How does adenosine triphosphate (ATP) become adenosine diphosphate (ADP)?
ATP releases energy as a phosphate bond is broken.
Which best lists the end products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
ATP, NADPH, and O2
Why is the Calvin cycle considered a dark reaction?
a. It occurs only at night.
b. It requires an absence of light.
c. It turns the plant dark green.
d. It can proceed in the dark.
d. It can proceed in the dark.
Name the 2 products of photosynthesis.
glucose (sugar) oxygen (O2)
List the three stages of Aerobic Cellular Respiration in order.
Stage 1 - Glycolysis
Stage 2 - Kreb's Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle
Stage 3 - Electron Transport Chain
What is the main difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to proceed, but anaerobic respiration does not.
Name the 2 reactants of cellular respiration .
oxygen (O2) and glucose (sugar).
What happens during glycolysis?
Glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate
What are the components of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
Ribose
Adenine
Phosphates (3)
Which events take place in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
a. Light energy is converted to sugars; sugars are broken down for energy.
b. Light energy is captured by plants; light energy is used to make sugar.
c. Light energy is converted to chemical energy; chemical energy is used to make sugar.
d. Light energy is captured by plants; light energy is converted to chemical energy.
d. Light energy is captured by plants; light energy is converted to chemical energy.
Which compound is produced during carbon fixation?
PGA
The organelle where photosynthesis takes place.
chloroplast
During which stage of cellular respiration is glucose broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid?
a. electron transport chain
b. glycolysis
c. Krebs cycle
d. acetyl CoA formation
b. glycolysis
What do aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration have in common?
a. Both begin with glycolysis.
b. Both occur in mitochondria.
c. Both require oxygen to proceed.
d. Both end with the electron transport chain.
a. Both begin with glycolysis.
The mitochondria is the location of these 2 aerobic processes.
Kreb's Cycle and Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The part of photosynthesis that does not directly require sunlight
light independent reactions, calvin cycle, or dark reactions.
The organic compound below consists of an adenine molecule (blue), a ribose (purple), and three phosphate groups (orange).

Which compound is shown?
ATP
Which specific process in the light-dependent reactions produces oxygen and hydrogen ions?
a. the formation of NADPH
b. the production of ATP
c. the splitting of water
d. the excitation of electrons in photosytem I
c. the splitting of water
Which speeds up (enzyme) the reaction between carbon dioxide and RuBP to restart the Calvin Cycle?
rubsico
What is the balanced equation of photosynthesis (number of each molecule needed).
6CO₂ + 6H₂O (+ light energy) → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
What role does cellular respiration play in the carbon cycle?
a. It removes CO2 from the atmosphere during glycolysis.
b. It removes CO2 from the atmosphere during the citric acid cycle.
c. It releases CO2 to the atmosphere during acetyl CoA formation.
d. It releases CO2 to the atmosphere during electron transport.
c. It releases CO2 to the atmosphere during acetyl CoA formation.
During which process is water produced?
a. alcohol fermentation
b. acetyl CoA formation
c. electron transport chain
d. citric acid cycle
c. electron transport chain
The main function of cellular respiration (main product).
ATP energy
How many times does the Calvin Cycle have to run in order to produce one molecule of glucose?
twice (2)
by the addition of one phosphate group
Which statement describes thylakoids?
a. Glucose is formed here.
b. Water molecules are formed here.
c. Only photosystem II functions here.
d. Photosystems I and II function here.
d. Photosystems I and II function here.
At which point is G3P removed from the Calvin cycle to be used in the production of carbohydrates?
immediately after reduction
Free Points
Free Points
Which process connects glycolysis and the citric acid cycle?
a. lactic acid formation
b. acetyl CoA formation
c. electron transport
d. Krebs cycle
b. acetyl CoA formation
What do alcohol fermentation, acetyl CoA formation, and the Krebs cycle have in common?
a. All produce water.
b. All produce carbon dioxide.
c. All produce ATP.
d. All produce alcohol.
b. All produce carbon dioxide.
