Often confused with Timothy, it causes sores in the horse's mouth when chewed.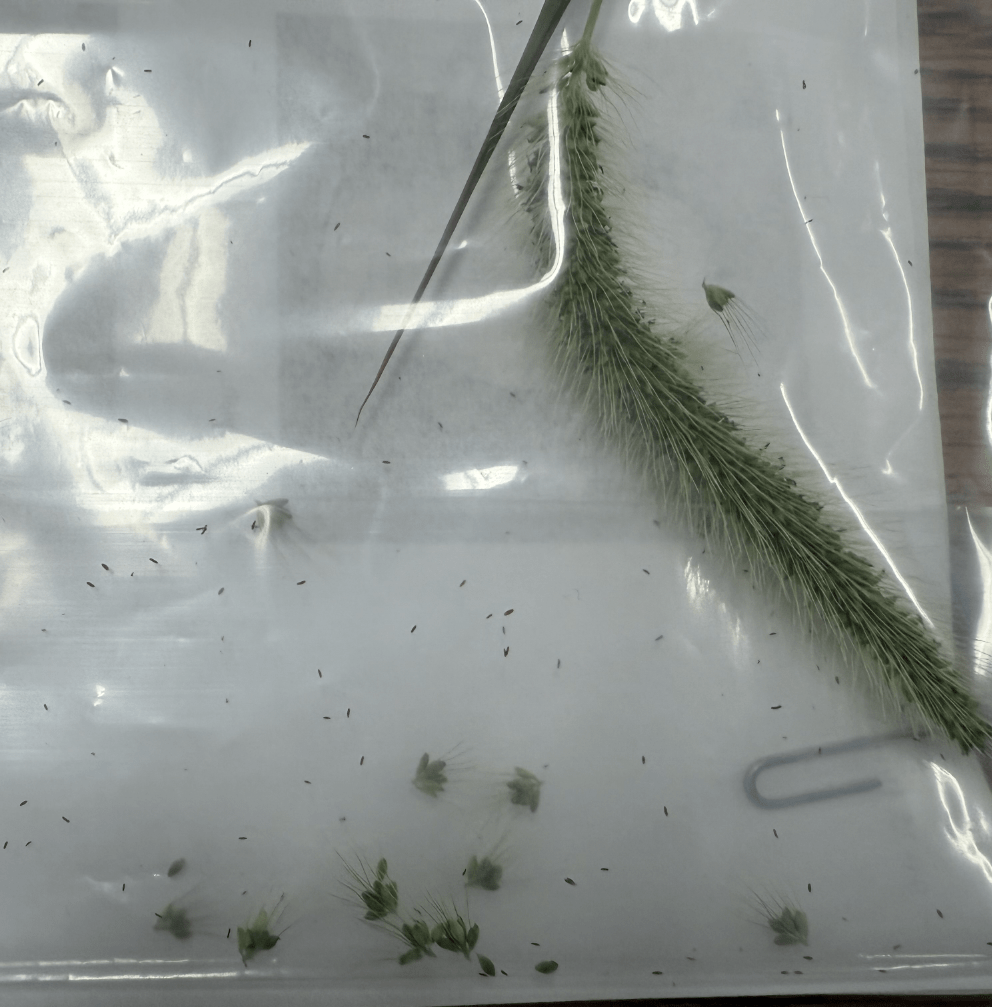
What is Fox Tail?
Should provide most if not all of the energy in a maintenance horse's diet
What is forage?
Overeating, working on a hard surface, and metabolic diseases
What are some causes of laminitis?
2.0 % of the horse's bodyweight
Amount of Dry Matter Intake (DM) that the average maintenance horse requires.
Portion of a plant that is digested in the hindgut of the horse.
What is Fiber or Structural Carbohydrates?
