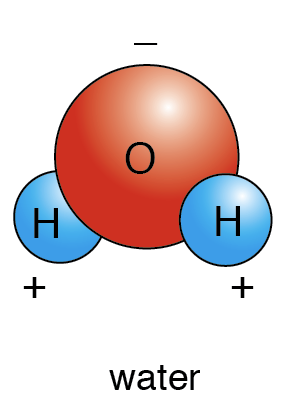
In water, which element is more positive and which one is more negative?
Oxygen - negative
Hydrogen - positive
An attraction between molecules of different substances and can cause capillary action.
Adhesion
What is the monomer for proteins?
Amino acids
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (single sugar unit)
Enzymes _____________ activation energy.
lowers / decreases
The bond within a water molecule between the hydrogen and oxygen - makes H2O
Covalent Bond
The attraction between a hydrogen atom on one substance to a negatively charged particle on another substance (usually a negative oxygen of H2O)
Hydrogen Bond
Give an example of a monomer and a polymer?
Monomer - amino acid
Polymer - Protein
What is the function of nucleic acids?
Enzymes speed up or slow down a reaction?
Speed up
Ice expands when it is formed and therefore makes ice less dense that liquid water. Explain how this impacts life in a pond.
Ice formed on the surface of the pond will act as a barrier to the air and therefore insulate the water below which helps fish survive during the winter
The attraction between molecules of the same substance and can cause surface tension.
Cohesion
When this molecule below is broken down in the body it produces energy. Which macromolecule is this?

Carbohydrate
Which macromolecule has the following examples: phospholipids, fats, oils, and waxes?
Lipids
Enzymes function at specific conditions (ex. temperature & pH) - what happens when an enzyme leaves that ideal condition?
Denature - enzyme looses its shape and therefore function
Waters ability to use adhesion and cohesion to move upwards in a confined space or on a material.
Capillary action.
Water's _____________allows it to dissolve compounds such as table salt (NaCl).
Polarity
Draw the structure of a nucleotide.

Which macromolecule is built from this monomer?

That is glucose a monosaccharide so therefore makes carbohydrates
A specific enzyme is shaped for a specific substrate. What is this called?
Lock and Key model / theory
It takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of water, especially in large bodies of water. What is this property of water?
High specific heat capacity
The substance in a solution that dissolved the solute......Water is the universal one of these.....
Solvent
Which macromolecule has the following function: transportation, enzyme function, storage, structural, and movement
Proteins
Which macromolecule has the following functions: long term energy storage, protect & insulate, chemical messenger, & cell membrane composition
Lipids
Which line shows a reaction done with an enzyme?

Green solid line