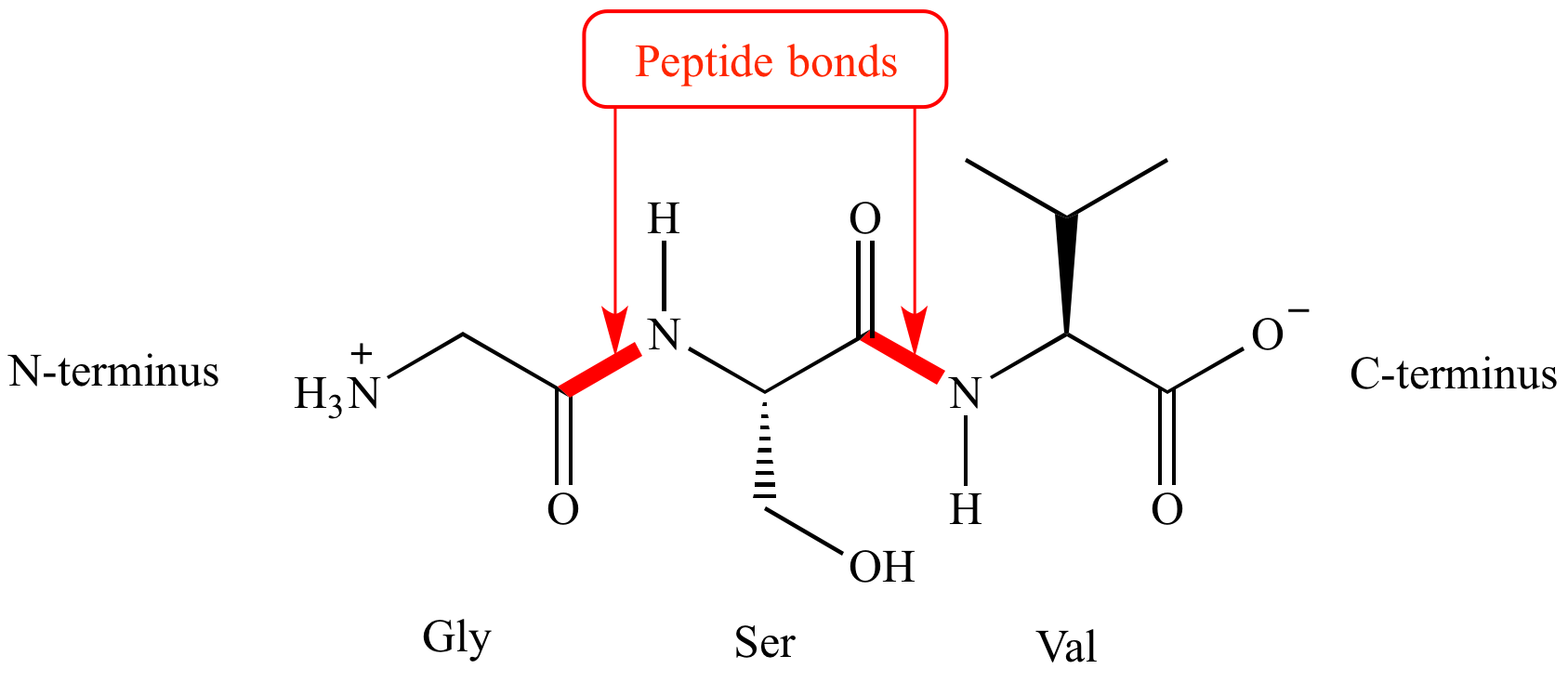
Describe the amide bond.
An amide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) and an amine group (-NH2). During this reaction, a molecule of water is removed (a condensation or dehydration reaction), and the resulting bond is called an amide bond.
What role does hydrogen bonding play in protein structure, and why is it important?
Hydrogen bonding is a key non-covalent interaction that helps stabilize the folding of a protein. It occurs between the backbone atoms or side chains of amino acids. These bonds are especially important in forming secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets, and they also help maintain the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins. Without hydrogen bonding, proteins would not maintain their proper shape and function.
