The main difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What is oxygen is used in aerobic respiration, but not in anaerobic respiration?
The meaning of arrows in food chains and webs.
What is the flow of energy, from the source to the destination?
The 10% rule.
What is only 10% of energy can move from a lower trophic level to the next higher trophic level?
The main processes involved in cycling carbon between the atmosphere and the biosphere.
What are photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The molecule that makes up approximately 78% of the atmosphere.
What is atmospheric nitrogen (N2)?
The type of anaerobic fermentation used in human muscle cells during periods of great exertion.
What is lactic acid fermentation?
Two terms for the trophic level in which organisms photosynthesize.
What are producers and autotrophs?
The trophic level that breaks down organic matter and recycles it.
What are decomposers?
The part of the day when plants release more CO2 and they absorb.
What is nighttime?
The key organisms that bring atmospheric nitrogen to the biosphere.
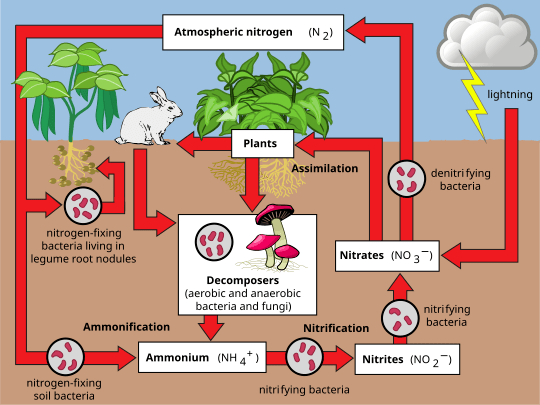
What are nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
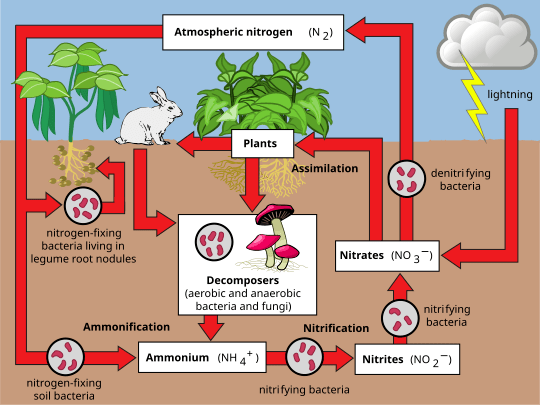
Organisms that primarily use anaerobic respiration.
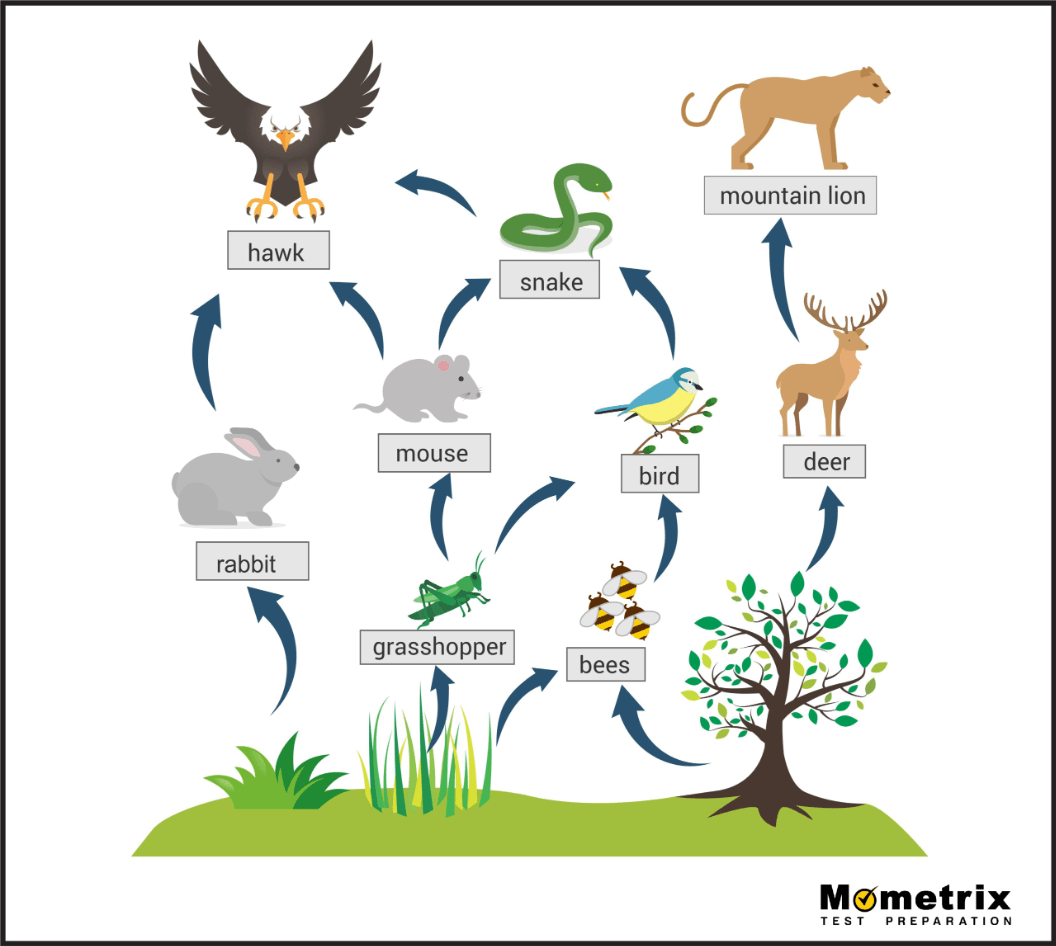
All of the primary consumers in this food web.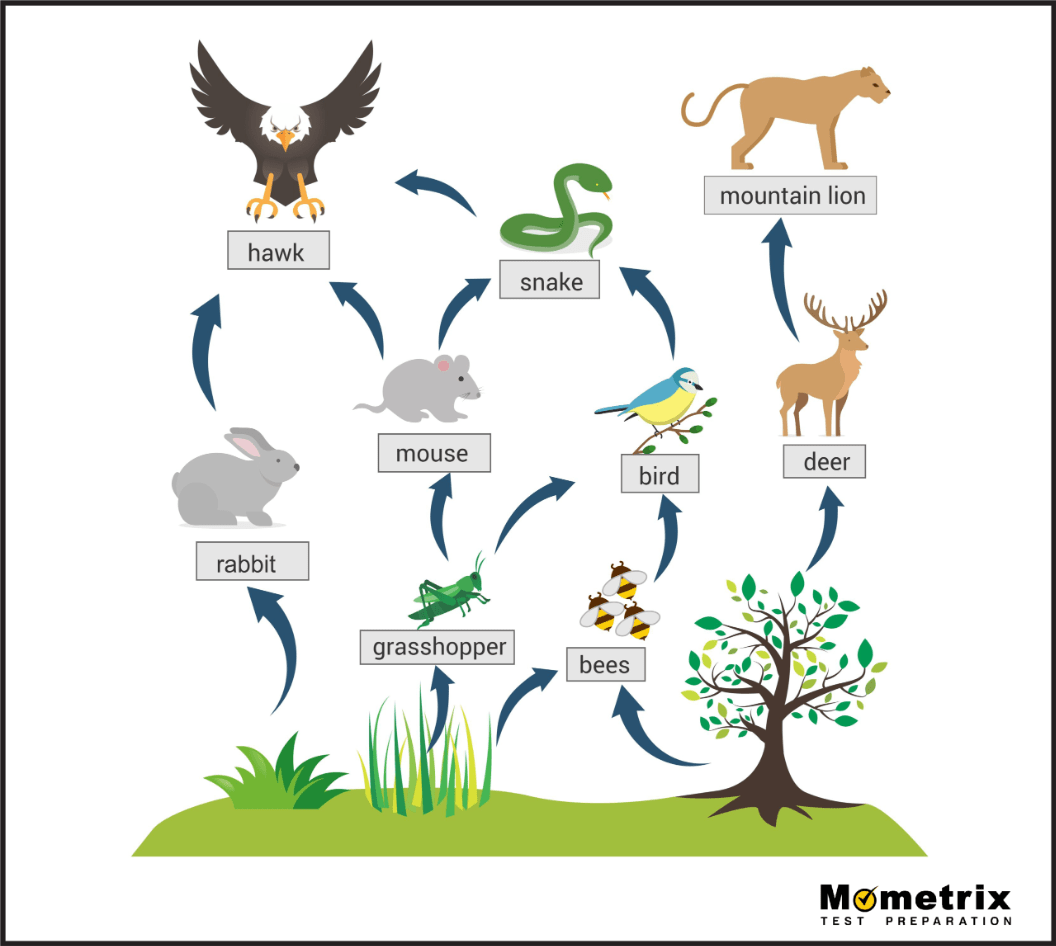
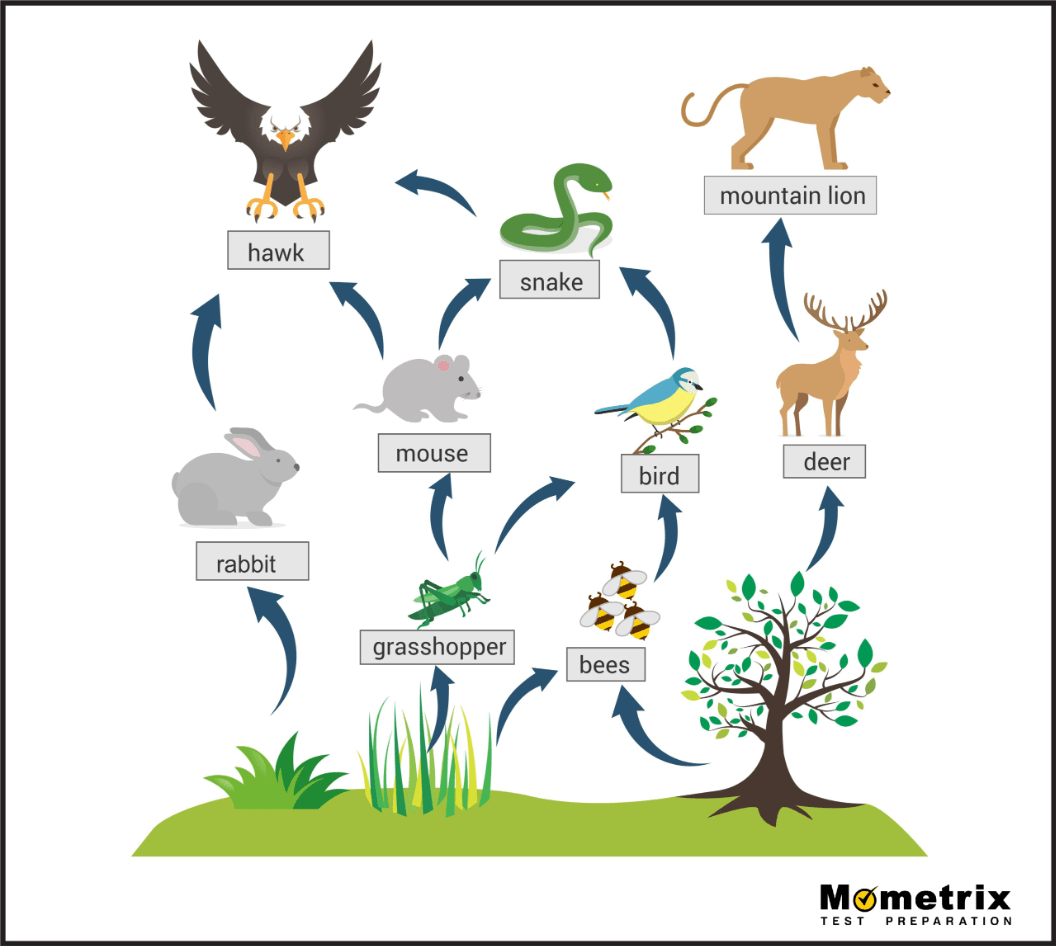
What are rabbit, grasshopper, bees, and deer?
