According to KMT, how do gas particles move?
In random, constant, straight-line motion.
Under what conditions do real gases behave most like ideal gases?
High temperature and low pressure.
A gas at 2.0 L and 1.0 atm is compressed to 0.5 L. What’s the new pressure? State the Gas Law.
4.0 atm (Boyle's Law)
The boiling point of a pure substance is defined as
the temperature at which vapor pressure...
The vapor pressure equals the external
pressure
What are the STP conditions?
273 K (0°C) and 1 atm (101.3 kPa).
According to KMT, how is average kinetic energy related to temperature?
Average kinetic energy is directly proportional to temperature in kelvin.
Why do real gases deviate from ideal behavior?
They have volume and intermolecular attractions.
What is the combined gas law? Describe the combined gas law and when it’s used.
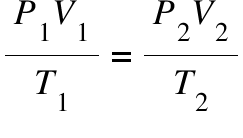
Used when pressure, volume, and temperature all change.
As the temperature of a liquid increases, its vapor
pressure
As temperature increases, vapor pressure increases.
What does Avogadro’s Hypothesis state?
Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules.
What causes gas pressure in a container?
Collisions of gas particles with the container walls.
Which gas behaves most ideally: Ar, H₂, or NH₃?
Ar (small and weak IMF).
What is the relationship between temperature and volume? What is the law? Sketch a graph.
Direct
Charle's Law
How do intermolecular forces affect vapor pressure?
Stronger IMF → lower vapor pressure.
1 mole of any gas occupies how many liters at STP?
22.4 L.
What assumption of KMT is not true for real gases?
Gas particles have no volume and no intermolecular forces.
When do gases behave least like ideal gases?
Low temperature and high pressure.
A gas has an initial pressure of 2.0 atm, an initial volume of 5.0 L, and a temperature of 300 K. If the temperature is increased to 600 K while the volume remains constant, what will be the final pressure?
4.0 atm
What is the vapor pressure of water at 75°C?
38 kPa
Three 1 L samples of CO₂, He, and O₂ are at 298 K and 101.3 kPa. Which has the most molecules?
They all have the same number of molecules.
Explain why a heated aerosol can may explode, using KMT.
Higher temperature → particles move faster → more collisions → increased pressure → can explodes.
Explain why O₂ deviates more from ideal behavior than Kr.
O₂ has larger molecules and stronger intermolecular forces.
A pressure cooker contains 1.5 L of steam at a pressure of 2.0 atm and a temperature of 400 K. If the temperature and pressure of the steam decreases to STP what is the new volume ?
2.05 L
Which liquid will evaporate more rapidly? Explain your answer in terms of intermolecular forces.
The higher vapor pressure of liquid A indicates that the intermolecular forces between its molecules are weaker, allowing the molecules to escape more readily to the vapor phase.
A weather balloon has a volume of 52.5 liters at a temperature of 295 K. The balloon is released and rises to an altitude where the temperature is 252 K.
What pressure, in atmospheres (atm), is equal to 45.6 kPa?
.45 or 0.45 atm