What is the adaptive humoral immune response?
It is the immune response where B lymphocytes produce antibodies (immunoglobulins) to target specific foreign substances (antigens). It takes some time because B cells must recognize the antigen and activate before making antibodies.
Identify Activation Energy in a Potential Energy Diagram.
Activation energy is the energy difference between the reactants and the peak of the curve (the transition state). Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a reaction to start.

Classify amino acids by their side chain as polar, nonpolar, acidic or basic.
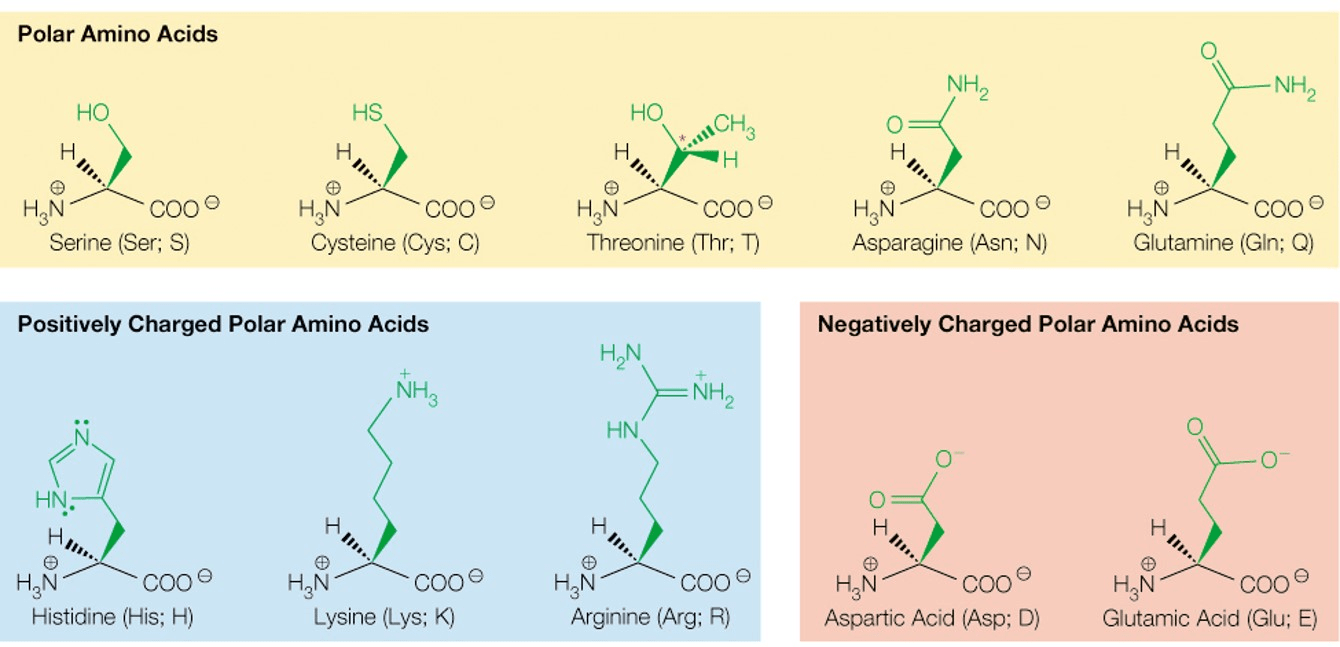
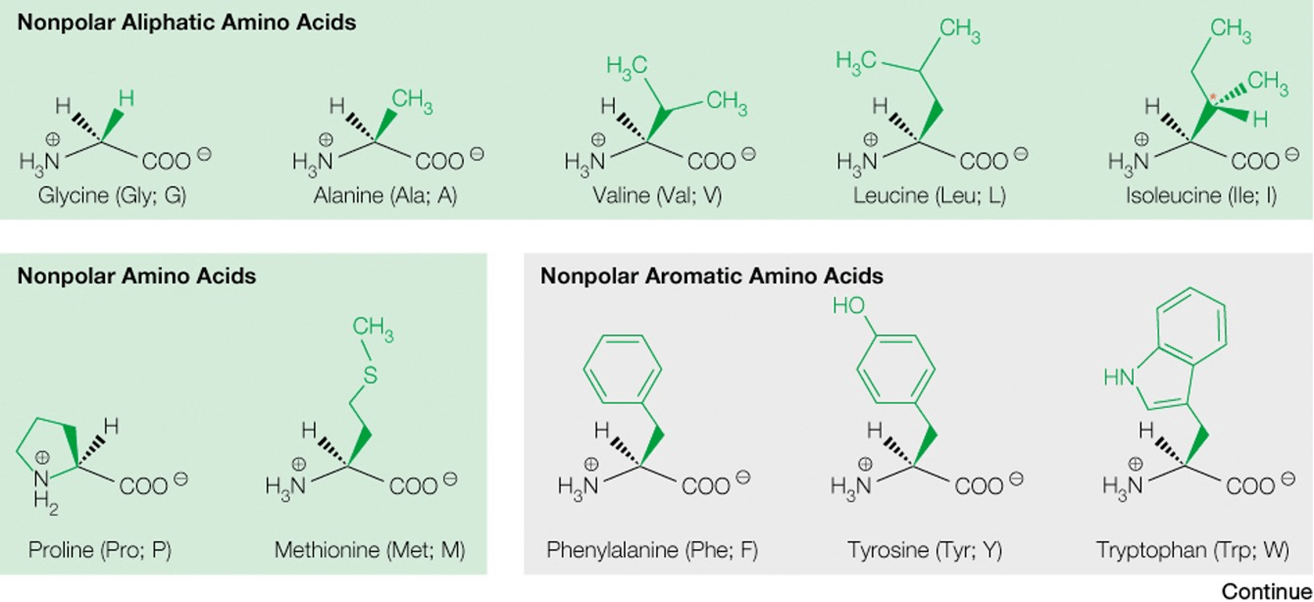
Describe the various features of globular proteins.
