In ionic bonds, valence electrons are _____.
Transferred
They are good conductors of electricity.
What are ionic compounds?
This model represents this type of bond.
What is a Covalent Bond (shared electron)
Bonus if you said a sigma bond.
This is the reason NaF has a lower lattice energy than MgF2.
The charge of the Mg cation is larger than the charge of the Na cation.
This is the reason an ionic solid will not conduct electricity in solid state.
What is there are no free electrons due to being held in place in a lattice structure.
The tendency of an atom or molecule to attract electrons and form bonds.
What is electronegativity?
Molecular compounds are normally _____ or _____ (states of matter) at room temperature.
liquid or gas
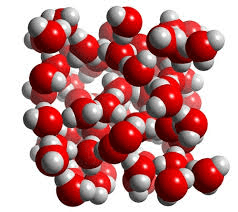 Water is said to be this due to unequal distribution of electrons in the bonds.
Water is said to be this due to unequal distribution of electrons in the bonds.
What is polar
This model best represents the CH2O molecule.
What is Diagram 2.
Bonus for why.
The structure below that has a bond angle closest to 120 degrees.
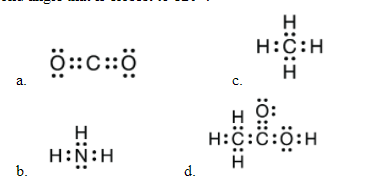
What is d
This diagram represents how an ionic solid, NaCl, would be arranged to maximize the coulombic attractions and minimize repulsions.
What is a lattice where the metal ions are smaller than the nonmetal ions?
The separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or group having a dipole moment.
What is polarity?
Regarding melting point, match each term to the corresponding thermometer.
Ionic Bond Covalent Bond
Covalent Bond- first, cold thermometer
Ionic Bond- second, hot thermometer
This molecule would be considered this because its polar bonds cancel each other out.

What is nonpolar?
Daily Double
This is the best Lewis Structure for H3NO.
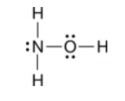
These combinations of orbitals will produce a sigma bond.
What are s and s, s and p along the molecular axis, and p and p along the same axis (head on).
The reason this substance conducts electricity.
What is it conducts electricity because the electrons are free to move through the substance.
Bonus: Identify the type of structure.
VSEPR stands for this.
What is valence shell electron pair repulsion.
It is a type of structure in the metallic element copper.

What is an extended, repeating pattern?
Diatomic iodine
What is nonpolar?
This is the molecular geometry for something that has 5 domains and 0 lone pairs.
What is trigonal bipyramidal
Fluorine has 10 bonding and 8 antibonding electrons. This is the bond order.
What is 1?
The picture in b represents this.
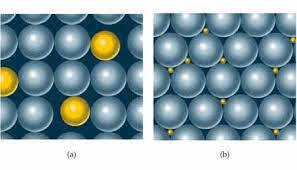
What is an interstitial alloy.
A measure of energy contained in the crystal lattice of a compound.
What is lattice energy?
Particles of all mater are always in constant random motion (true or false)
What is true?
If like dissolves like, then a nonpolar substance will dissolve in this type of substance.
What is nonpolar?
This is the proper geometry for XeCl4
What is square planar?
Daily Double
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for fluorine (F2)

The scenarios an ionic compound would conduct electricity.
What are molten state or dissolved in water?
The method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics.
What is the molecular orbital theory?