The driving forces of tectonic plates are related to convection currents in Earth’s ____.
A) crust
B) mantle
C) inner core
D) outer core
B) mantle
____ are formed when two continental plates collide.
A) Volcanoes
B) Strike-slip faults
C) Mountain ranges
D) Rift valleys
C) Mountain ranges
At an oceanic-oceanic convergent plate boundary, ____.
A) new crust is created
B) old crust is recycled by subduction
C) old crust is deformed or fractured
D) plates side past one another
B) old crust is recycled by subduction
Looking at the figure that shows world-wide earthquake distribution, the white lines represent plate boundaries. Which statement is true?
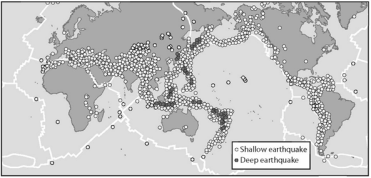
A) Earthquakes always occur along plate boundaries.
B) Earthquakes most frequently occur along plate boundaries.
C) Earthquakes rarely occur along plate boundaries.
D) Earthquakes never occur along plate boundaries.
B) Earthquakes most frequently occur along plate boundaries.
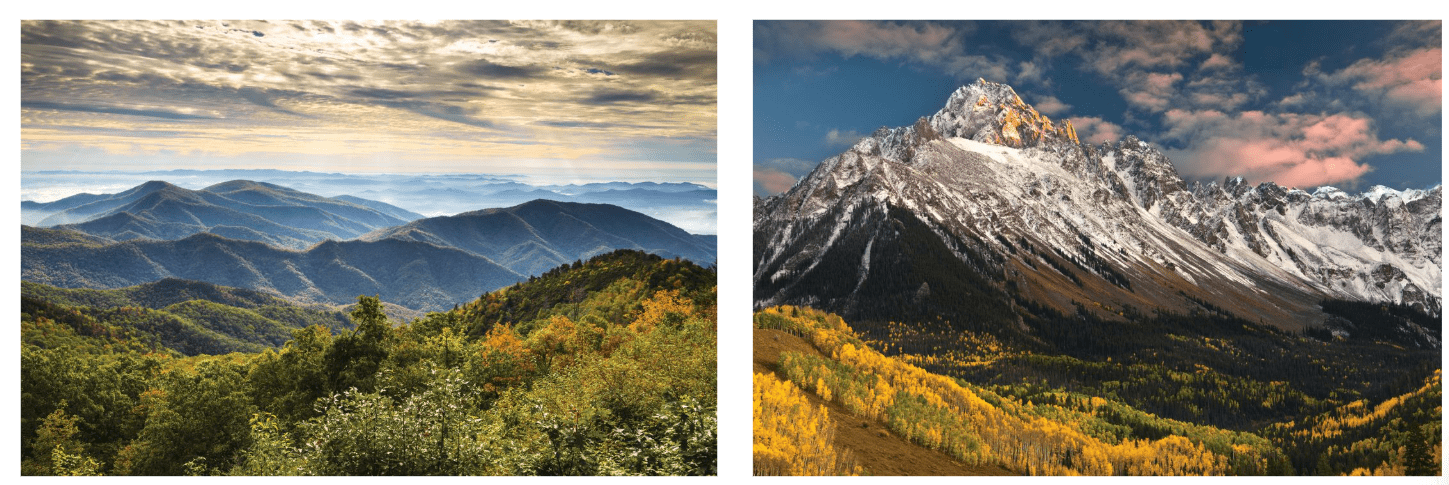
Compare the Appalachian Mountains (left) to the Rocky Mountains (right) below. Which mountain range do you think is older? Why?


Where is Earth's heat energy most concentrated?
A. The mantle
B. The lithosphere
C. The core
A. The mantle
What type of mountains are formed when molten rock erupts onto Earth’s surface and hardens?
A) uplifted mountains
B) fold mountains
C) volcanic mountains
D) fault-block mountains
C) volcanic mountains
Fault-block mountains occur where _____.
A) compression squeezes the crust
B) tension pulls the crust apart
C) tension squeezes the crust
D) compression pulls the crust apart
B) tension pulls the crust apart
Volcanoes can form over a plume, or rising current of hot mantle. As a tectonic plate slowly moves over a plume, a volcano will form and then become extinct as it moves away from the hot spot. Then the next volcano will form. If the hot spot shown made all the islands in the figure, is the plate pictured below moving toward you or away from you?
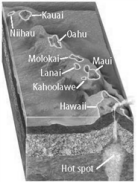
A) The plate is moving toward me.
