What is the relationship between pressure temperature?
Directly proportional
Draw the Lewis dot structure for the carboxylic acid functional group -COOH.
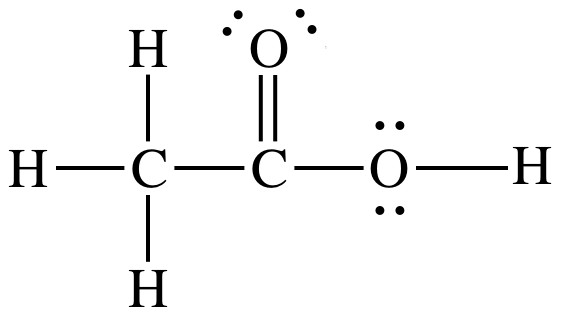
List all intermolecular forces exhibited by molecules of this substance:

London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces
What are the two types of electron groups or domains (regions of electron density) that determine molecular geometry?
Bonds and lone pairs.
What is the electron configuration of Ti+2?
1s22s22p63s23p64s2
If the temperature of a gas sample is tripled while pressure is held constant, what happens to the volume?
The volume triples.
What are the two key criteria for valid Lewis dot structures?
1. Correct number of valence electrons.
2. All atoms have complete octets.
What are two atomic properties to consider when comparing magnitudes of lattice energy? (Think Coulomb's Law).
Charge of the ion and size of the ion.
(distance or radius also acceptable for "size")
This is one resonance form of the nitrate ion. What is the molecular geometry?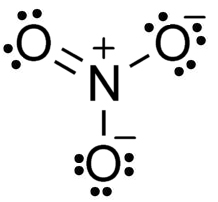
Trigonal planar.
Identify the hybridization of carbon 4.
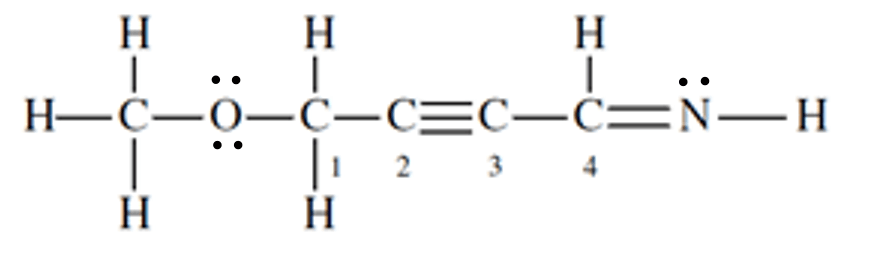
sp2
What is the final gas pressure exerted by a sample of gas if the absolute (Kelvin) temperature of a gas is doubled and the volume is tripled?
a. 1/6 the original pressure
b. 2/3 the original pressure
c. 3/2 the original pressure
d. 6 times the original pressure
b. 2/3 the original pressure
(P and T directly proportional, P and V inversely proportional)
What's the formula for calculating formal charge?
F.C. = (# valence e-) - (# lone pair e-) - (# bonds)
Why does NaBr melt at a temperature of 800℃, while solid NaI melts at a temperature of 750℃?
The Br- anion is larger than the I- so there is a greater distance between the ions in NaI requiring less energy to break the bonds when melting.
What is the molecular geometry of phosphorus trichloride?
Label the peaks in the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution from left to right for the following gases: O2, NH3, or HBr. (# particles on y-axis, speed on x-axis)
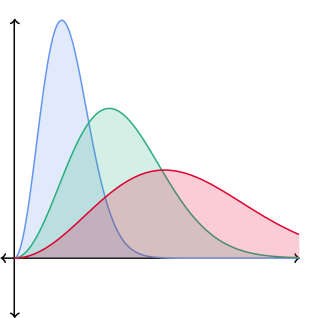
HBr, O2, NH3
What are the 4 principles of Kinetic Molecular Theory? (Think ideal gas behavior)
- Gas particles have negligible volume.
- Gas particles are in constant, random motion.
- The average kinetic energy is directly proportional to the temperature.
- All collisions between gas molecules and walls are perfectly elastic (Energy is conserved in collisions).
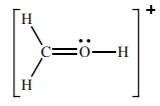 Write the formal charge for all atoms in this molecule
Write the formal charge for all atoms in this molecule
H = 0
C = 0
O = +1
Explain why at 25℃ and 1 atm, F2 is a gas, whereas I2 is a solid.
I2 is larger and more polarizable resulting in stronger London dispersion forces holding the molecules closely in a solid structure.
What is the molecular geometry of XeF4?
Square planar.
The freezing point of helium is -270℃. The freezing point of Xenon is -112℃. Which of the following statements is supported by these data?
a. Helium and Xenon form highly polar molecules.
b. As the molecular weight of the noble gas increases, the freezing point decreases.
c. The London dispersion forces between the helium molecules are greater than the London dispersion forces between the xenon molecules.
d. The London dispersion forces between the helium molecules are less than the London dispersion forces between the xenon molecules.
A mixture of helium and neon gases is collected over water at 28.0oC and 745 mm Hg. If the partial pressure of Helium is 368 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of Neon? (Vapor pressure of water at 28oC = 28.3 mm Hg).
Ptotal = PHe + PNe +PH2O
PNe = Ptotal - PHe - PH2O
PNe = 745 - 368 -28.3
PNe = 348.7 mmHg
Draw all valid resonance structures for the NO3- ion
AND
Identify the hybridization of the nitrogen atom.
sp2
Which type of IMF is mostly responsible for the difference in boiling points of ethanol and propanol shown below?
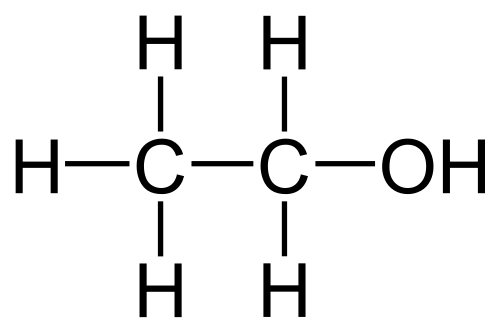
Ethanol (b.p. 78oC)
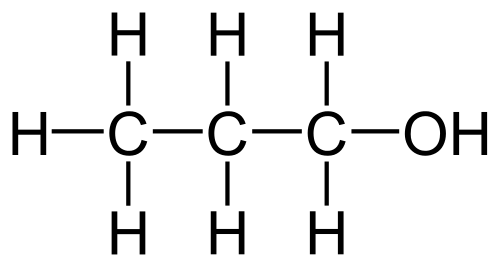 Propanol (b.p. 97oC)
Propanol (b.p. 97oC)
London dispersion forces.
(Both exhibit equal amounts of hydrogen bonds and dipole forces. However, propanol is slightly larger and thus more polarizable so it will form additional LDFs, raising the boiling point)
Explain why BCl3 has trigonal planar molecular geometry but NCl3 has trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry.
There is a lone pair of electrons on the N atom which repels the bonding electrons away into a trigonal pyramidal formation, but the B atom has no lone pair electrons so the three Cl atoms are arrange in a trigonal planar formation.
Order the reactions below from greatest increase in pressure to least increase in pressure, using the >, <, and/or = signs.
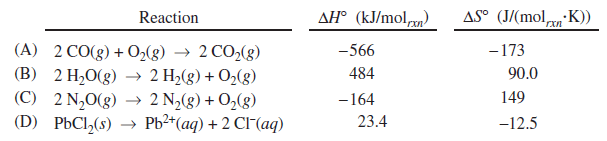
D>C=B>A