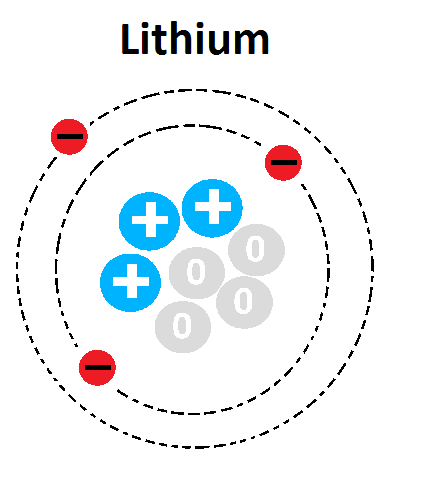
What three subatomic particles make up an atom?
Protons (+), Neutrons (0), Electrons (-)
What does it mean for a molecule to be considered "polar"?
A partial positive charge on one end of the molecule and a partial negative charge on the other end of the molecule.

Why do bonds form between atoms?
Allows unstable atoms to become stable
What are the four macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Most large biological molecules are __________, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called ___________.
Polymers, Monomers
Describe the structure of an atom - detailing where each subatomic particle is located.
Nucleus holds to protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus - creating an electron cloud.
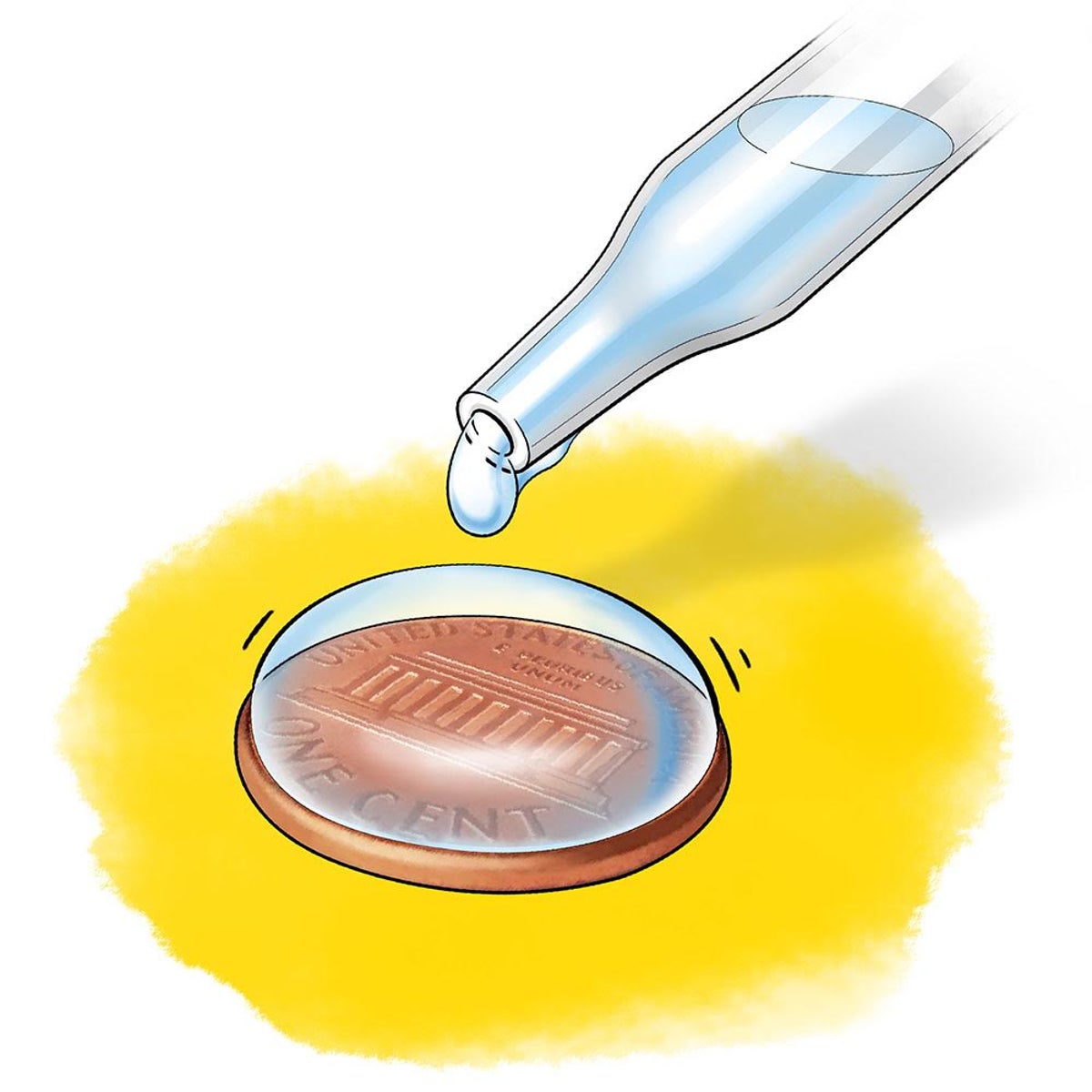 What property of water is being shown?
What property of water is being shown?
Cohesion
What are the three main types of bonds that form between atoms?
Ionic, Covalent, Hydrogen
Which molecule is considered to be organic?
a. H2O
b. O2
c. C6H12O6
d. N2
c. C6H12O6

