Genetics is the study of this...which is the process in which traits are passed from parents to offspring.
What is heredity?
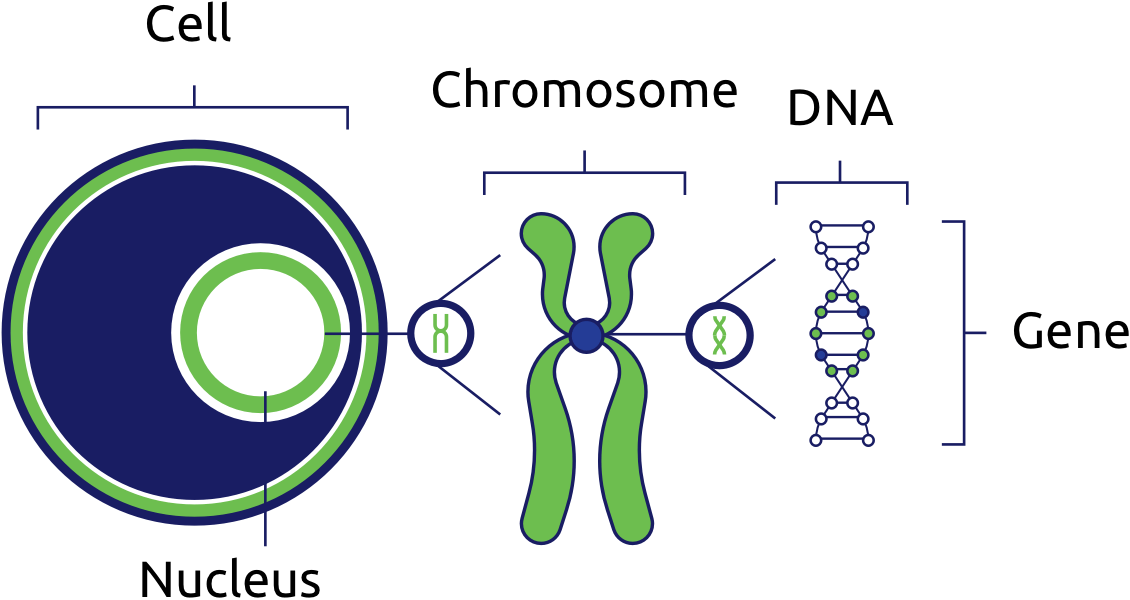
The part of the cell that holds the DNA.
What is the nucleus?
The length of time a mutated change stays on someone's DNA.
What is permanent?
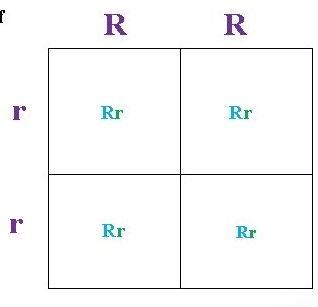
The possible GENOTYPE for the offspring of the parents on this Punnett Square?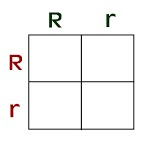
RR, Rr, rr
(25% Homozygous dominant, 50% homozygous recessive, 25% heterozygous)
Known as the "Father of Genetics" who studied pea plants and their traits.
Who was Gregor Mendel?