The reason why biomass tends to decrease as you go up the ecological pyramid.
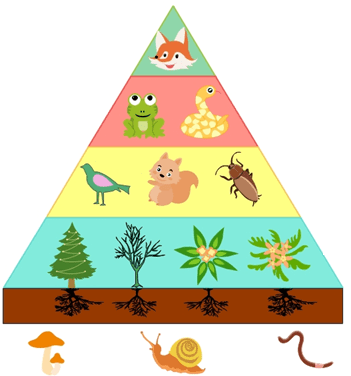
What is the loss of energy due to life processes and heat between trophic levels (10% rule)?
The largest carbon sink and the largest carbon reservoir on the planet.
What are the oceans and rocks/sediments?
The importance of biogeochemical cycles to life on Earth.
What is the cycling of nutrients critical to building organic molecules?
Two types of fermentation and their byproducts.
What are alcoholic (ethanol fermentation), which produces ethanol and CO2, and lactic acid fermentation, which produces lactic acid?
The various trophic levels that the hawk occupies.
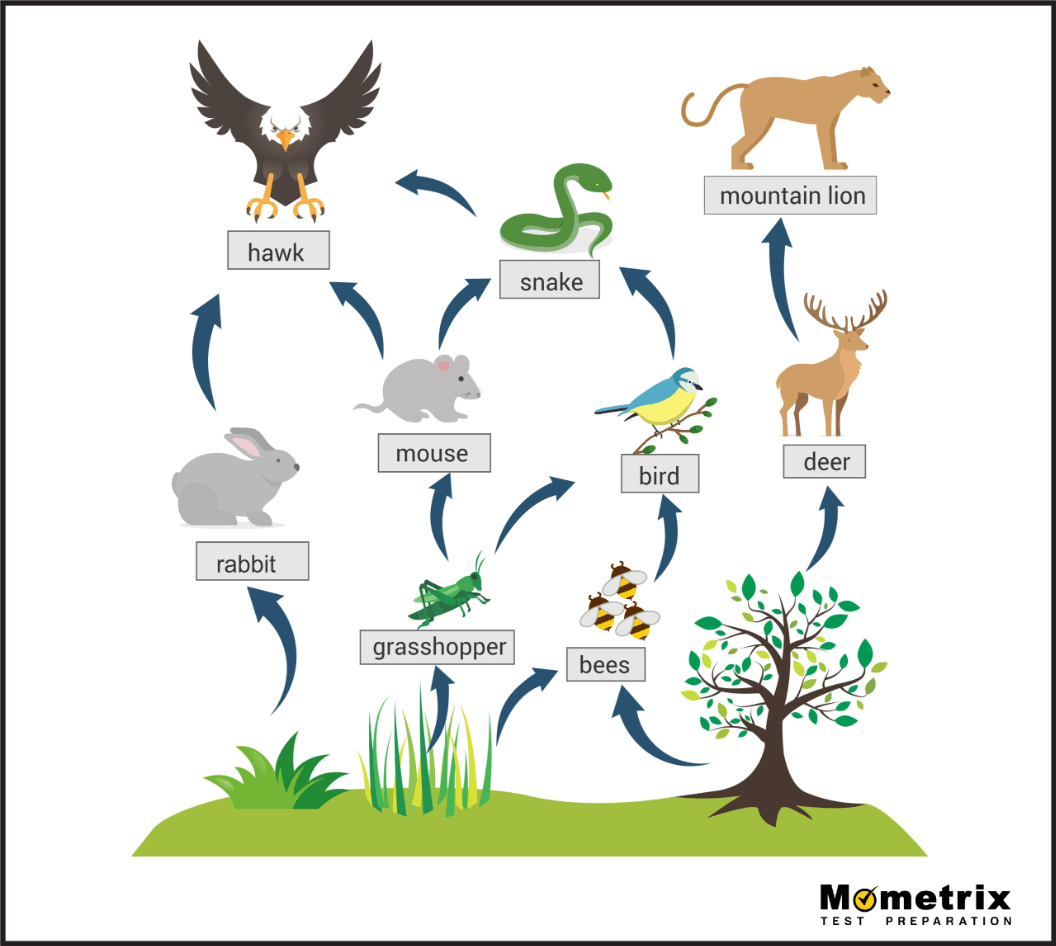
What are secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumer?