1. Compact and spherical in shape.
2. Soluble in water due to hydrophilic side chains on the surface.
3. Hydrophobic side chains are buried inside the protein.
4. Have primary, secondary, tertiary, and sometimes quaternary structures.
5. Functionally active – act as enzymes, transporters, antibodies, etc.
6. Have a dynamic and flexible shape for interacting with other molecules.
7. Folded into a specific 3D shape essential for their function.
What must be present for an antibody to bind its antigen?
The charge and shape of the antibody and antigen must match (complementarity) for proper binding to occur.
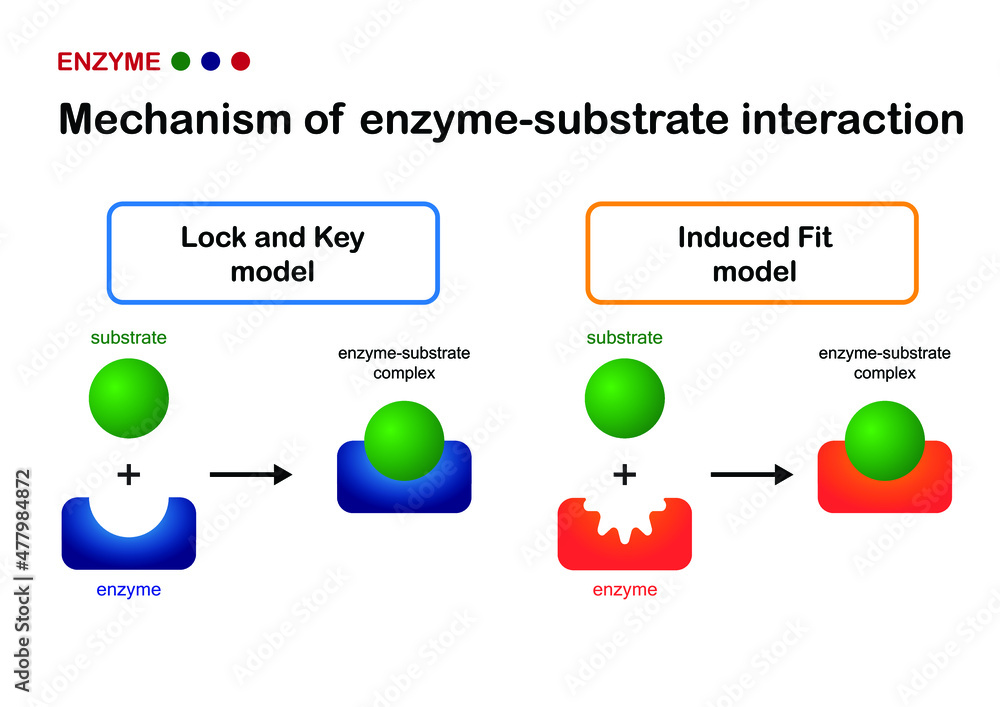
How does the induced fit model differ from the lock-and-key model?