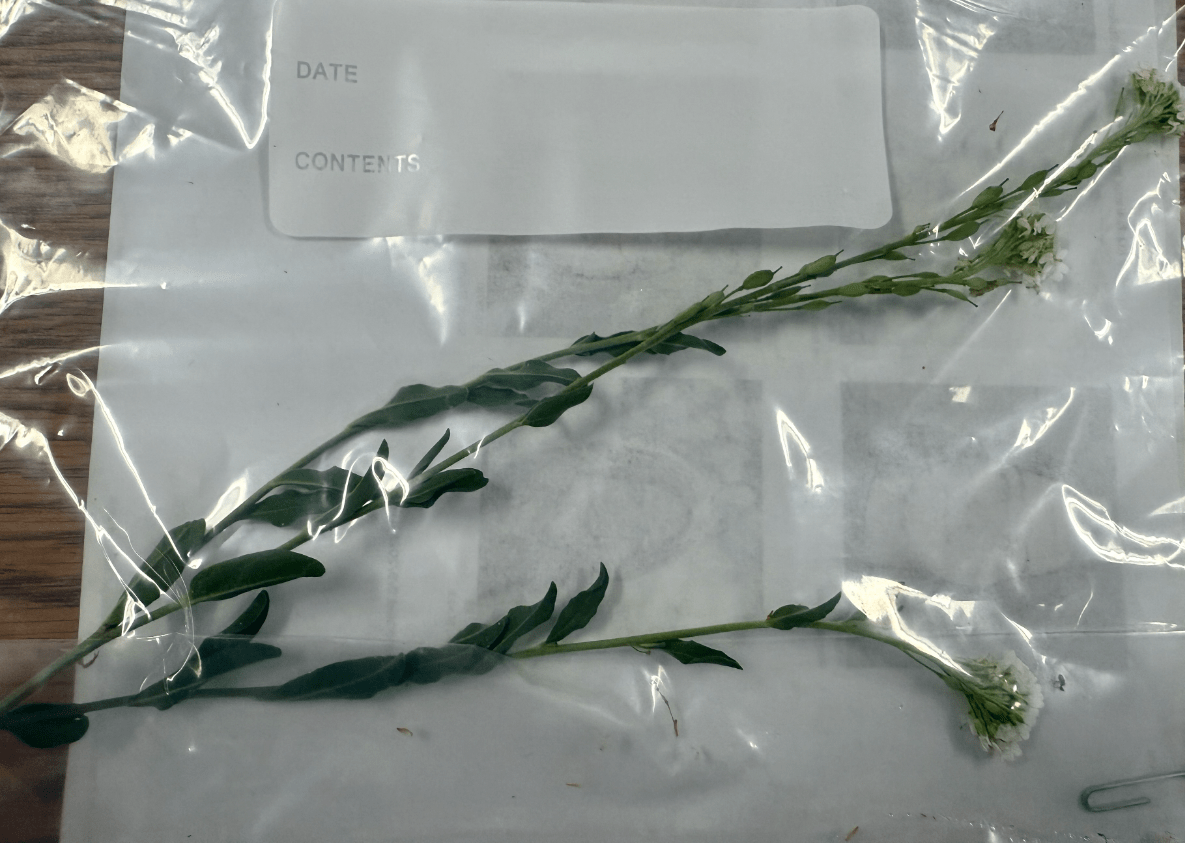 Palatable in the dried form. May cause depression and swelling in a horse's lower legs
Palatable in the dried form. May cause depression and swelling in a horse's lower legs
What is hoary alyssum
Low, Average, and High
What are the three metabolism types of the maintenance horse as described by the Nutrient Requirements Council for Horses?
Associated with pasture-induced laminitis
What are fructans
Measures the nutrients in feed and can include energy, crude protein, minerals, and fiber
What is a feed analysis conducted in a laboratory?
Sugars, starches, and fructans
What are Non-Structural Carbohydrates (NSC)
The wood shavings or exposed roots of this plant pose a significant concern.
What is Black walnut?
Must be added to the maintenance horse's diet when feeding a pasture diet in Michigan
What are salt and selenium?