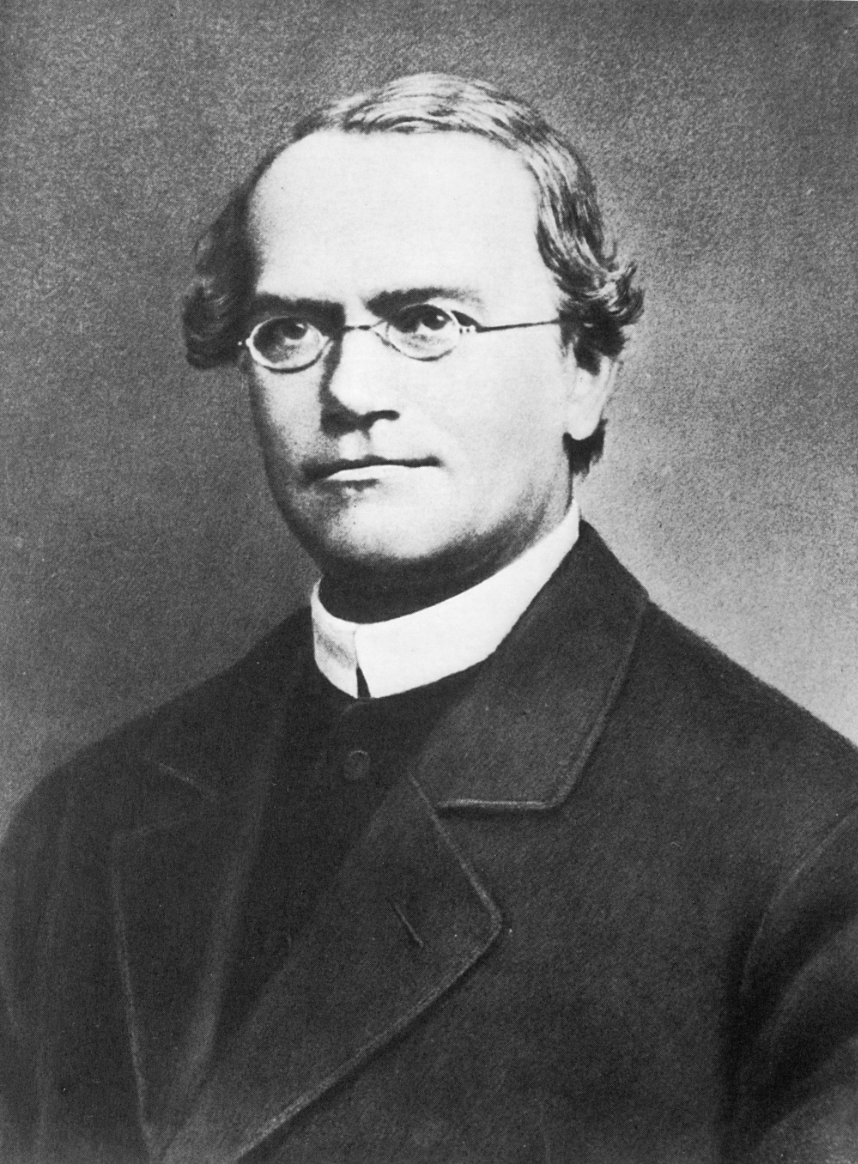
Characteristics that can be passed from a parent to its offspring.
What is a trait?
The shape of DNA.
What is the Double Helix?
The difference between natural and environmental causes of mutations.
Natural is inherited and passed from parents to offspring.
Environmental are caused by exposure to radiation or chemicals.
The possible PHENOTYPES for the offspring of the fox parents with red fur dominant and white fur recessive on this Punnett Square?
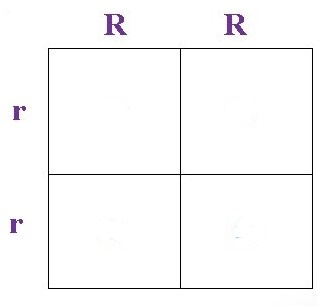
100% Red heterozygous
The scientist who discovered the shape of DNA but did not receive any credit for her discovery.
Who is Rosalind Franklin?

The genetic makeup of an organism, the letters on the Punnett Square.
What is the genotype?
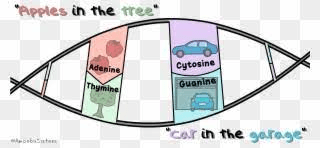
A saying from the Ameoba sisters to help you remember how the nitrogen bases are paired up.
What is "Apples in the Trees... Car in the Garage"?
Type of mutation (explain):
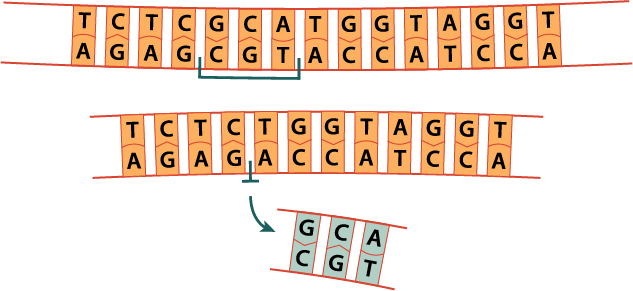
What is deletion because a section has been removed?
