Lines the blood vessels, flat, used to exchange O2 and CO2.
Squamous

Stratified Cuboidal cells are an example of what type of tissue?
Epithelial

Name two microscopic membranes.
Basement & Cell membrane

What macronutrient can pass through a cell membrane without any help?
Lipids

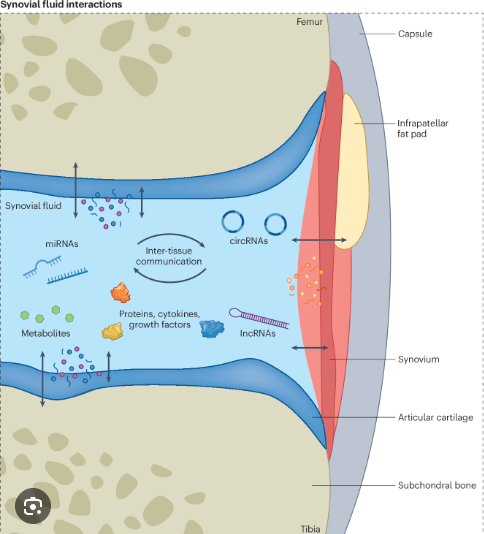
What is the purpose of synovial fluid?
To lubricate and protect.
More than one layer
Stratified.

What type of tissue are sensory in the skin?
Neurons

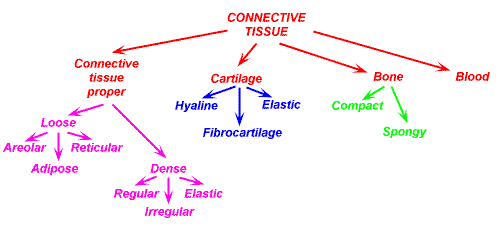
Name the types of connective tissue.
Dense, Loose, Cartilage, Bone, Blood
When an epithelial layer is glued to connective tissue by a microscopic membrane.
Membrane
Which membrane does NOT have epithelial tissue?
Synovial.

Located beneath the skin, around the kidneys and other organs, behind the eyeballs, stores energy, protects organs.
Fat or Adipose
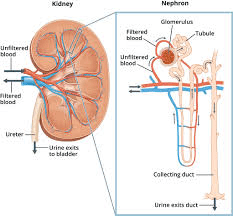
Cells that line the Kidney
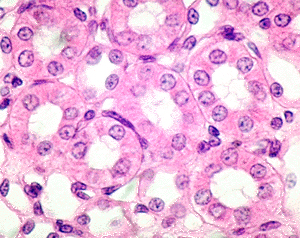
Cuboidal
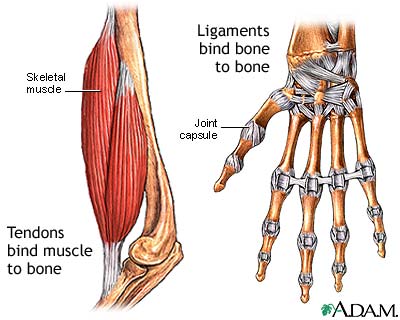
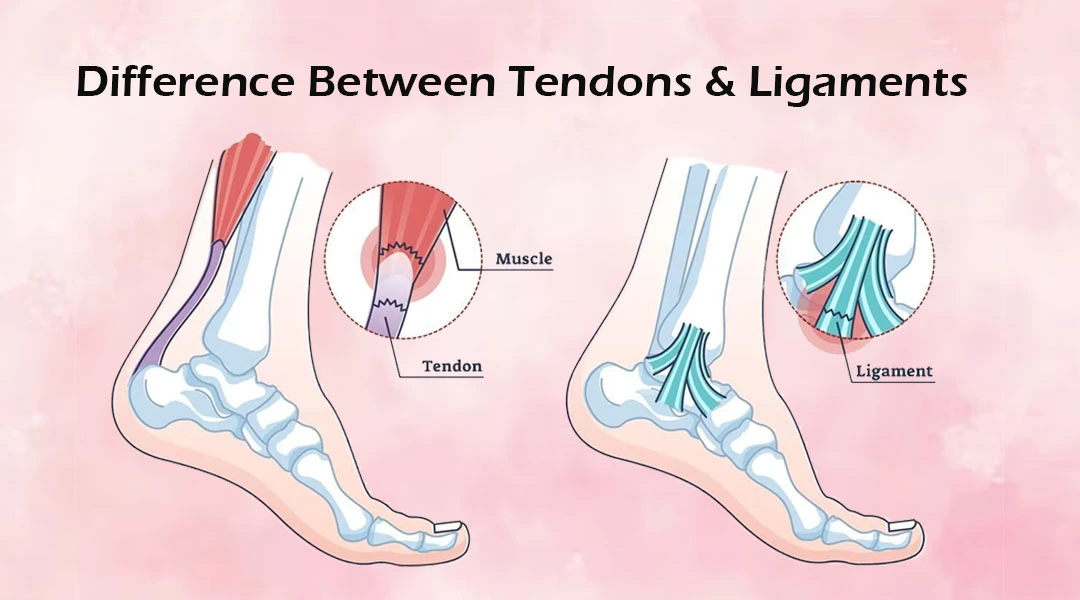
What is the difference between tendons and ligaments
Tendon - myo to bone, Ligament - bone to bone
What membrane would I find lining my digestive tract.
Mucous

What is a blister?
Separation of epithelial and connective tissue, (epidermis and dermis) at the basement membrane.

