The process by which water passes into or out of a cell is called __________.
Osmosis
What word describes a cell’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment?
homeostasis
Which type of transport does not require energy?
diffusion, simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
What are the main components of the cell membrane? (Name at least two.)
phospholipids & proteins
How many seconds are there in a year?
12
Jan. 2nd, Feb. 2nd, March 2nd…
Diffusion moves substances from areas of ______ concentration to areas of ______ concentration.
high to low
Animal cells prefer what type of solution?
isotonic
Glucose enters a cell using carrier proteins but no energy. What type of transport is this?
Facilitated Diffusion
The plasma membrane is described as “selectively permeable.” What does this mean?
Allow certain molecules in while blocking other molecules
A rooster lays an egg on a rooftop. Which way does it roll?
Nowhere—roosters don’t lay eggs
Which side will the water be higher?
Left, Right, Neither, Both
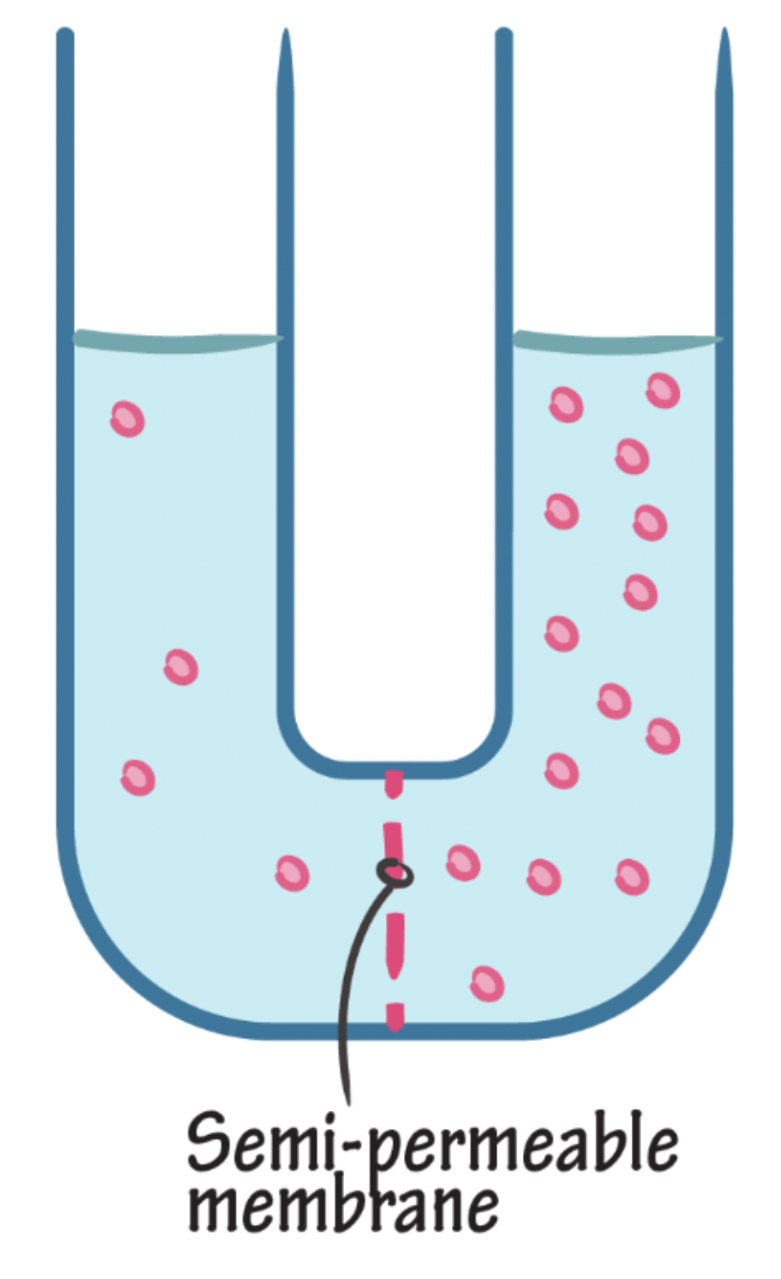
Right
In what type of solution does a plant cell become plasmolyzed?
in a hypertonic solution
Which process moves large molecules out of the cell?
exocytosis
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic and which part is hydrophilic?
phosphate head is hydrophilic
fatty acid tail is hydrophobic
Solve this
Blanket
Your lungs exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through what type of diffusion?