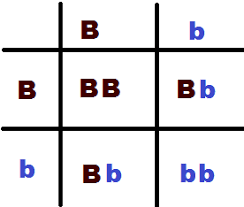
The possible GENOTYPES of the offspring for the parents on this Punnett Square.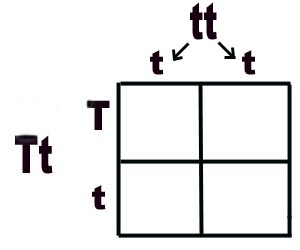
Tt, tt
(50% Heterozygous, 50% Homozygous Recessive)
The reward James Watson and Francis Crick received for their work on discovering the shape of DNA.
What is a Nobel Peace Prize?
Another term for heterozygous.
What is a hybrid?
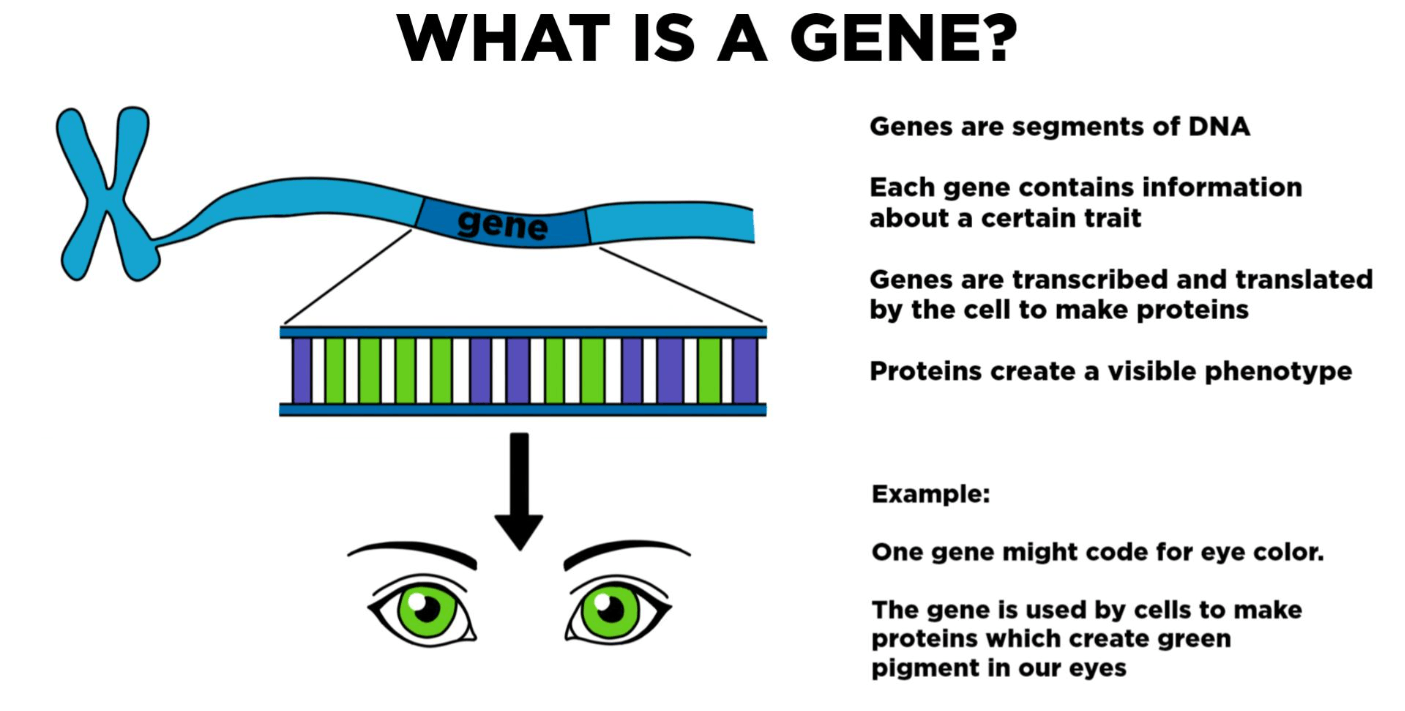
A specific section of DNA that codes for a trait.
What is a gene?
Type of mutation (and describe it):
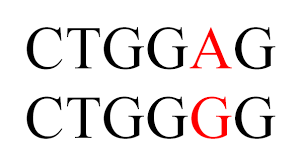
What is substitution because a section is exchanged with another?