In the lock-and-key model, the enzyme’s active site has a fixed shape. In the induced fit model, the active site changes shape slightly to fit the substrate better after binding starts.
Identify the N- and C-terminals in the following polypeptide sequence.
A-R-D-G-F-K
N-terminal (first amino acid)=A= Alanine
C-terminal (last amino acid)=K=Lysine
What is a holoprotein?
A holoprotein is a protein plus its cofactor, making it fully functional.
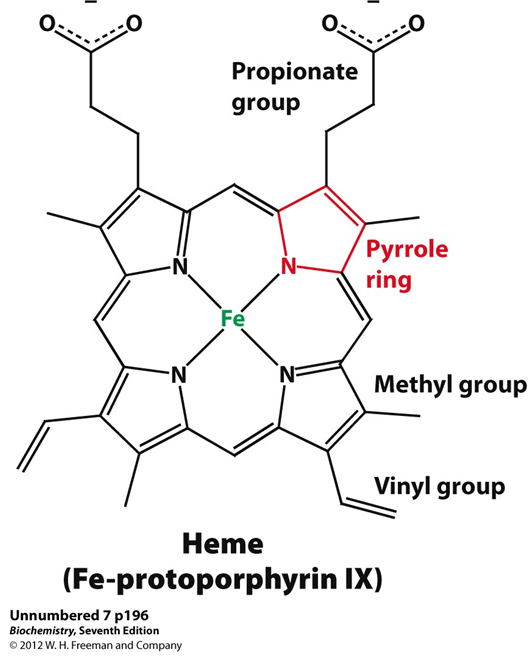
Example: Hemoglobin is a holoprotein because it contains the heme group, which helps it bind oxygen.

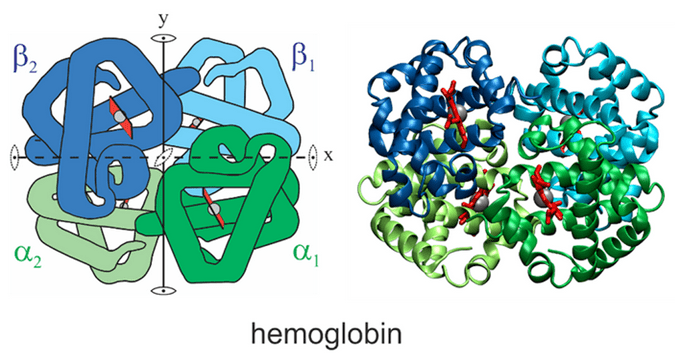
What is hemoglobin’s quaternary structure?
Hemoglobin is made of four subunits (2 alpha and 2 beta chains). This is called a quaternary structure, and it allows hemoglobin to carry up to four oxygen molecules.
What are metalloenzymes, and what do they have in common?
Metalloenzymes are enzymes that contain a metal ion (like Fe, Zn, Cu) at their active site. The metal helps in catalysis or stabilizing the structure. They all require metal ions to function properly.
You are given a mixture of three proteins:
Protein X: 150 kDa
Protein Y: 50 kDa
Protein Z: 25 kDa
If you run this mixture through a size-exclusion chromatography column, in what order will the proteins elute from the column?