Separates during laminitis
What are the sensitive and insensitive laminia? 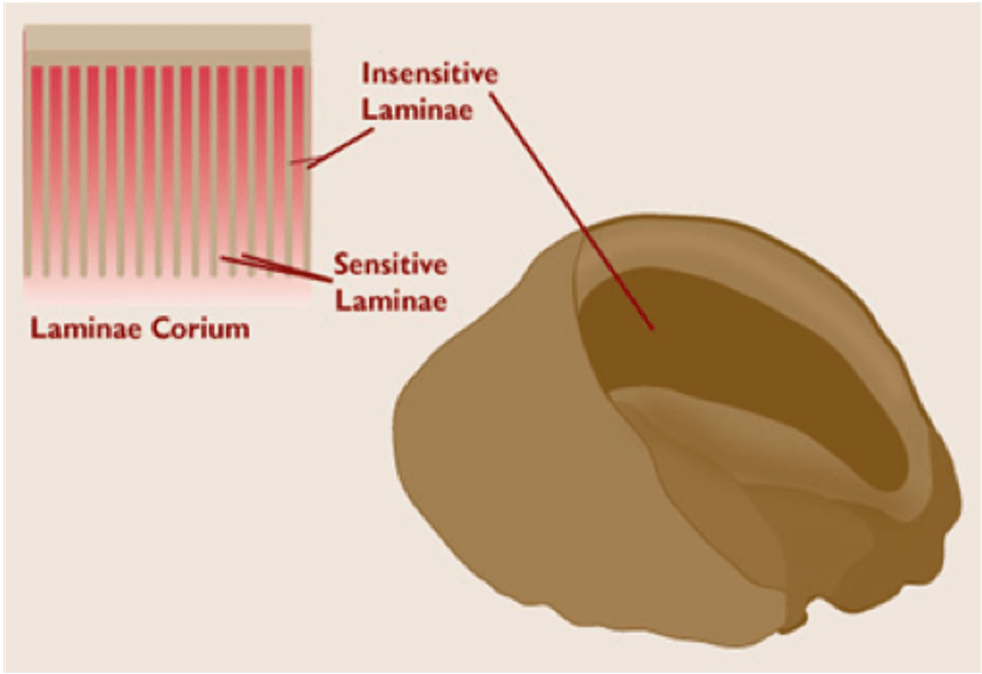
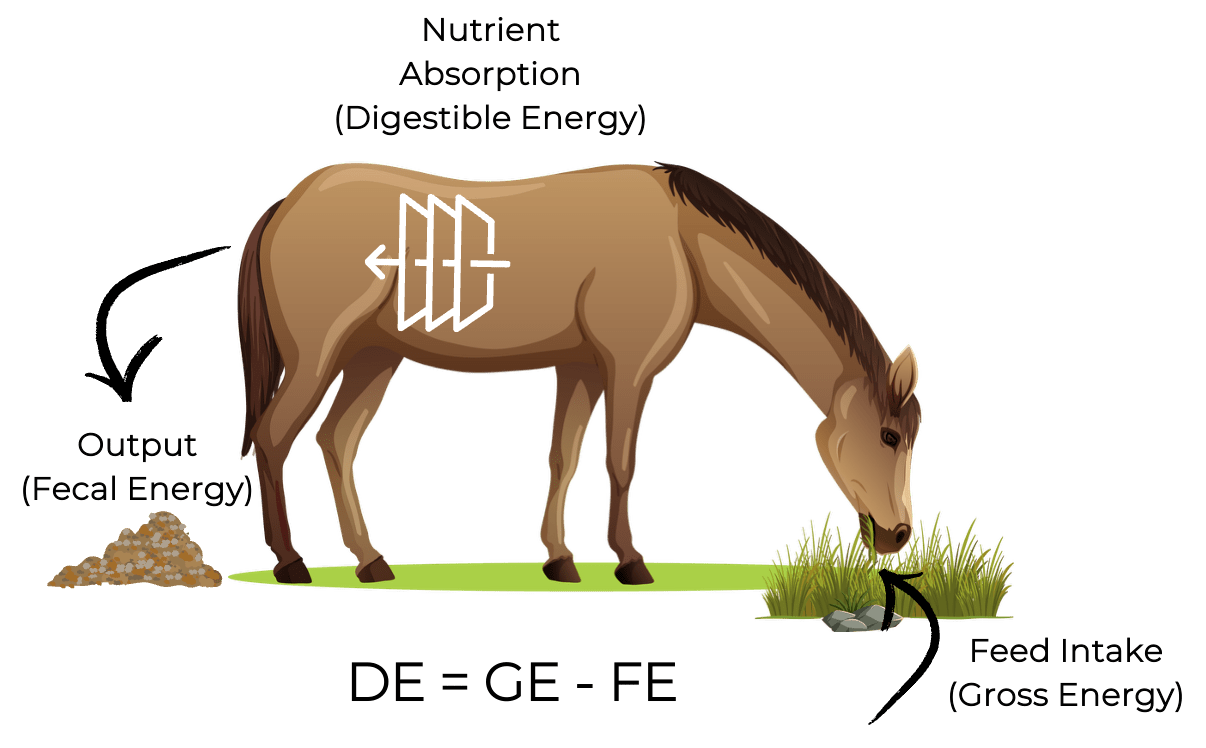
Estimates the amount of energy in feed that is available for maintenance, work, growth, and reproduction.
