properties
molecules
molecules
What is the charge of the following subatomic particles
electron
proton
neutron
-
+
0
describe cohesion
attraction between molecules of the same substance
What pH range should something acidic be in?
0-6
example of lipids
enzymes are what type of macromolecule?
protein
what is an isotope?
same element but different # of neutrons
what is adhesion
attraction between molecules of different substances
What pH range should something that is basic be in?
8-14
What are the 4 types of macromolecules
carbohydrate, lipid, nucleic acid, protein
1. What is the monomer of nucleic acids
2. examples of nucleic acids
1. Nucleotide
2. DNA, RNA
what are examples of radioactive isotopes?
detect cancer
kill bacteria that spoil food
determine ages of rocks
What is the property of water that is happening in the tube called?
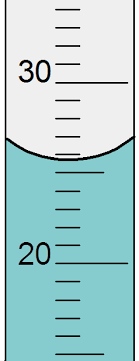
meniscus
What would you call a solution with more H+ ions than OH- ions.
acidic
monomer of proteins
amino acids
what is the function of lipids?
store energy for long term use
waterproofs membranes and body coverings
What is a chemical compound? give examples
substance formed by 2 or more elements
NaCl
H2O
describe what heat capacity is
the amount of energy needed to raise a substances temperature by making its molecules move faster
Label the parts of this equation
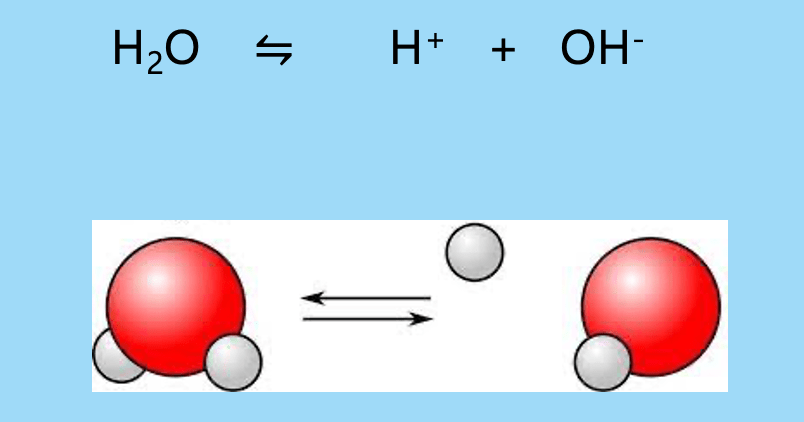
Water H2O
H+ Hydrogen
OH- Hydroxide
explain polymerization
process where monomers (smaller units) come together to form polymers (bigger units)
define the following words in terms of sugar
1. Monosaccharide
2. Disaccharide
3. polysaccharide
1. 1 simple singular sugar (glucose)
2. 2 simple single sugar join together (glucose + fructose)
3. multiple simple sugars joined together
explain differences between covalent and ionic bonds
ionic formed when one or more electrons are TRANSFERRED from one atom to another
What is polarity? Why is water considered to be polar?
polarity- uneven partial positive/ negative charges
the oxygen on a water molecule has a partial negative charge, while the 2 hydrogens have a partial positive charge, allowing for more attraction to other polar molecules
What is a buffer and what role does it play in our lives?
weak acids/ bases that help to combat other strong acids/bases, maintain homeostasis
explain what enzymes do
speed up chemical reactions
what type of bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide
covalent bonds