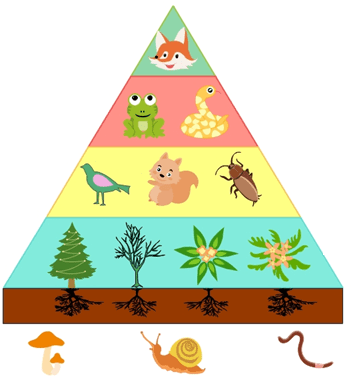
The short-term effects of the removal of foxes in this ecosystem.
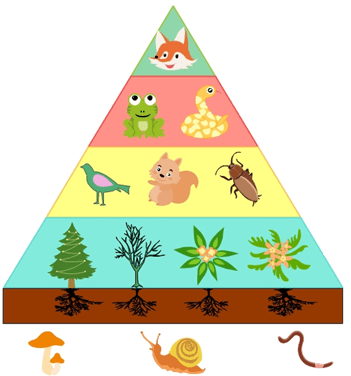
What is the increase in frogs and snakes and decrease in birds, squirrels, and beetles?
The most significant factor in adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
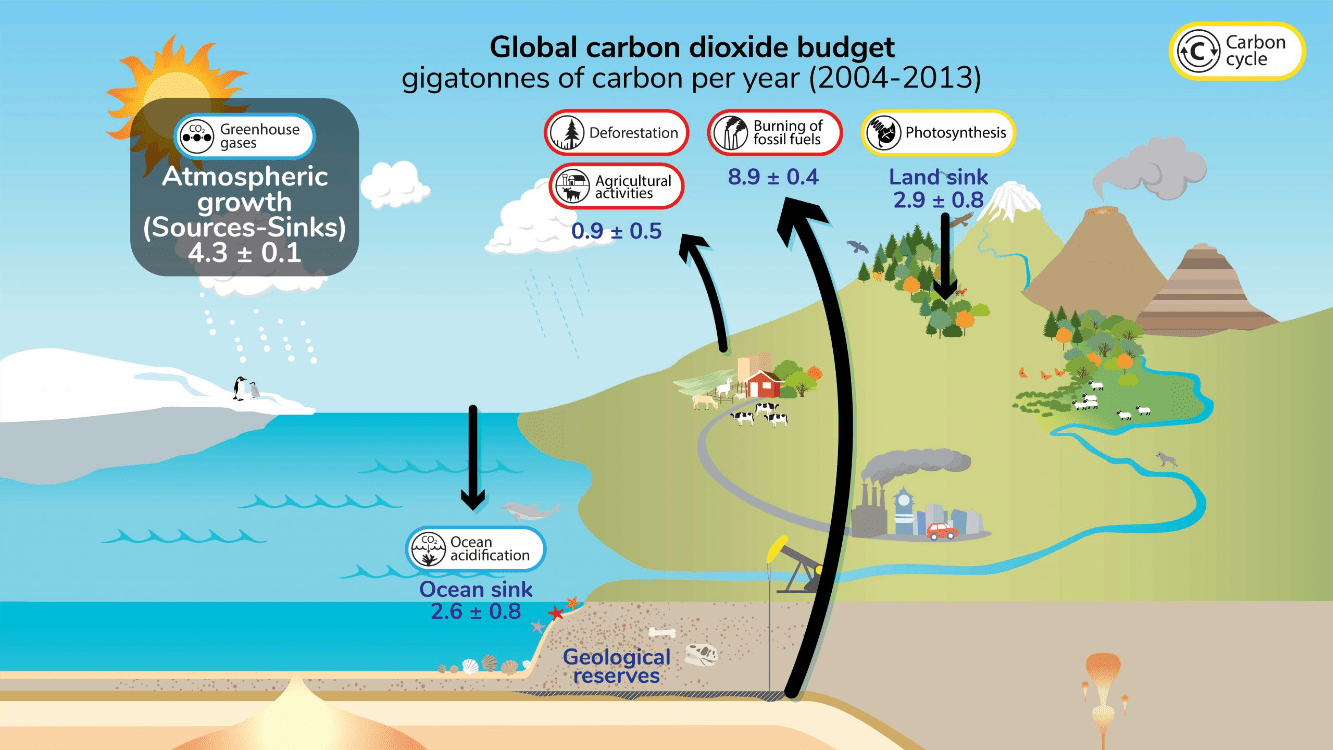
What is the burning of fossil fuels?