B) The plate is moving away from me.
C) There is no way to tell.
D) It is stationary.
B) The plate is moving away from me.
Which student is correct in how long it takes for the motion of Earth's tectonic plates to produce changes on Earth's surface:

Akoni: The movement of Earth's plates forms landforms over millions of years and causes rapid events.
Which describes the location of the asthenosphere?
A. Above the crust
B. Between the crust & the lithosphere
C. Between the crust & the core
C. Between the crust & the core
Volcanoes are common in places where two plates collide that differ in _______ .
A. Speed
B. Density
C. Thickness
D. Temperature
B. Density
What is the underlying force that drives plate tectonics?
A. Ocean tides
B. Volcanic eruptions
C. The rock cycle
D. Convection currents
D. Convection currents
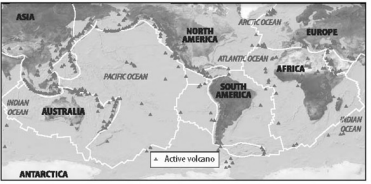
Look at the figures showing the distribution of volcanoes and earthquakes. Why do volcanoes and earthquakes occur in so many of the same areas?
Volcano Distribution
Earthquake Distribution
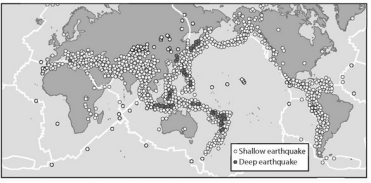
Both earthquakes and volcanoes often form at tectonic plate boundaries.
Volcanoes in Hawaii began forming in the seafloor, about 5,100 m below the surface. If a volcano reaches the surface in 300,000 years, what was its rate of vertical growth per year?
rate = (distance)/(time)
A. 0.017 m/y
Convergent boundaries are where two plates ____________.
a.) collide
b.) pull apart
c.) slide past each other
a.) collide
How is it that the Himalayan mountains are still growing higher and higher each year?
The Himalayan mountains are a result of the convergence of two continental tectonic plates. These two plates are of equal density, so rather than one plate subducting under the other, the plates are continually smashing into one another and the mountain range is getting lifted higher and higher as this happens.
Transform boundaries are where two plates _________.
a.) collide
b.) pull apart
c.) slide past each other
c.) slide past each other
Point out two changes that occur between the 65 mya time period and the present.

India has collided with Asia to form the Himalayas. Australia has separated from Antarctica. A rift valley is forming in east Africa.
Over what time scale did it take the volcano on the left to form?
How does this compare to the time scale it took for the same volcano to appear as it does on the right?

