Trendy
The smallest building blocks of matter
Atoms
Who came up with the plum pudding model?
JJ Thomson
These are substances that have lost electrons
Cations
What is the current model of the atom?
The Quantum Model or the Electron Cloud Model discovered by Schrodinger and Heisenburg. Shows us s, p, d, f electrons 
These are forms of same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative atomic mass.
Isotopes
A student is analyzing an unknown sample of metal using the flame test. The student burns the unknown metal and finds it to be a bright cherry red when burned. What is the possible identity of this metal based on your own lab experience?
Possible answers: Lithium, Strontium
All of the elements in Group 1, except for hydrogen, are known as the _____________
Alkali Metals
Which of the following elements is a transition metal?
a. cesium (Cs)
b. copper (Cu)
c. silicon (Si)
d. aluminum (Al)
b. copper (Cu)
These are the three subatomic particles that make up the atom
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
Alpha decay: what is the mass and charge? What is being emitted?
mass is 4 amu. charge is 2+. A helium nucleus is being emitted
How many protons and electrons are in the phosphorous ion?
Protons = 15
Electrons = 18
What is the Heisenburg Uncertain Principle?
You cannot know both the location and velocity of an electron at the same time
Silicon-31 contains this many neutrons
17 neutrons
This is the electron configuration for Arsenic
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3
Elements in the same group on the periodic table can be expected to have similar
Physical and chemical properties
This highly reactive element is nonconductive but would be useful as an insulator. They only need one more electron to complete their octet. What group is this element likely in?
Halogens
Substances like aluminum, copper, zinc, and oxygen are often classified as
Element
This is why copper appears blue when burned and a diagram that depicts this phenomenon
Because as electrons fall back from an excited state to ground state, they emit light.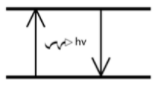
What is the most common ion for the following elements?:
a) K
b) Mg
c) Al
d) N
e) C
f) O
g) F
a) K+1
b) Mg+2
c) Al+3
d) N-3
e) C-4f) O-2
g) F-1
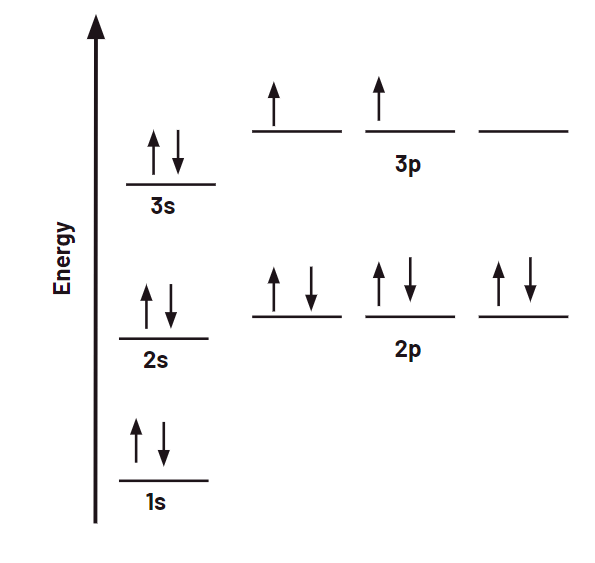
What is the electron configuration and orbital diagram for Silicon?
1s22s22p63s23p2
The element copper (Cu) has two naturally occurring isotopes, copper-63 (62.930 amu) and copper-65 (64.928 amu). The average atomic mass of copper listed on the periodic table is 63.55 amu. Of these two isotopes, this one is the most abundant for this reason
Copper-63 because the average atomic mass of the element is closer to its mass
This is the noble gas configuration of sulfur
[Ne]3s23p4
Which element has the largest atomic radius?
a. lithium (Li)
b.potassium (K)
c. beryllium (Be)
d. carbon (C)
b.potassium (K)
True or False: Francium is the most reactive element on the periodic table.
True
Substances such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and sodium chloride (NaCl) are classified as
Compounds
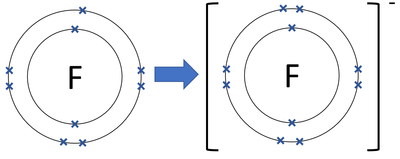
Draw the Bohr model for the fluorine ion
What is the electron configuration of the chloride ion?
1s22s22p63s23p6
What are the names of the 4 quantum numbers and what do they tell us?
n - principal quantum number - tells us the energy level of the electron
l - angular momentum quantum number - tells us the shape of the orbital the electron is in (s, p, d, f)
mL - magnetic quantum number - tells us the orientation in space of the orbital
ms - spin quantum number - tells us the spin of the electron
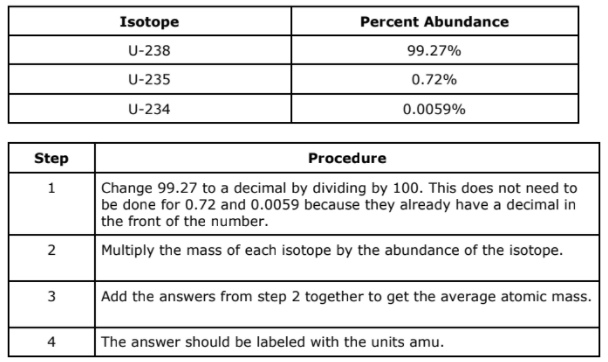 A mistake was made in this step of the process for solving for average atomic mass
A mistake was made in this step of the process for solving for average atomic mass
Step 1
What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy
wavelength and energy-- indirect frequency and wavelength-- direct
Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius?