The biogeochemical cycle that rarely involves the atmosphere.
What is the phosphorus cycle?
The name of the process shared between aerobic and anaerobic respiration and how much ATP is produced during that process.
What is glucose and 2 ATP?
Two impacts of the loss of trees in this food web.

What are: a decrease in deer and bees and an eventual decrease in mountain lions and grasshoppers?
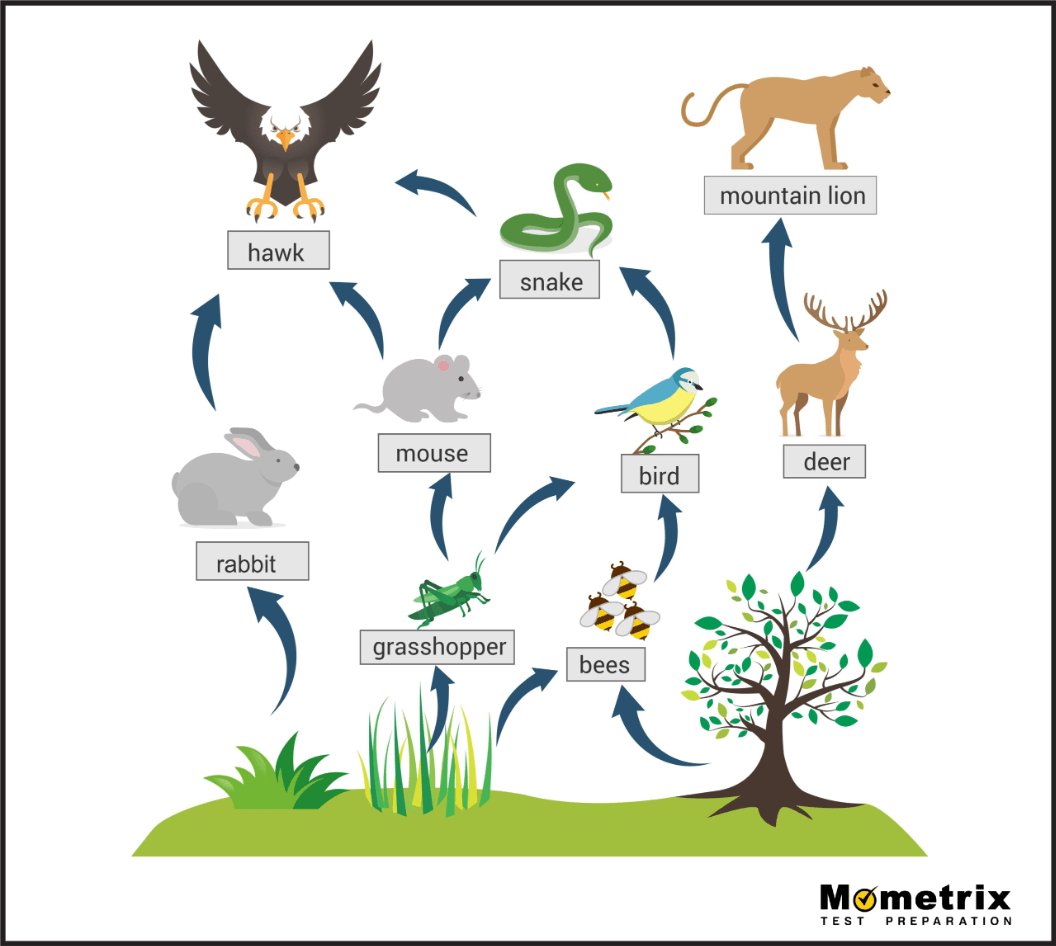
The most critical trophic level in an ecosystem and why.