Order of elution:
Protein X (150 kDa) — elutes first
Protein Y (50 kDa) — elutes second
Protein Z (25 kDa) — elutes last
When can a protein refold into its native conformation?
A protein can only refold into its correct (native) 3D structure if its amino acid sequence hasn’t changed. The sequence itself (called the primary structure) contains all the information needed for proper folding.
What is the given structure?
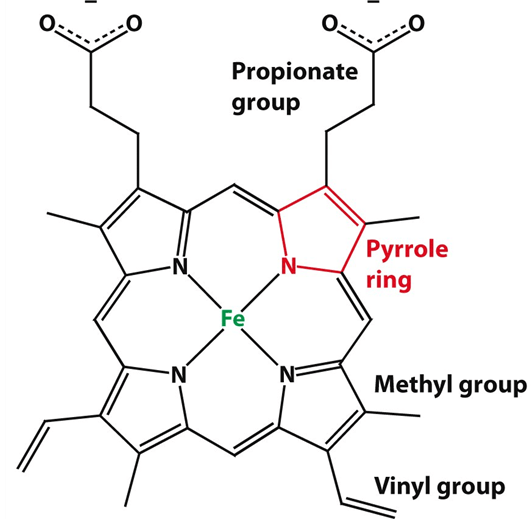
Heme is a ring-like structure in hemoglobin that contains iron (Fe²⁺). It’s the part that binds oxygen and gives blood its red color.
How do toxic nerve gases affect enzymes?
Nerve agents irreversibly inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This causes continuous nerve signals and muscle spasms.
Explain how ion-exchange chromatography works.
Ion exchange chromatography separates proteins based on their charge by using beads in the column that carry either a positive or negative charge. For example, in cation exchange chromatography, the beads are negatively charged, so they attract and bind positively charged proteins, while negatively charged proteins flow through. To release the bound proteins, a salt gradient (like increasing NaCl) is added, and the sodium ions compete to displace the proteins. For instance, if a mixture contains lysine (positively charged) and glutamate (negatively charged), glutamate would elute first, and lysine would elute later after increasing salt concentration.
How can proteins can become denatured?
Proteins can be denatured by heat and pH changes.
What is the Bohr effect?
When CO₂ increases and pH drops in tissues, hemoglobin releases more oxygen there. This helps oxygen go where it’s most needed.
What are some coenzymes that come from vitamins?
NAD⁺ (from Vitamin B3 - niacin)
FAD (from Vitamin B2 - riboflavin)
Coenzyme A (from Vitamin B5 - pantothenic acid)