Name of the 1st stage of cellular respiration for either aerobic or anaerobic respiration.
Glycolysis and aerobic
Aerobic cellular respiration results in this amount of total ATP molecules.
36-38
Which structure is depicted by the arrow?
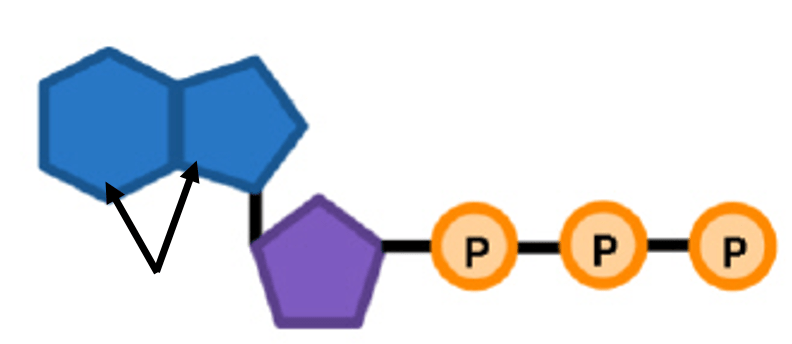
Adenine
Which statement best describes the process of chemiosmosis (ATP Synthase) and the direct result of its occurrence?
a. Hydrogen ions flow from the thylakoid down a concentration gradient through ATP synthase channels into the stroma. ADP is converted to ATP.
b. Hydrogen ions flow from the thylakoid down a concentration gradient through ATP synthase channels into the stroma. ATP is converted to ADP.
c. Hydrogen ions flow from the stroma down a concentration gradient through ATP synthase channels into the thylakoid. ADP is converted to ATP.
d. Hydrogen ions flow from the thylakoid against a concentration gradient through ATP synthase channels into the stroma. ADP is converted to ATP.
a. Hydrogen ions flow from the thylakoid down a concentration gradient through ATP synthase channels into the stroma. ADP is converted to ATP.
Which is an important difference between light-dependent (L-D) and light-independent (L-IND) reactions in photosynthesis?
a. The L-D reactions need CO2 and light energy, and the L-IND reactions needs water and O2.
b. The L-D reactions require light energy and water, and the L-IND reactions require ATP, NADPH, and CO2.
c. The L-D reactions can only occur during daylight, and the L-IND reactions can only occur during the night.
d. The L-D reactions need water and CO2, and the L-IND reactions need CO2 and light.
b. The L-D reactions require light energy and water, and the L-IND reactions require ATP, NADPH, and CO2.
List the three parts of an ATP molecule
adenine, ribose, phophate
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
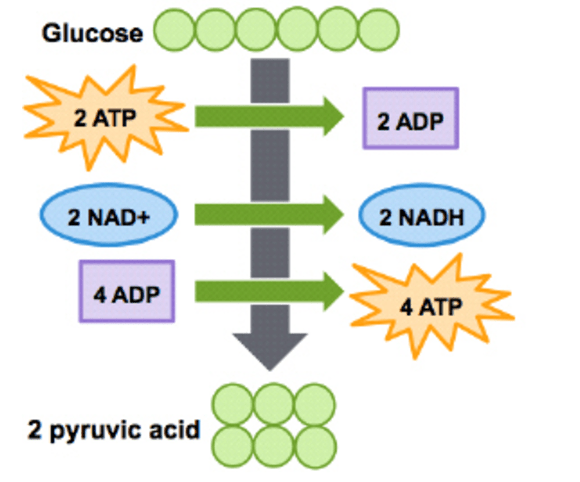
What is the main transformation that occurs during glycolysis?
Glycolysis produces pyruvate, ATP, and NADH by oxidizing glucose.
If a runner is doing vigorous exercise, which results from the anaerobic cellular process?
a. accumulation of lactic acid
b. accumulation of oxygen
c. depletion of ethanol
d. depletion of carbon dioxide
a. accumulation of lactic acid
What is the balanced equation of cellular respiration (number of each molecule needed).
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O [+ energy (32-36ATP)]
Free Points
Free Points