What are producers/autotrophs because they are the only ones who can convert sunlight energy into a form usable by organisms?
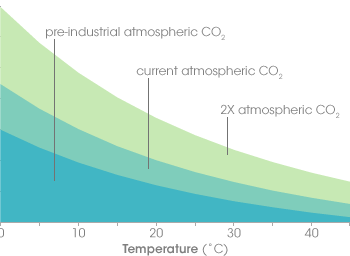
The relative ability of the ocean to absorb CO2 as temperatures rise due to climate change.
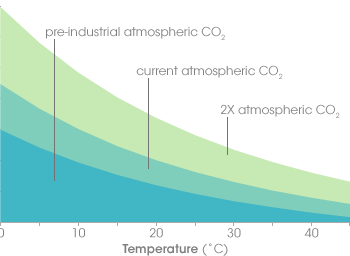
What is decreasing?
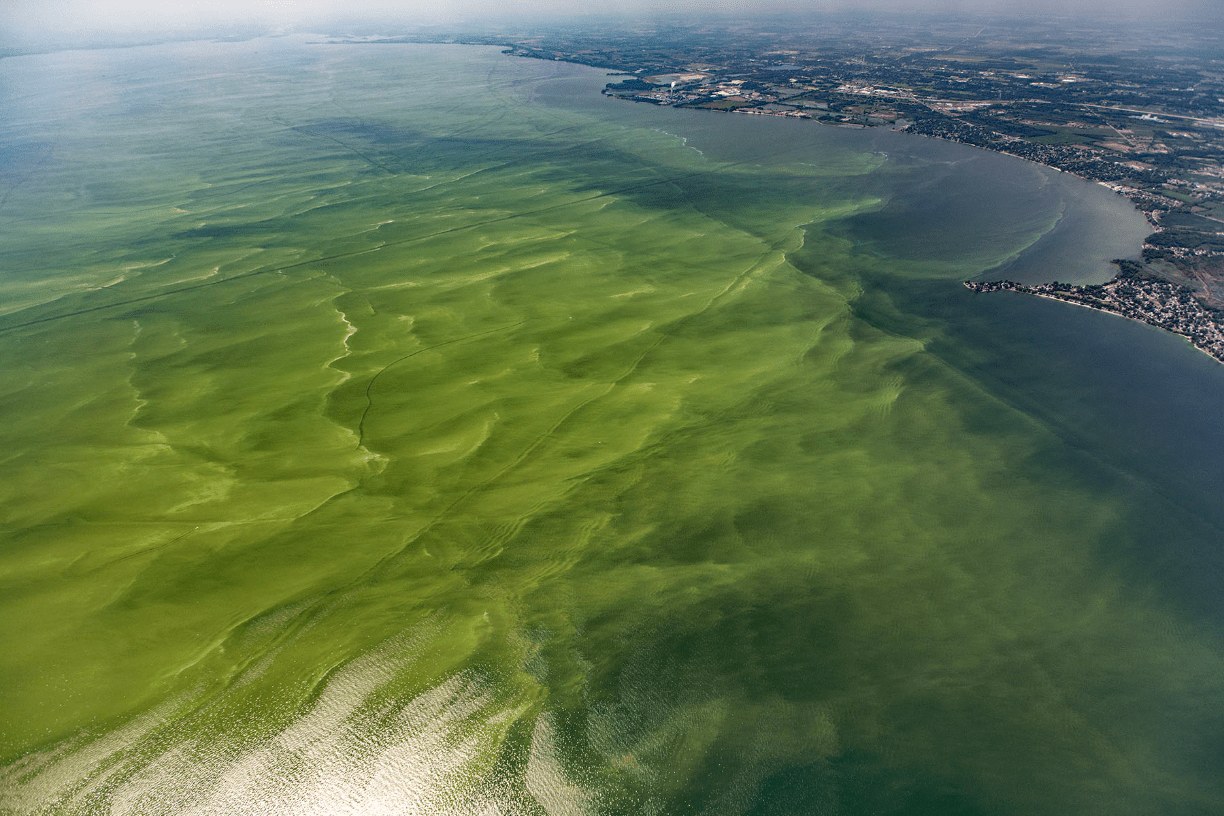
The phenomenon shown in the image and a possible human cause for it.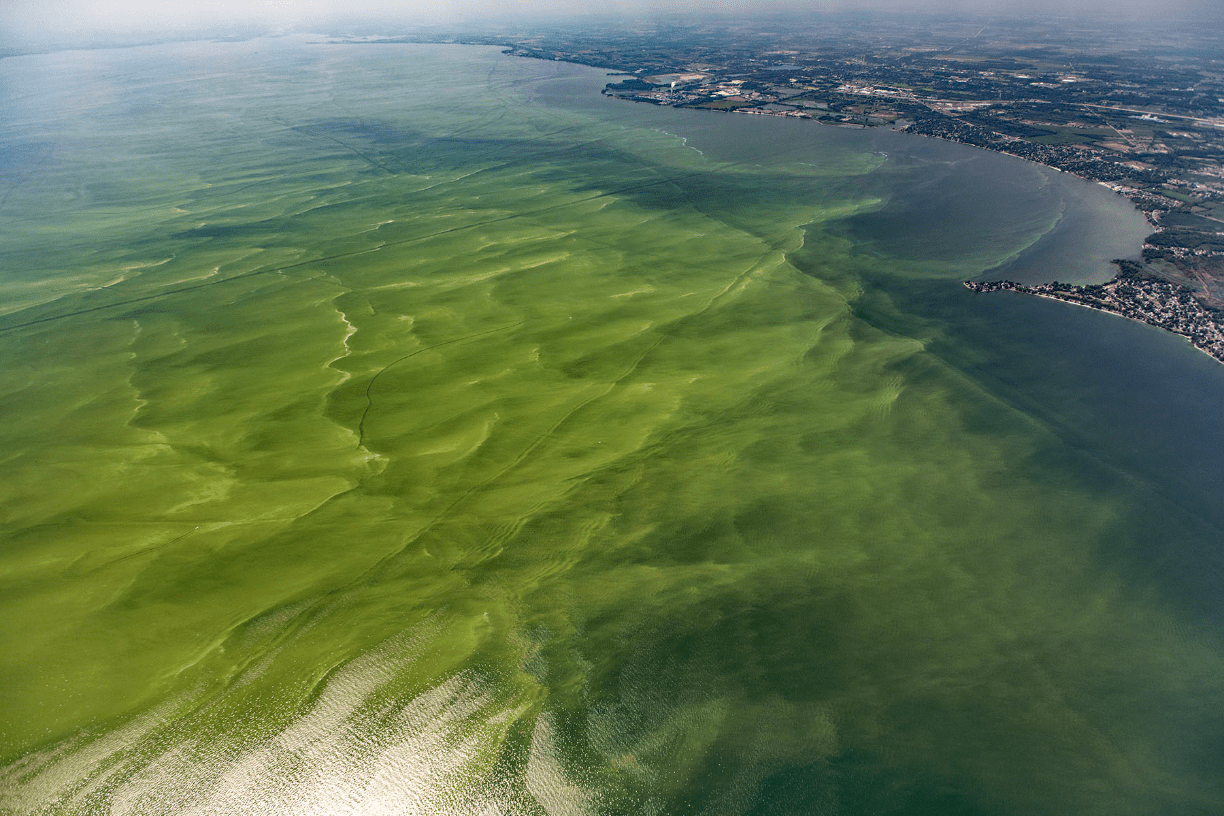
What is an algal bloom (eutrophication) and human overuse of fertilizers (containing nitrogen and phosphorus)?