What is the key instrument in protein sequencing?
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful technique used to determine the mass of molecules, especially proteins and peptides. In protein sequencing, it helps identify the amino acid sequence of a protein by measuring the mass of fragments.
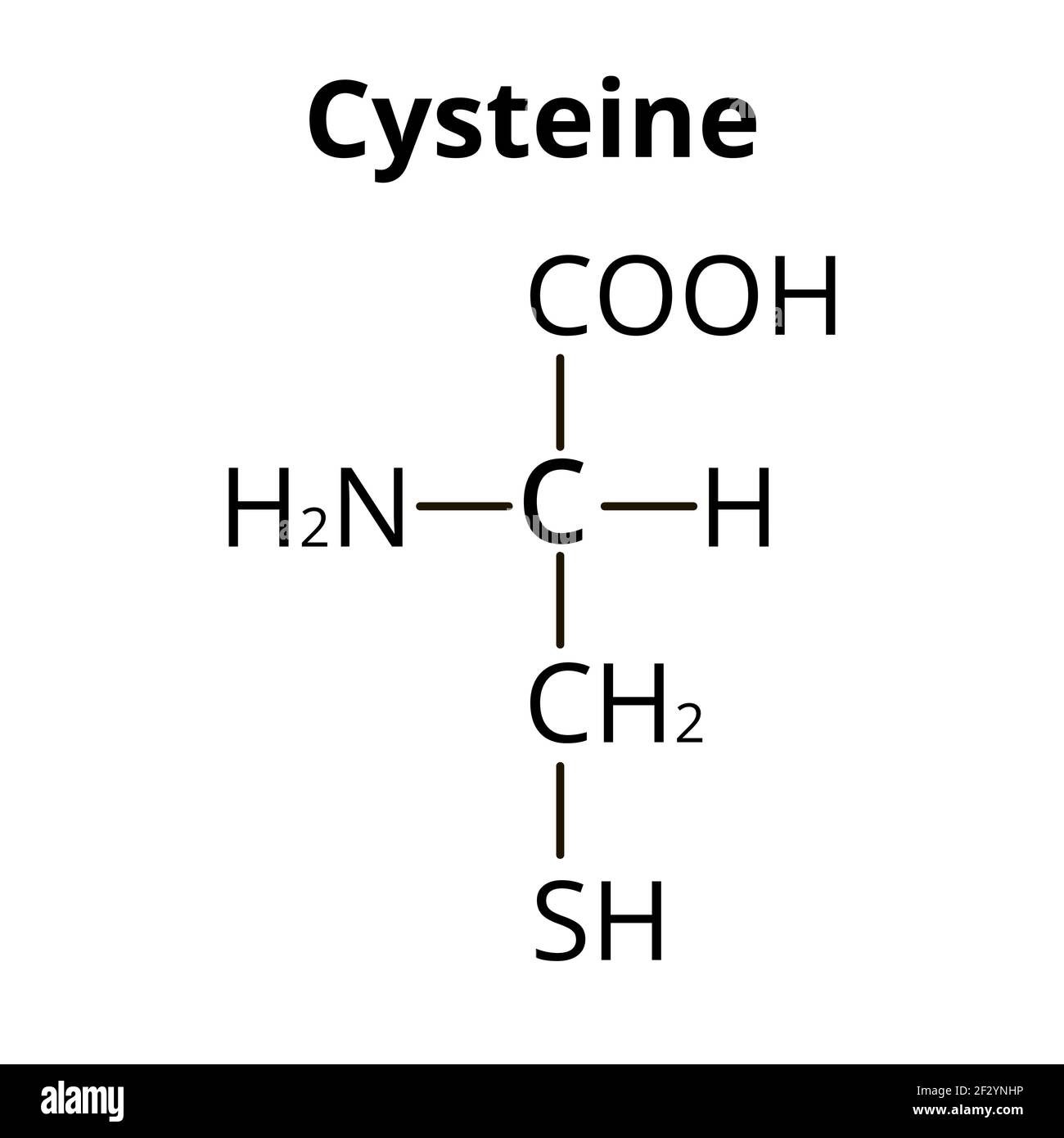
What role does cysteine play in protein structure?
Cysteine has a sulfur atom in its side chain. When two cysteine residues come close together in a protein, their sulfur atoms can form a disulfide bond (–S–S–). This disulfide bond links different parts of the protein chain, helping to stabilize the 3D structure of the protein and keep it folded correctly.
Which one of the four types of point mutations is considered synonymous and does not affect the protein structure?
Silent (Synonymous) mutation – changes a nucleotide but does not change the amino acid (protein stays the same).
What do ATP-dependent enzymes like kinases do?
They use energy from ATP to add a phosphate group (phosphorylation) to a substrate.
Given the following mRNA sequence, translate it into a protein sequence using single-letter amino acid abbreviations. Start from the first codon.
mRNA sequence:
AUG UUU CGA GGC UAA
What is the resulting protein sequence?
AUG = M (Methionine, start codon)
UUU = F (Phenylalanine)
CGA = R (Arginine)
GGC = G (Glycine)
UAA = Stop codon (translation stops here)
Protein sequence:
MFRG
Beta sheet structure.

What happens during the T-state to R-state change in hemoglobin?
When oxygen binds to one subunit, hemoglobin changes shape from a Tense (T) state (low oxygen affinity) to a Relaxed (R) state (high affinity), making it easier for more oxygen to bind.
Define the transition state.
The transition state is a high-energy, unstable state the molecules go through before forming products.
