What are the stages of Meiosis
Meiosis 1: Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1 (PMAT 1)
Meiosis 2: Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2, Telophase 2 (PMAT 2)
How many divisions does mitosis have?
One
Both mitosis and meiosis start with ...
One parent cell
What occurs in the S phase
DNA is replicated
What phase is pictured below?
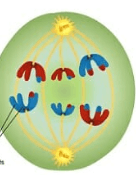
Anaphase 1
Mitosis results in two ________ ________ ________
Identical daughter cells
What number of chromosomes are in a human?
46
Describe the G1 phase. Why might a cell go into the G0 phase?
Growth
Cells typically enter the G0 phase after they finish mitosis. They have no need to divide again. Sometimes, however, they may enter into the G0 phase from G1 because their environments lack the necessary nutrients with which to enter the nutrient-expensive cell cycle.
What products do you get from meiosis?
4 daughter cells with 23 chromosomes
gametes: sperm cells and egg cells
Mitosis occurs in what type of cells?
Somatic cells/Body Cells/Non-reproductive cells
haploid=23 chromosomes(n)
diploid=46 chromosomes(2n)
Describe Interphase
Interphase is G1, S, and G2 phase.
G1 and G2 are all about growth
Synthesis phase is all about DNA replication
What two events cause genetic variation in meiosis?
Independent assortment and crossing over
During what phase of mitosis does the nucleus break down?
Prophase
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Meiosis and mitosis both start the same, however, meiosis has an extra division with no replication
How does Cancer happen? If a scientist wanted to cure cancer what should they focus on?
Cancer: unregulated cell growth
Cause: mutations (errors) in the cell cycle
A scientist could focus on cell cycle check points as well as carcinogens impacts on cell cycle
What is the difference between anaphase I and anaphase II
Anaphase I - homologous chromosomes split
Anaphase II - sister chromatids split
Prophase: Nuclear envelope dissolves, Chromosomes condense
Metaphase: Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase: Sister Chromatids are pulled apart by microtubules and pulled to opposite sides of the cell
Telophase: The nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes uncoil into chromatin
Cytokinesis (separate): cytoplasm splits
What is crossing over?
When two chromosomes — one from the mother and one from the father — line up, parts of the chromosome can be switched. The two chromosomes contain the same genes, but may have different forms of the genes.
(in prophase I)
What is apoptosis? Why might a cell do this?
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death. It is used during early development to eliminate unwanted cells; for example, those between the fingers of a developing hand. In adults, apoptosis is used to rid the body of cells that have been damaged beyond repair. Apoptosis also plays a role in preventing cancer.