Which indicator test is being shown?
Benedict's Reagent - tests for simple sugars, turning orange (+)
How many bonds can this carbon atom make? Why?
4 - Atom has four unpaired electrons in the outermost energy level.
Why is water considered to be a universal solvent?
Dissolves a variety of POLAR substances (or solutes) - "like dissolves like"
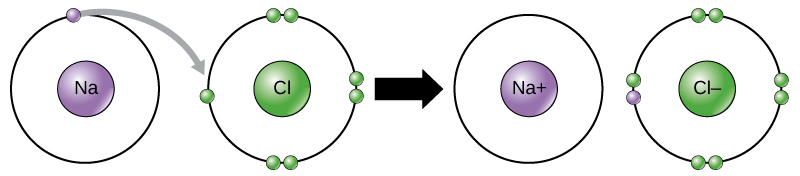
What type of bond has formed between this Na atom and Cl atom?
Ionic Bond
What are the monomers for the following polymers?
a. ____________ come together to form carbohydrates.
b. ____________ come together to form proteins.
c. ____________ come together to form nucleic acids.
a. monosaccharides
b. amino acids
c. nucleotides
What is the atomic number for the following element? Why?
3 - Three protons present in the nucleus of the atom.

Identify the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for the given element, based on the provided information.
Protons - 20
Electrons - 20
Neutrons - 20 (40-20)
One water molecule dissociates (or breaks down) into...

 Identify the bond:
Identify the bond:
a. Polar or Nonpolar
b. Covalent, Ionic, Hydrogen
Nonpolar (- charge on both sides)
Covalent (electrons being shared)

What process is shown?
Dehydration Synthesis
Which of these is rich in unsaturated fats?
a. a fat that is solid at room temperature
b. butter
c. bacon fat
d. vegetable oil
d. vegetable oil
Why is that all compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
Molecules can contain atoms from the same element or atoms from different elements.
Compounds must contain atoms from two or more different elements.
Compounds are molecules, not all molecules are compounds
When a small amount of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of Na2HPO4, the pH of the solution does not change markedly. The pH also does not change drastically when a small amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to the same solution. Based on these observations, the compound Na2HPO4 is acting as a what?
Buffer
What type of bond forms between the atoms of a single water molecule? Why?
What type of bond forms between two, adjacent water molecules? Why?

Indicators are used to determine whether or not a particular substance is present. Which indicators are used for the following:
a. Simple Sugars
b. Complex Carbohydrates
c. Proteins
d. Salt
e. Lipids
a. Benedict's Reagent
b. Lugols Iodine
c. Biruet
d. Silver Nitrate
e. Paper Test
How are each of the following bonds formed?
a. Ionic Bonds
b. Covalent Bonds
c. Hydrogen Bonds
a. transfer of electrons from one atom to another - atom that gains electron (-) whereas atom that lost electron (+)
b. electrons are shared between atoms
c. attraction between opposite charges - partial positive end of one water molecule is attracted to the partial negative end of another water molecule