The possible PHENOTYPES of the offspring for the tall (T) and short (t) pea plant parents on the Punnett Square.
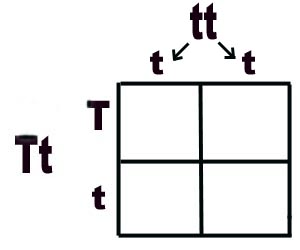
Tall and short
50% Tall and 50% short
Who is the scientist who created the square which shows the probability of parents passing on traits to their offspring?
Who is Reginald Punnett?
The only way for a physical trait to show up on an organism.
What is a dominant trait?
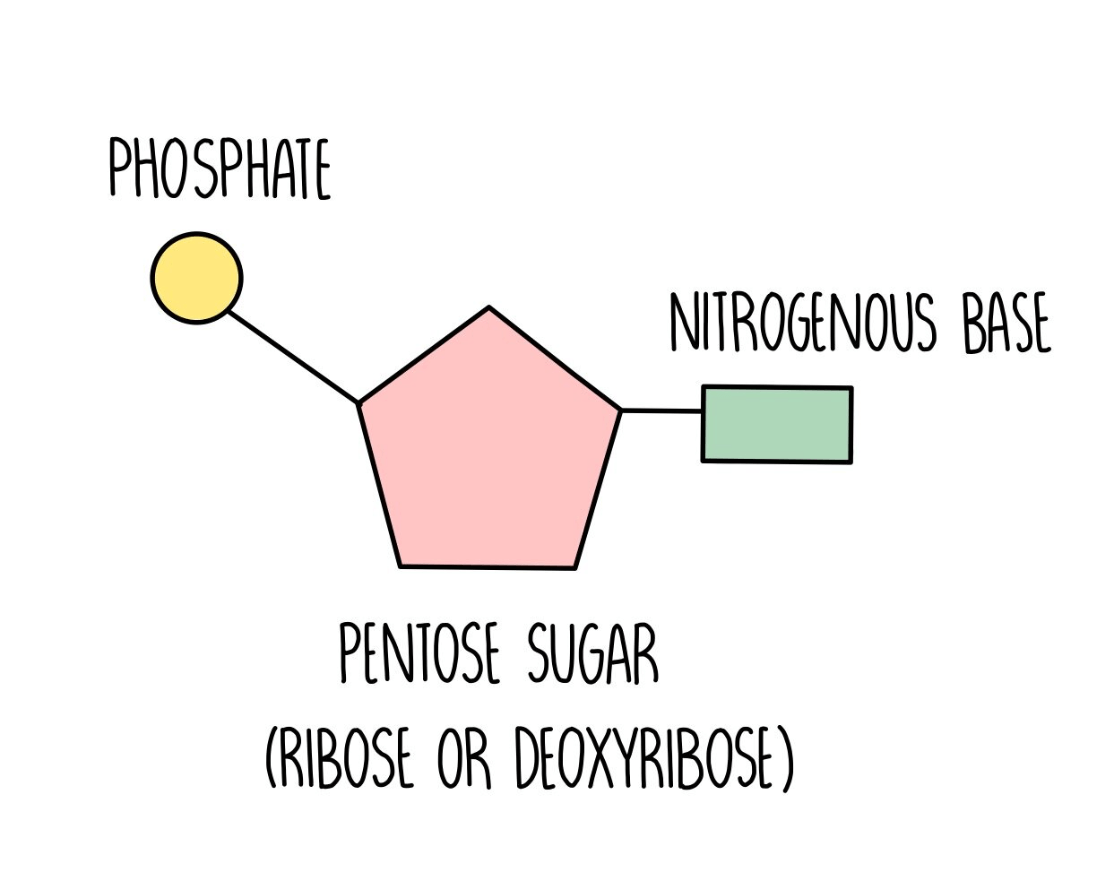
The three parts of the Nucleotide Structure (written on your notes on page 23, colored on the Color Code worksheet, and built on the Edible DNA Strand).
Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base
Heterochromia is a discoloration of the eye, skin, or hair. What effect of mutation is this an example of?
What is neutral/ no effect?
The genotypes of the parents when their offspring has a probability of 100% heterozygous.
One parent is homozygous dominant and one parent is homozygous recessive.
The scientist who took Rosalind Franklin's work to James Watson and Francis Crick.
Who is Maurice Wilkinson?