The amount of time needed for the volcano to look like it does in the photograph on the left is millions of years. The volcano builds up slowly after repeated eruptions because after each eruption there is lava that pours down the side of the volcano that cools to become more rock and because rocks that are thrown from the volcano pile up around the crater. The amount of time it takes for the volcano to look like it does in the photograph on the right is minutes. During a volcanic eruption, lots of rock, lava, and ash are thrown into the air as pressure is released from the volcano, which destroys the cone shape of the volcano.
Name all three boundaries shown in the diagram below:
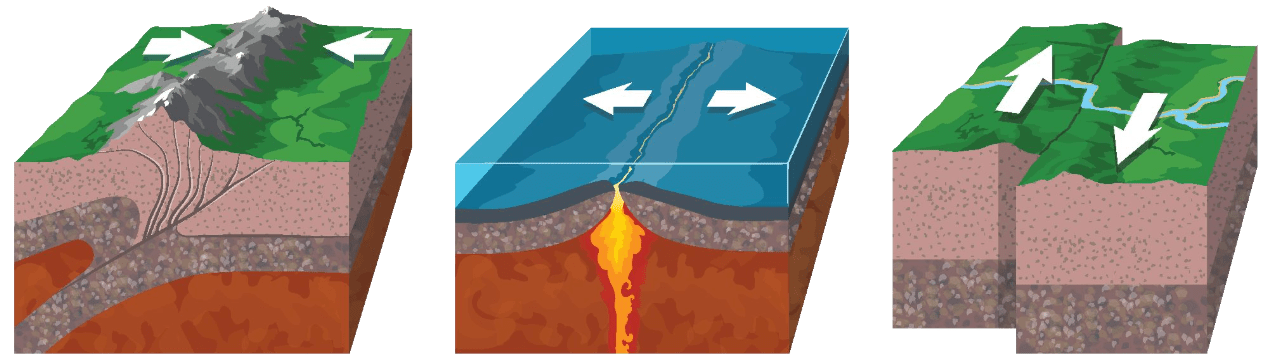
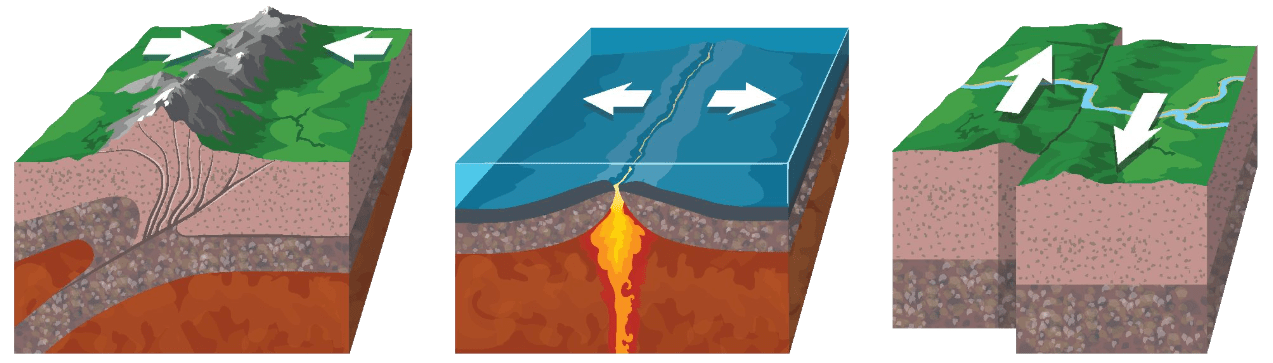
Convergent Divergent Transform
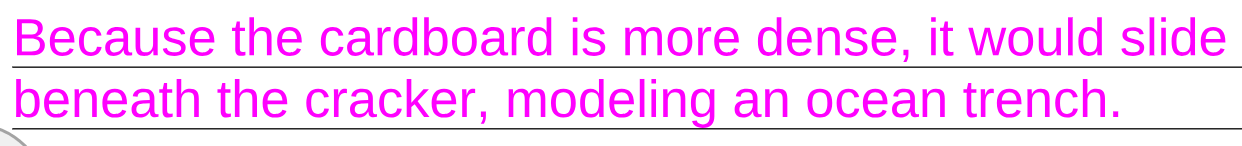
Recall the graham cracker lab where water was added between the two "plates" and then collided.
Suppose you substituted a piece of thick cardboard for one of the graham crackers. Which material would slide beneath the other? What ocean structure might this model?
Divergent boundaries are where two plates ______________.
a.) collide
b.) pull apart
c.) slide past each other
b.) pull apart
The top map shows the location of Earth’s mid-ocean ridges, and the bottom map shows the boundaries of Earth’s tectonic plates.
Based on the data shown in the maps, select two tectonic plates that meet along a Type 1 boundary. Identify the plates and describe the movement of those plates along that boundary.
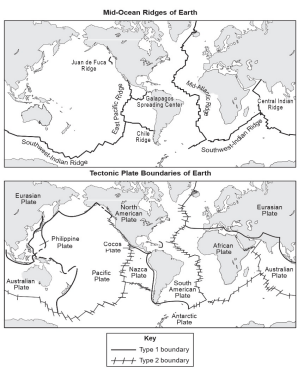
Plates that have a Type 1 boundary include those listed below. The plates along a Type 1 boundary move toward one another, or converge.
-Pacific and Eurasian‚ Pacific and North American
-Philippine and Eurasian‚ Philippine and Pacific
-Nazca and South American‚ African and Eurasian
-Australian and Eurasian‚ Antarctic and South American
-Pacific and Australian
The top map shows the location of Earth’s mid-ocean ridges, and the bottom map shows the boundaries of Earth’s tectonic plates.
Based on the data shown in the maps, select two tectonic plates that meet along a Type 2 boundary. Identify the plates and describe the movement of those plates along that boundary.
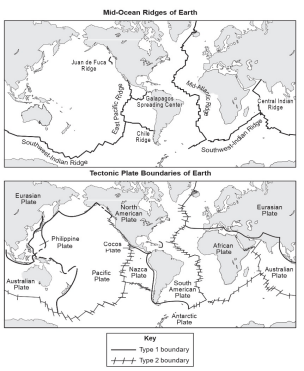
Plates that have a Type 2 boundary include those listed below. The plates along a Type 2 boundary move away from one another, or diverge.
-North American and Eurasian‚ Pacific and North American
-Nazca and Pacific‚ Antarctic and Nazca
-Antarctic and Australian‚ South American and African
-Antarctic and African‚ Antarctic and Pacific