a molecule that has a positive end and a negative end; aka unequal chargers
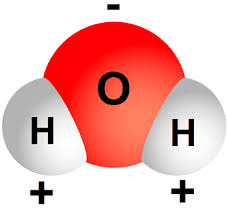
polar
water has a pH of 7, so it is considered
neutral
large biomolecules (proteins, lipids, Carbs, & nucleic acids) are also called
macromolecules
This macromolecule is passed from generation to generation and codes for genes
nucleic acids
Enzymes are this type of macromolecule
protein
Property of water where water hydrogen bonds/is attracted to other water molecules
Bonus 100 is you give me an example of cohesion
cohesion
This substance has a pH below 7 and a high concentration of H+ ions
acid
the building blocks/subunits of macromolecules
monomers
This macromolecule can be saturated ir unsaturated
lipids
An enzyme is considered a catalyst because it
speeds up chemical reactions and/or lowers the activation energy
Property of water by which water sticks to other substances
adhesion
This substance has a pH above 7 and releases OH- ions
Base
repeating chains of monomers form
polymers
This macromolecule is a quick energy source used in the body
carbohydrate
Draw an enzyme substrate complex on the board
(label the active site, enzyme, and substrate)
teacher checked
Waters ability to move up a thin tube
capillary action
Explain why water and oil do not mix
water is polar and oil is nonpolar
Name the monomers of proteins and carbohydrates
proteins: amino acids
Carbs: monosaccharides
This macromolecule is joined together by peptide bonds and contains the elements CHON
proteins
What is the optimal pH of Gastric Protease
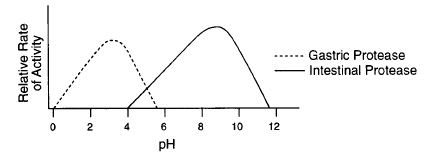
3
Identify what time of bond is represented by 6 and 7 (no I did not label it this way on purpose, chill)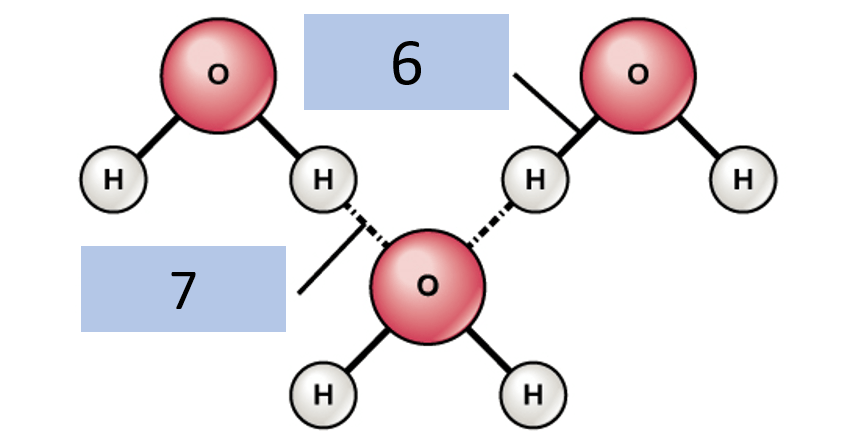
6. Covalent Bond
7. Hydrogen Bond
Due to it's polarity water is great at dissolving solutes. It is said to be the universal
solvent
Name the monomers of nucleic acids and lipids
NA: nucleotides
Lipids: glycerol and 3 fatty acids
the ratio of this macromolecule (C:H:O) is 1:2:1
carbohydrates
An enzymes shape determines its function. When it loses its shape it is said to be
denatured
Why does ice float?
Please mention something about bonds
When water freezes hydrogen bonds space out and expand causing ice to become less dense then water
Stomach acid has a pH of 1. How many times more acidic is it than tomato juice, which has a pH of 4
1000
examples of this macromolecule include myosin, keratin, hormones, and antibodies
proteins
ATP is an energy source in living organisms. It is considered a special
nucleotide
Explain and draw what competitive inhibition is on the white board
teacher checked