What is Digestible Energy?
Stored in the liver and muscles for energy during intense exercise
What is glycogen?
Wilted/dried leaves are toxic, and a horse's urine may become dark in color if ingested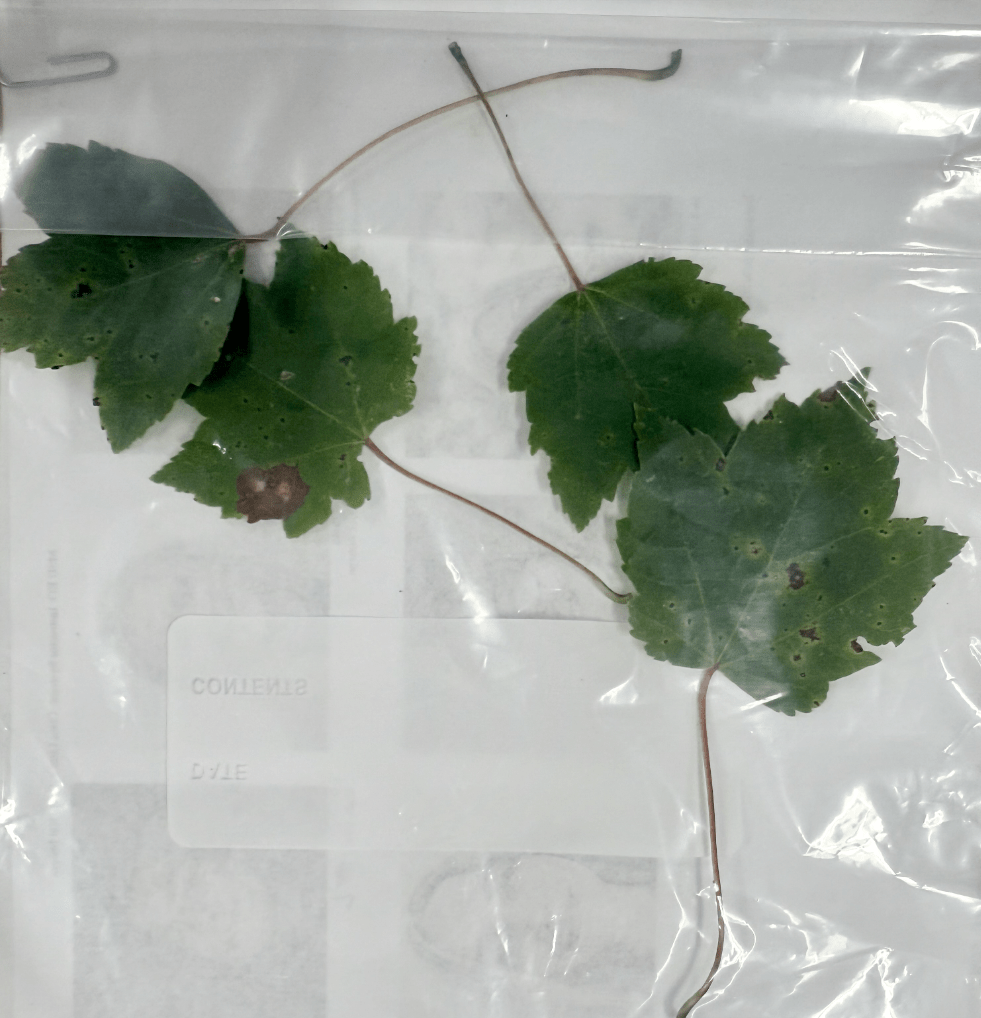
What is a Red Maple Tree?
NRC Horse Program is based on this book
What is the 2007 Nutrient Requirements of Horses?