a. nitrogen (N)
b. fluorine (F)
c. carbon (C)
d. oxygen (O)
b. fluorine (F)
How is the trend in ionization energy related to the trend in atomic radii? What impact does it have on ionization energy?
Ionization energy increases as you move closer to the noble gasses because you get closer to having a full octet of electrons. This also reduces the atomic radius because the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons is greater, drawing the valence electrons closer to the nucleus, making the atom appear smaller.
What is the proper name for the following groups on the periodic table:
a) Group 1
b) Group 2
c) Groups 3 - 12
d) Group 17
e) Group 18
a) Alkali Metals
b) Alkaline Earth Metals
c) Transition Metals
d) Halogens
e) Noble Gases
Who developed each of the following models and what is the limits and merits for the planetary model?
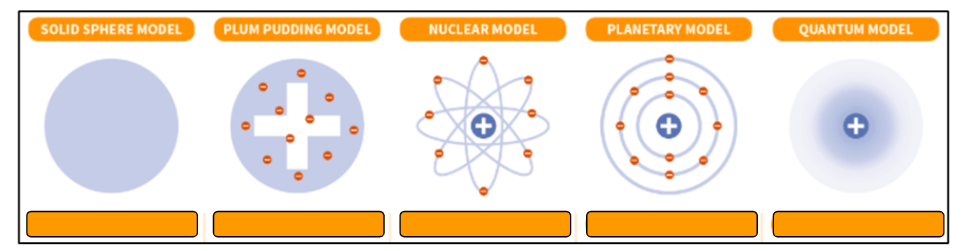
Solid Sphere - Dalton/Democrateous
Plum Pudding Model - J. J. Thompson
Nuclear Model - Rutherford
Planetary Model - Bohr
Quantum Model - Schrodinger/Heisenburg
The Bohr model finally shows us that electrons exist in orbitals (merit) but their placement isn't 100% correct (limit)
What is the electron configuration (using noble gas notation) of the oxygen ion?
[He]2s22p6
What are the four quantum numbers for the following selected electron?
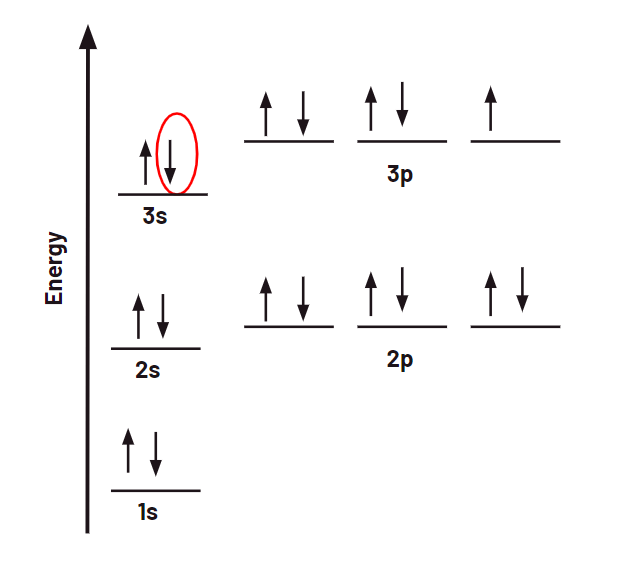
n = 3
l = 0
mL = 0
ms = -1/2
The average atomic mass for element X is 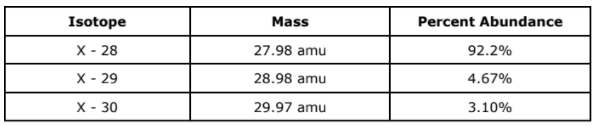
28.08 amu
Fluorine’s electron configuration is 1s22s22p5 and it is a very reactive nonmetal. Which of the following elements do you think will exhibit properties similar to fluorine?
a) 1s22s22p4
b) 1s22s22p6
c) 1s22s22p63s2
d) 1s22s22p63s23p5
d) 1s22s22p63s23p5
1s22s22p5 is Fluorine, which is in group 17
1s22s22p63s23p5 is chlorine, which is also in group 17, meaning they have similar properties
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
A. O B. Ne C. C D. Be
a. Oxygen
Why does electronegativity increase going across a period but not down a group?
As you move across a period, the elements are closer to having a full outer shell and the electrostatic attraction between the valence electrons and the nucleus is stronger, making it easier for them to pull in more electrons. However, as you go down a group, the elements are increasing in size and the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus, making it more difficult to pull in new electrons.