109 of these equals one meter.
What is a nanometer?
The chemical formula for sulfur trioxide.
What is SO3?
The relative ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself.
What is electronegativity?
VSEPR stands for this theory used to determine molecular shape.
What is Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory?
Without polar bonds, a compound is only capable of this type of intermolecular force.
What are London dispersion forces?
The number of valence electrons for the N3- ion.
What is 8?
The three main subatomic particles.
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons?
The name for the compound CrO3
What is chromium(VI) oxide?
A difference in electronegativity between 0.4 and 1.7 indicates this type of covalent bond.
What is polar covalent?
The number of domains, including lone electron pairs and bonding electron pairs, determines this.
What is electron pair geometry?
The presence of H bonded directly to a strongly electronegative atom like N, O, or F makes a molecule capable of this intermolecular force.
What is hydrogen bonding?
H, B, Be, Al, and elements in the third period and below share this distinction.
What are exceptions to the Octet Rule?
DAILY DOUBLE!
In nuclide notation shown below, the letter Z represents this.

What is atomic number, or the number of protons?
CO32- ion has this name
What is the carbonate ion?
A bond is considered nonpolar if the electronegativities of participating atoms is less than this value.
What is 0.4?
The shape of this molecule, SF6
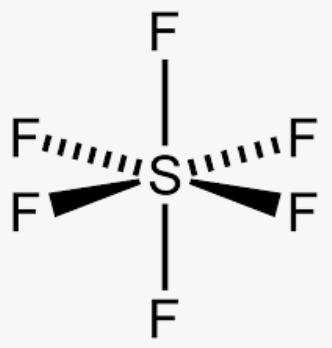
What is octahedral?
For dipole-dipole forces to occur, molecules must possess this.
What is a net dipole/permanent dipole/be polar molecules?
In this situation, atoms are arranged in the same order, but electron pairs are arranged differently.
What is resonance/resonance structures?
When describing a wave, these two characteristics are inversely related.
What are frequency and wavelength?
The chemical formula for magnesium sulfate heptahydrate is this.
What is MgSO4 . 7H2O?
A polar molecule is identified by these two features.
What is a polar bond and a net dipole moment (or shape that is not symmetric, uneven distribution of the polar bonds)?
This thirst-quenching substance is a common example of bent molecule geometry.
What is water?
Considering the strengths of interactions between molecules, ion-dipole forces hold this distinction.
What are the STRONGEST interactions?
DAILY DOUBLE!
The formal charge of Selenium in this ion
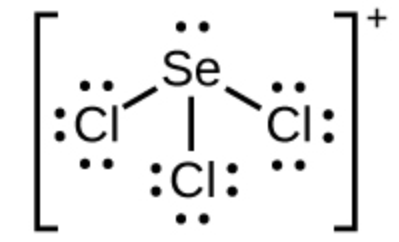
What is +1?
Einstein first identified this phenomenon where electromagnetic energy exceeding minimum frequency can strike a metal surface and cause a current to flow.
What is the photoelectric effect?
An aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide, HI, is named this.
What is hydroiodic acid?
PF3 is a good example.
What is a polar molecule?
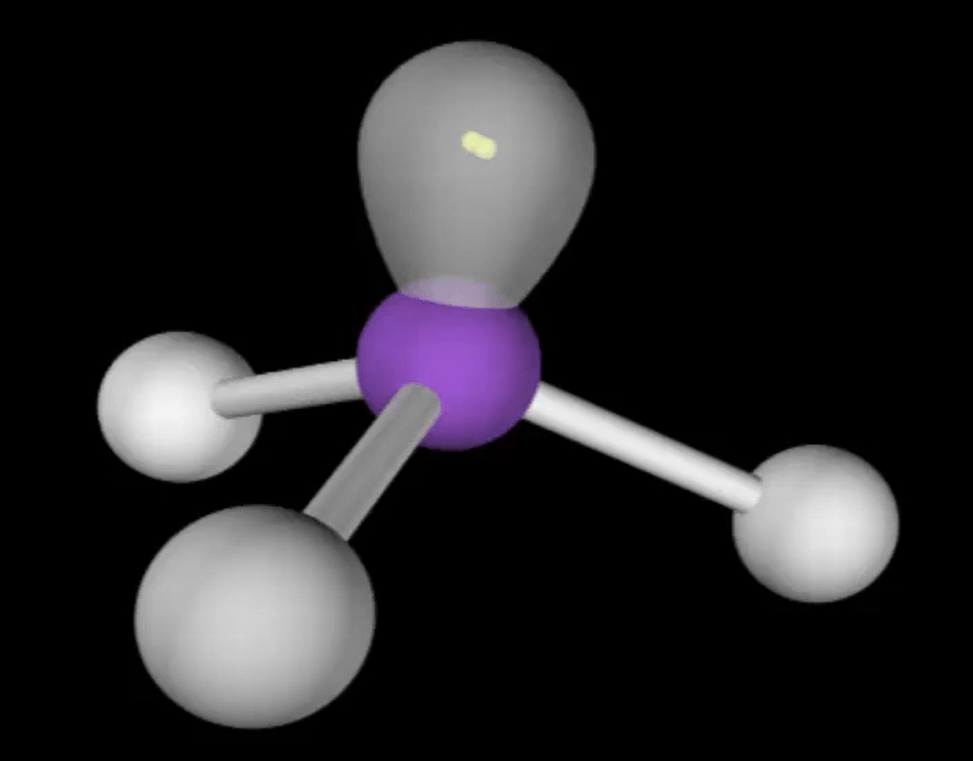
DAILY DOUBLE!
Steric number 2, steric number 5 (with 3 lone pairs), and steric number 6 (with 4 lone pairs) have this shape in common.
What is linear?
Two physical properties influenced by the strength of IMFs present.
What are physical state, solubility, melting point, boiling point, viscosity?
(Any two are acceptable.)
The number of lone pairs and the number of bonding pairs in this molecule, HBr.
What is one bonding pair and 3 lone pairs?