Simple
A student fills a dialysis bag with a 70% glucose solution and places it in a beaker of 10% glucose. The bag is in what type of solution?
hypotonic solution
Active transport requires energy from what molecule?
ATP
Identify the two structures below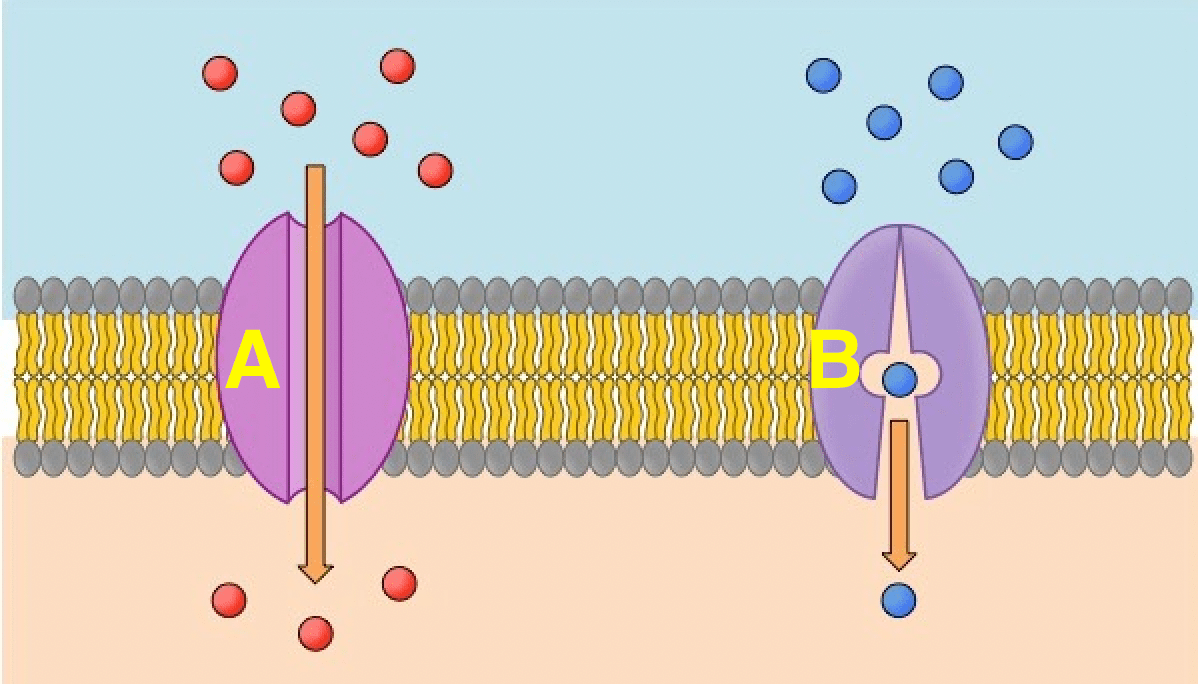
A) Channel Protein
B) Carrier Protein
Solve

Right under the nose
increase the concentration gradient, increase surface area, thickness of membrane, increase in temperature
After placing a crisp stalk of celery in a cup of distilled water, you return a few hours later to find it firm and crunchy. Which of the following best explains how water movement through the cell membrane caused this change in the celery?
Water moved into the celery cells, making them firmer.
What is the difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis?
A cell engulfing or eating another cell or parts of another cell
a cell "drinking" water
What is the function of cholesterol in the membrane?

Missing U
What does it mean when a cell membrane reaches dynamic equilibrium during diffusion?
Molecules continue to move across the membrane in both directions, but there is no net change in concentration.
A cell with 8% salt 10% sugar 2% calcium is placed in a 3% salt 15% sugar 5% calcium solution. Which direction will water move, and why?
Move out of the cell because there is a greater solute concentration/lower water concentration
The process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule, often from ATP, to activate or change the shape of a protein
phosphorylation
What do carbohydrate chains attached to proteins or lipids help with?
cell communciation (recognition, signaling,etc)
A woman shoots her husband, holds him underwater for five minutes, and hangs him. Later, they go out to dinner. How?
She took a photo of him