Two examples of dense connective tissue.
Ligaments and Tendons
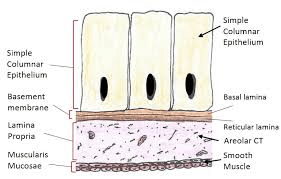
Which tissue lines the stomach? Please indicate if it is 1 layer or many layers.
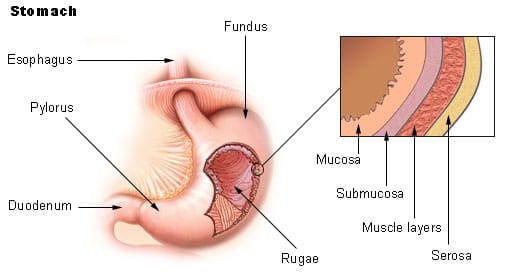
Simple Columnar

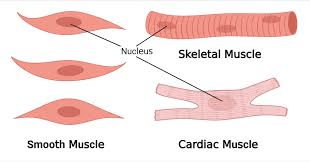
Name a muscle that is involuntary.
Smoothe or Cardiac.
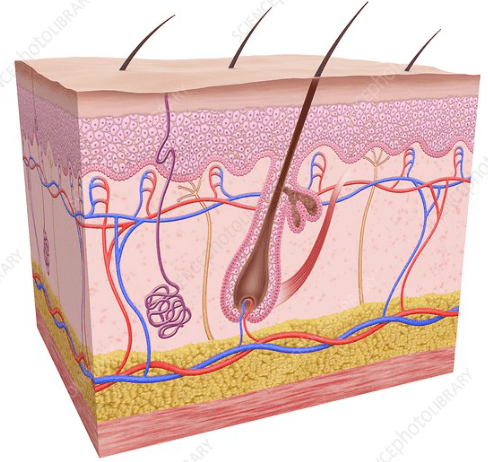
Name 5 tissues in this picture.
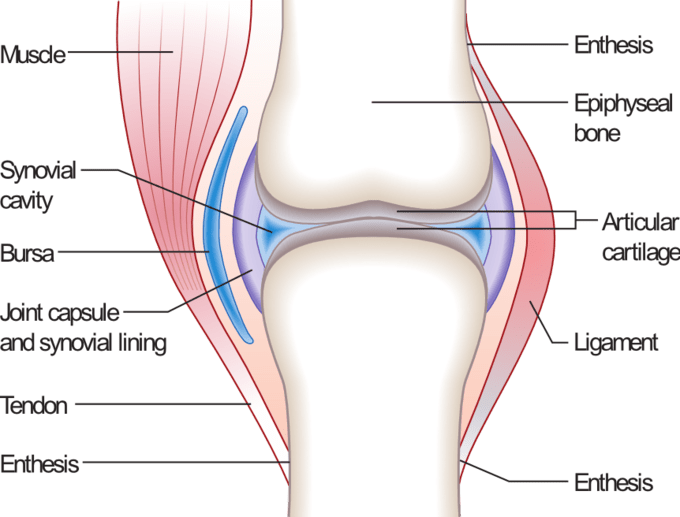
Bone, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage
What is pleurisy and how does it happen?
Lack of serious fluid in the pleural space causing inflammation. Premie babies that do not produce serous fluid will get it.

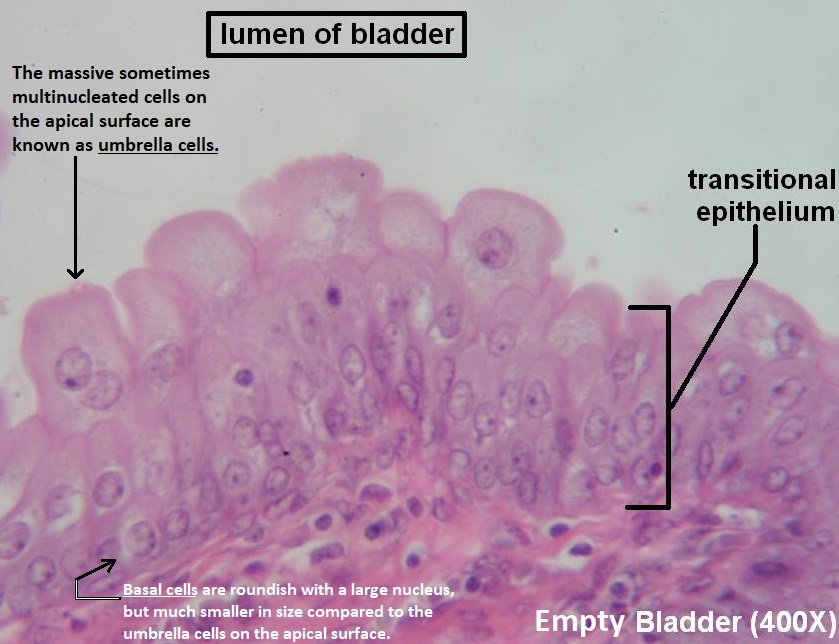
This tissue can change from squamous to cuboidal. Found in the bladder.
Transitional
Name a muscle that lacks striations
Smooth
Name a tissue that is avascular.
Epithelial

Name 6 locations of mucous membranes
Eyes, ears, mouth, nose, vagina, anus, urethra

Explain how you get an ulcer.
H.Pylori makes an alkaline home and digs into your simple columnar wall.
