The following are a mix between disaccharides and polysaccharides, which is the only monosaccharide?
A. Glucose
B. Glycogen
C. Maltose
D. Cellulose
A. Glucose
A ____________ reaction joins two molecules together, while a ____________ reaction breaks them apart
A. Hydrophobic, Hydrophilic
B. Hydrolysis, Dehydration
C. Dehydration, Hydrolysis
D. Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic
C. Dehydration, Hydrolysis
Which macromolecule does not have true monomers?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Lipids
C. Proteins
D. Nucleic Acids
B. Lipids
This is the site in which ribosomes are assembled
A. Nucleus
B. Nucleolus
C. Nucleoid Region
D. Nuclear envelope
B. Nucleolus
Which of these structures is not surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer?
A. Mitochondria
B. Endoplasmic Reticulum
C. Golgi Apparatus
D. Ribosomes
D. Ribosomes
All polysaccharides and disaccharides are held together by this type of bond
A. Peptide
B. Ionic
C. Glycosidic
D. Hydrogen
C. Glycosidic
These make up most of the cell membrane
A. Phospholipids
B. Proteins
C. Triglycerides
D. Cholesterol
A. Phospholipids
Complete the other DNA sequence: 5' AGTGGCTA 3'
A. 3' UCACCGAU 5'
B. 5' UCACCGAU 3'
C. 3' TCACCGAT 5'
D. 5' TCACCGAT 3'
C. 3' TCACCGAT 5'
Select all the structures that make up the endomembrane system:
A. Nuclear envelope
B. Ribosomes
C. Golgi apparatus
D. Lysosomes
E. Peroxisomes
F. Chloroplasts
G. Plasma Membrane
A. Nuclear envelope
C. Golgi apparatus
D. Lysosomes
G. Plasma Membrane
The cell is undergoing cell division, it needs to lengthen so that it has room to grow & then quickly shorten once it is split into two cells. Which type of fiber would the cell use?
A. Intermediate Filaments
B. Microtubules
C. Microfilaments
D. Actin
B. Microtubules
Which of the following are examples of disaccharides? Select all that apply:
A. Lactose
B. Glycogen
C. Glucose
D. Sucrose
E. Fructose
F. Maltose
G. Cellulose
A. Lactose
D. Sucrose
F. Maltose
Transcription is ___________ & translation is _____________
A. RNA -> DNA & Protein -> RNA
B. DNA -> RNA & RNA -> Protein
C. Protein -> DNA & RNA -> Protein
D. RNA -> Protein & DNA -> RNA
B. DNA -> RNA & RNA -> Protein
Is this amino acid polar or nonpolar? Is it hydrophilic or hydrophobic? How can you tell?
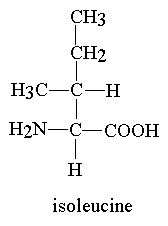
Nonpolar, hydrophobic, You look at the R group (at the top)
You decide to drown your sorrows after the test by drinking some alcohol. Which organelle in the cell will be responsible for breaking down the toxin?
A. Golgi Apparatus
B. Ribosome
C. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
D. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
D. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The following make up part of the cell membrane except for:
A. Proteins
B. Steroids
C. Nucleic Acids
D. Glycolipids
C. Nucleic Acids
A triglyceride contains what?
A. Hydrocarbon only
B. Four fused rings
C. Fatty acids, glycerol, polar group
D. A glycerol with three fatty acids
D. A glycerol with three fatty acids
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
Base
Phosphate
Sugar
What are the four components of an amino acid?
Amino Group, Central Hydrocarbon, Carboxyl Group, R Group
This type of protein in the membrane is located on the outside (hydrophilic region)
A. Integral protein
B. Peripheral protein
C. Transmembrane protein
D. Intermembrane protein
B. Peripheral protein
__________ is found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes & is used for mobility, but ___________ is only found in eukaryotes & is also used for mobility.
A. Flagella, Capsule
B. Flagella, Fimbriae
C. Fimbriae, Cilia
D. Flagella, Cilia
D. Flagella, Cilia
Name the three polysaccharides & briefly describe what they are used for & for who
Glycogen - animals, short term energy storage
Starch - plants, short term energy storage
Cellulose - plants, structural for the plant cell wall
What are all the functions of proteins?
Enzymes - speeds up chemical reactions
Defensive proteins - protection from disease
Storage proteins - store amino acids
Transport proteins - transport substances
Hormonal proteins - coordination of life activities
Receptor proteins - receive signals
Contractile & motor proteins - movement
Structural proteins - support; like keratin for hair; or collagen
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
What is the structure of that monomer?
What are the polymers of nucleic acids?
What are the 2 examples of polymers of nucleic acids?
What is their structure?
What is their function?
Monomer:
-Nucleotide
Structure:
-Base, phosphate, sugar
Polymer:
-Polynucleotides: DNA & RNA
Structure:
-DNA has deoxyribose, phosphate, base
-RNA has ribose, phosphate, base
Function:
-DNA stores genetic information
-RNA transmits genic information from DNA to ribosomes
Name the three animal & the one plant cell junctions
Animal:
Tight junction - membranes of cells next to each other are pressed together to prevent leakages
Gap junction - Provide a cytoplasmic channel between cells that are next to each other
Desmosomes - Fasten cells together into strong sheets
Plant:
Plasmodesmata - channels that perforate plant cells walls (think like the gap junction, but for plants)
Which organelles/structures are found in plant cells, but not animal cells
Central Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell wall
Glyoxysomes