Coffin Bone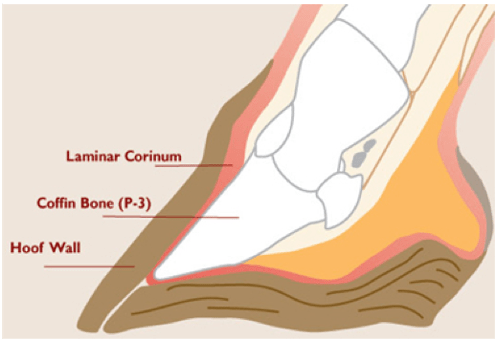
GE - FE
What is the calculation for Digestible Energy?
A form of energy that is absorbed in the hindgut as a byproduct of microbial fermentation.
What are volatile fatty acids (VFA)?
It takes as little as 6 ounces of consumption for this plant to cause death.
What is Japanese Yew?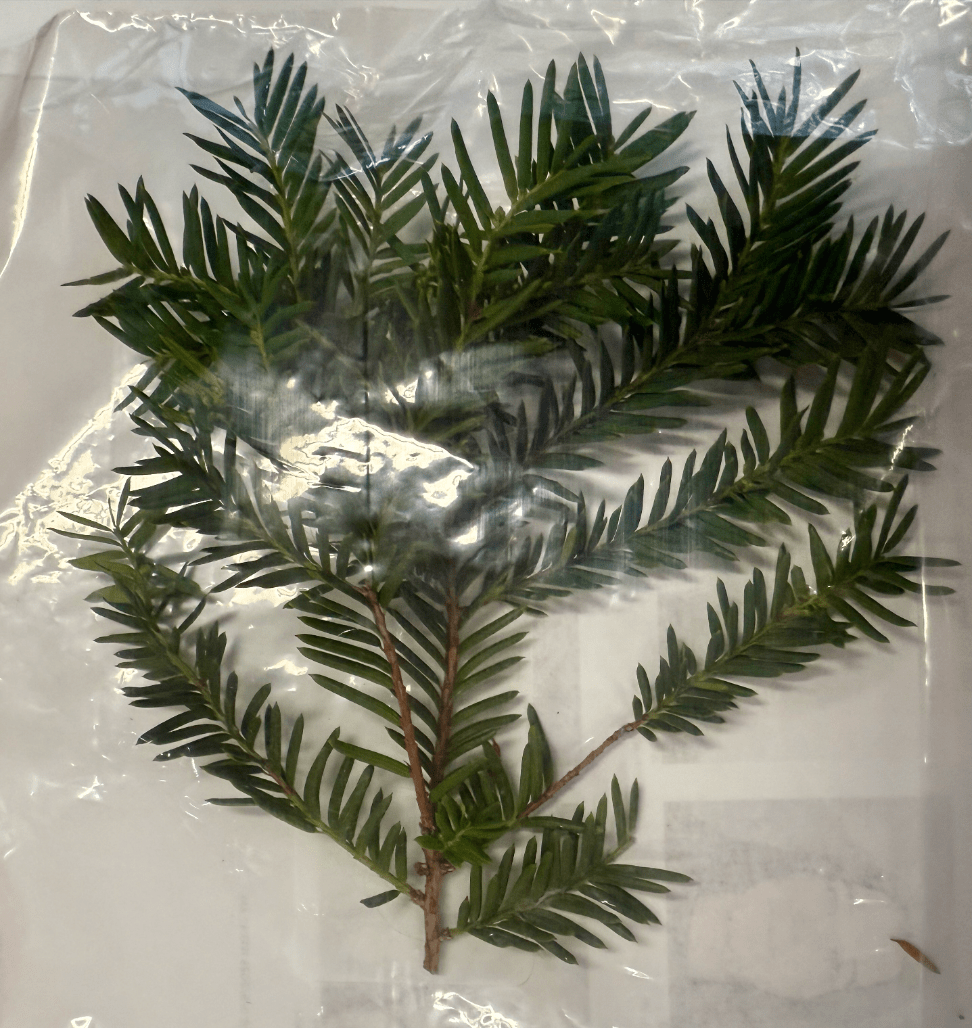 
What are muscle glycogen, adipose tissue (fat), liver glycogen, body protein (muscle tissue)
If there is no radiographic rotation of the coffin bone, the next 8 -12 weeks are considered the recovery stage.
What is the subacute phase of laminitis?
Unit refers to the amount of digestible energy in 1 kg of horse feed
What are Megacalories (MCals)?
Three structural carbohydrates found in plants
What are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin?